Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > A Complete Guide to PCB Transformer
In today's modern age of electronics, PCB transformers have become quite important for many reasons, like converting voltage levels, ensuring isolation, and delivering reliable power.
Unlike large traditional transformers, PCB transformers are designed to be directly mounted on a PCB, making them good for applications where space, weight, and reliability become priorities. From consumer electronics and industrial automation to communication systems and medical devices, these transformers ensure stable performance and also protect sensitive electronic components.
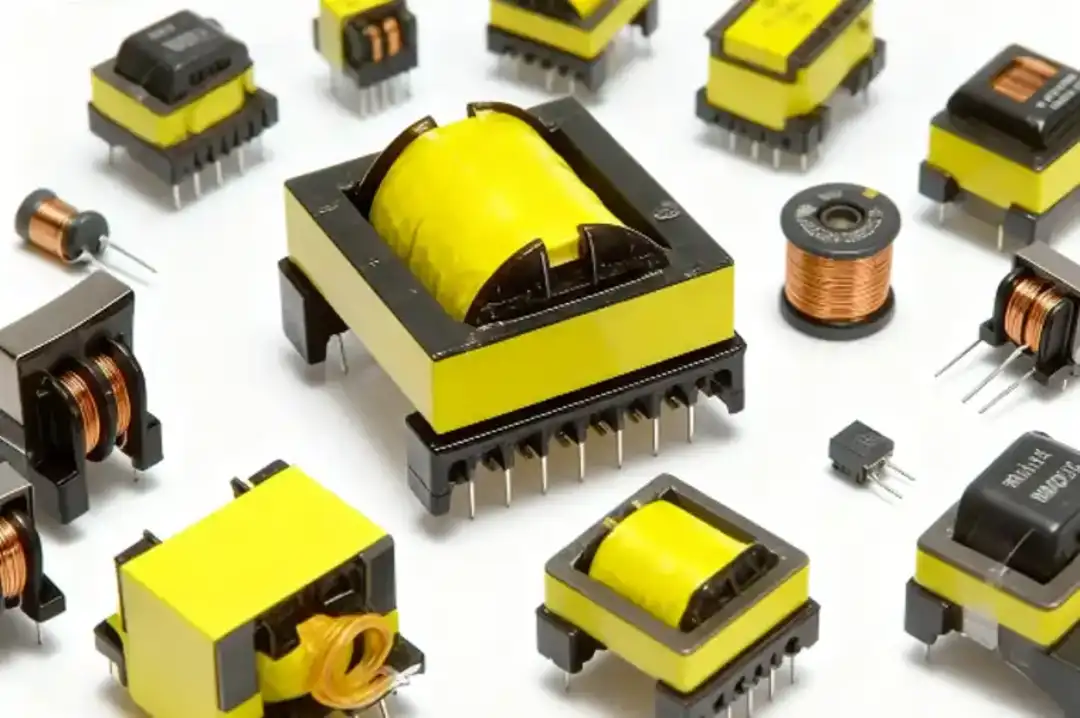

A PCB transformer, or a circuit board transformer, is actually a tiny transformer intended to be soldered directly to the printed circuit board. Its main functions are voltage conversion, isolation, and ensuring that the electronic circuit is powered at a steady and safe level.
Unlike traditional large transformers, which are used in power distribution on high voltage levels, PCB transformers are very compact in size, suitable for mounting on PCBs designed for lower power ranges. They can be found in mobile chargers, adapters, medical electronics, LED drivers, industrial controllers, and communication devices.
Key characteristics of circuit board transformers are:
• A very small size for PCB integration
• Low to medium power energy transfer
• Surface-mount or through-hole mounting configurations
• Different combinations of windings for different voltage conversions
The working principle of a PCB transformer is the same as that of a traditional large transformer, which is electromagnetic induction. Here are some aspects of the PCB transformer.
• Primary Winding: The input current flows through the primary winding and then generates a magnetic field.
• Magnetic Core: The core material, usually ferrite, channels the flux between windings.
