Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Getting a reliable PCB Manufacturer is essential if you want to make the most of your electronics projects. These are companies that can help you with everything from creating a prototype PCB to assembling the circuit boards. These companies will be able to work with you to make sure that your project is done on time and in the best possible way. This includes the advanced technology used by circuit board manufacturers to create PCBs to your exact specifications.
Among the many types of circuit boards, aluminum substrates are particularly favored for their excellent heat dissipation and mechanical stability, making them ideal for high-power devices and LED applications. Next, let's take a closer look at aluminum substrates. Before delving deeply into aluminum PCBs, we need to have a basic understanding of metal core PCBs.
Metal core PCBs, also known as thermal PCBs, are made to withstand temperatures of up to 130°C–200°C, depending on materials used. They are more thermally efficient than traditional FR-4 substrates and offer a faster cooling speed. They also have superior thermal conductivity and are better suited for high-temperature applications.
Metal core PCBs are commonly used in applications that produce a lot of heat. They are especially helpful in aerospace applications. Their thermal capabilities allow them to dissipate heat efficiently, preventing hot spots from occurring near active components. Metal core PCBs are commonly fabricated using aluminum substrate, though copper and steel are also used for specific applications. This is because aluminum is a non-toxic material that has a high thermal conductivity. It is also recyclable.
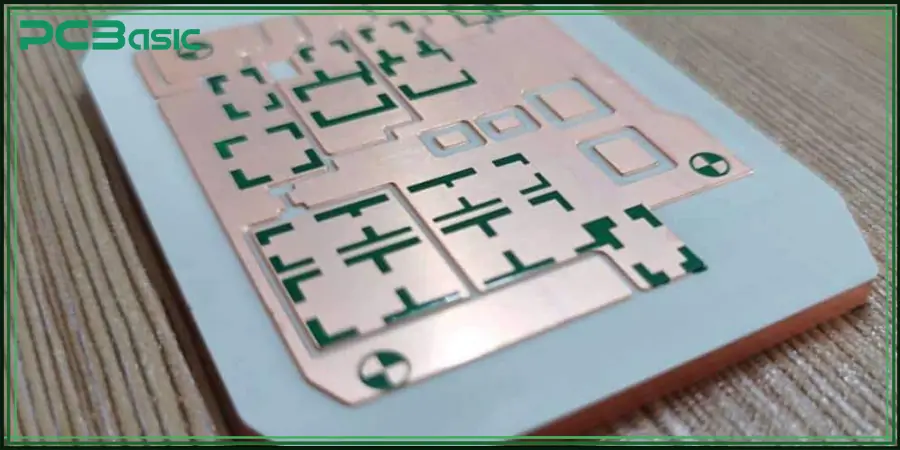
Aluminum PCB, also known as metal core PCB or aluminum core PCB, is a circuit board with aluminum substrate. Unlike traditional FR4 fiberglass boards, this aluminum-based material has good thermal conductivity and can effectively conduct heat away from key components, thereby improving the stability and durability of the circuit board in high-power and high-temperature environments. Aluminum PCBs are widely used in fields with high thermal management requirements such as LED lighting, power modules, and automotive electronics. Aluminum substrates have high requirements for storage methods: should be stored in a dry, constant temperature environment and sealed with anti-static vacuum packaging to avoid copper surface oxidation and performance degradation of the aluminum PCB board before SMT.

About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is the pcb assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB Assembly Services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB Assembly Manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB Prototype Factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
The key reason why aluminum is used in circuit boards is its excellent heat dissipation performance. Because circuit boards generate a lot of heat during operation, if the heat is not dissipated in time, it may cause component damage or shorten the service life of the device. And, aluminum substrates are light in weight and are more suitable for weight-sensitive applications such as automobiles and aviation than copper-based materials. In addition, aluminum has low cost and strong recyclability, making it more cost-effective than other metal substrates. Therefore, many industries have turned to using aluminum clad PCBs or aluminum backed PCBs to solve thermal management problems.
When designing an aluminum PCB stackup, it is critical to correctly select the aluminum layer thickness. Typical aluminum PCB manufacturers usually provide aluminum base thicknesses of 0.8mm to 3.0mm, and copper layer thicknesses of 1oz to 3oz. The specific thickness should be determined based on the current load and heat dissipation requirements.
Although there is no universal formula to measure the aluminum layer thickness, the selection of aluminum layer thickness can refer to the following dimensions:
1. Heat dissipation requirements
Use the thermal resistance formula to estimate:
Rθ = t / (k × A)
Where:
Rθ = thermal resistance (℃/W)
t = thickness of aluminum layer (millimeters), t = Rθ × k × A
k = thermal conductivity of aluminum (usually 200 W/m·K)
A = area of aluminum plate (square meters)
2. Mechanical Strength
For larger PCBs or applications with higher requirements for structural strength (such as automobiles and industrial control), it is recommended to use a thicker aluminum layer (such as 2.0mm-3.0mm).
3. Finished board thickness requirements
If the total thickness of the entire board is limited (such as 1.6mm or 2.4mm), the thickness of the copper layer and the insulation layer must be subtracted from the total thickness to determine the maximum available thickness of the aluminum layer.
If you need aluminum PCB prototyping, it is recommended to consult an experienced metal core PCB manufacturer (Metal Core PCB Manufacturer) - such as PCBasic, for thermal simulation advice.
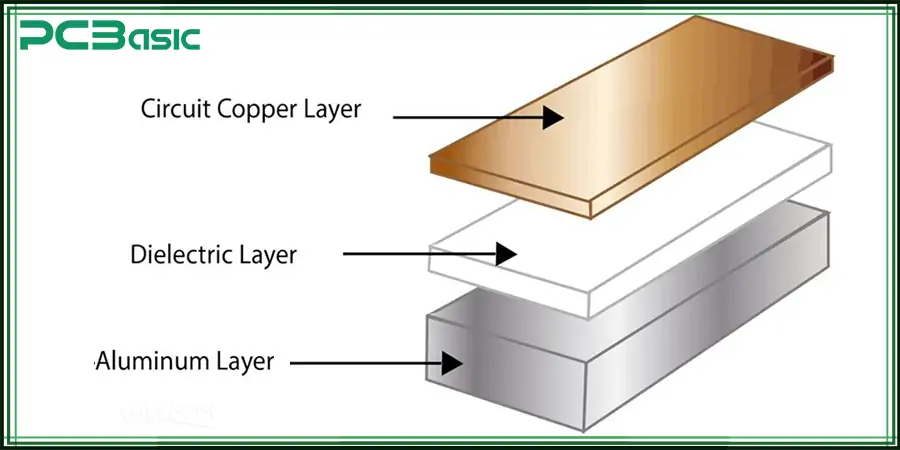
The structure of aluminum PCB is unique, which can greatly enhance the heat dissipation capacity and mechanical stability. Compared with the traditional FR4 board, the aluminum substrate has better thermal conductivity and is particularly suitable for high-power application scenarios.