• Secondary Winding: The induced voltage in the secondary winding provides the output current. The winding ratio of the transformer decides whether to step up, step down, or provide isolation for voltages.
In addition to voltage conversion, PCB transformers provide:
• Isolation: Protects circuits from having surges and leakage currents.
• Signal Transfer: Uses in communication systems for impedance matching and noise suppression.
• Safety: Stops high voltage levels from reaching sensitive electronics.
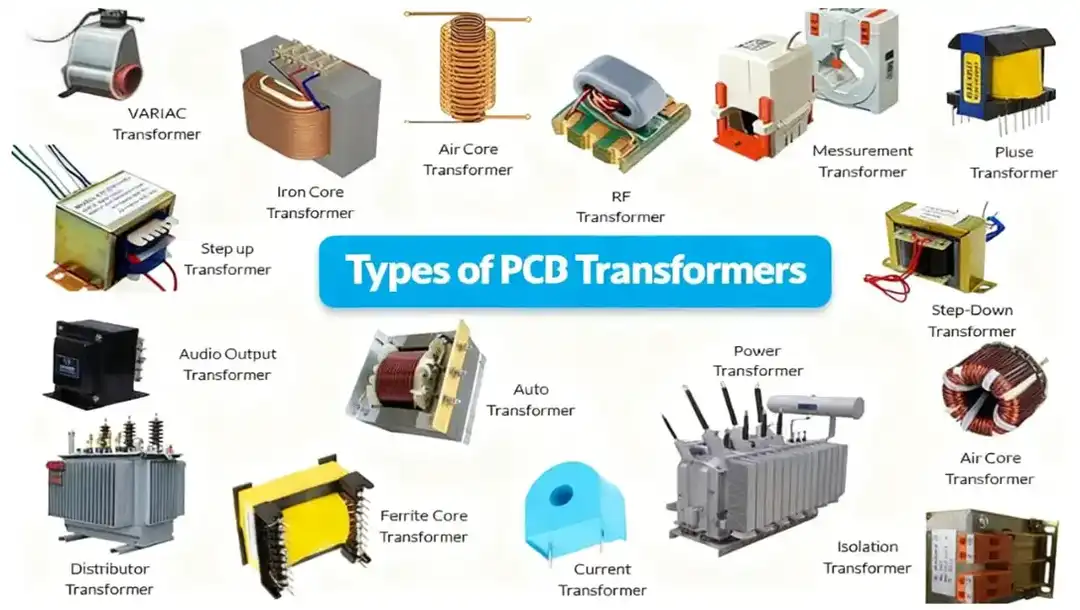
The step-down PCB transformer reduces high AC voltage to a lower level suitable for use with electronic appliances. For example, a charger-type PCB transformer would reduce 220V AC to 12V or 5V DC after rectification. These are the most common types of PCB transformers in consumer electronics.
It increases the voltage from lower to higher. It is normally found in circuits that have a high output from a low input source, like for backlighting, power supplies to sensors, or voltage-boosted circuits.
A signal PCB transformer is used for low-power applications like audio equipment, data communication, and impedance matching. Unlike power transformers, these circuit board transformers focus on ensuring the integrity of the signal and keeping noise out.
An isolation PCB transformer constitutes complete galvanic isolation of input and output circuits. Commonly, it finds use in safety-oriented and noise-critical medical apparatus, industrial controllers, and sensitive communications equipment.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
While designing or selecting a PCB transformer, engineers need to take several factors into account:
Core Material
Ferrite cores are a usual choice for high-frequency types.
For the lower-frequency supplies, one may use laminated cores.
Winding Type
Surface-mount technology (SMT) or through-hole mounting.
Layering and insulation affect the performance of the transformer on the circuit board.
Power Rating
The correct power rating prevents the transformer from overheating.
Thermal Management
Heat generated from PCB transformers must be managed by a proper PCB layout and copper traces.
Safety Distances
Creepage and clearance needs to meet IPC and IEC standards to ensure insulation and prevent arcing.
PCB Transformer Identification
Markings, labels, or codes on PCB transformers show their specifications.
Proper PCB transformer identification is important during repairs and replacements.
PCB transformers are versatile components and have many applications.
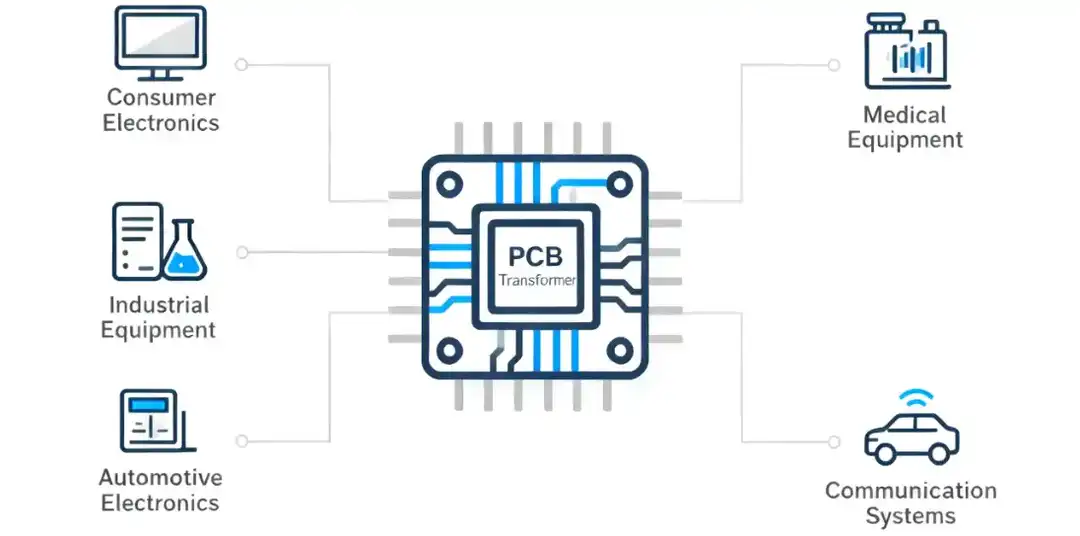
• Consumer Electronics: These are used for voltage conversions in many electronic devices like phones, laptops, chargers, and TVs.
• Industrial Equipment: Automation systems or sensors rely on these transformers for power regulation.
• Medical Equipment: Isolation PCB transformers help with safety by blocking those leakage currents.
• Automotive Electronics: Electric vehicles use a transformer on circuit board designs in onboard chargers and control modules.
• Communication Systems: Signal PCB transformers help in impedance matching and noise suppression in networking devices.
The widespread application of circuit board transformers makes it fundamental for modern technology.
There are many advantages that PCB transformers provide over traditional big transformers. Some of them are:
1. Compact Size – Best for space-constrained PCBs.
2. Cost-Effective – Mass manufacturing reduces the cost per unit.
3. Efficient Integration – Direct mounting simplifies assembly.
4. High Frequency Performance – Ferrite cores enable efficient high-frequency operation.
5. Safety – Isolation designs enhance circuit protection.
To ensure safety and reliability, circuit board transformers need to comply with global standards:
• IEC/EN 61558 – Safety of power transformers
• UL 5085 – U.S. safety standard for transformers
• IPC Standards – Cover PCB layout and creepage/clearance
• RoHS & CE – Environmental and conformity requirements
Proper testing and PCB transformer identification must be done for regulatory compliance, particularly in areas such as automotive and medical electronics.
PCB transformers are one of the most important parts in electronics today. They have a wide range of applications from consumer gadgets to industrial and medical systems, performing voltage conversion, isolation, and signal transfer.
The development of these tiny PCB transformers has helped modern devices to become smaller, smarter, and more reliable.
So when you see these tiny transformers mounted on a PCB, recall they play a big role in keeping our devices working safely and efficiently.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
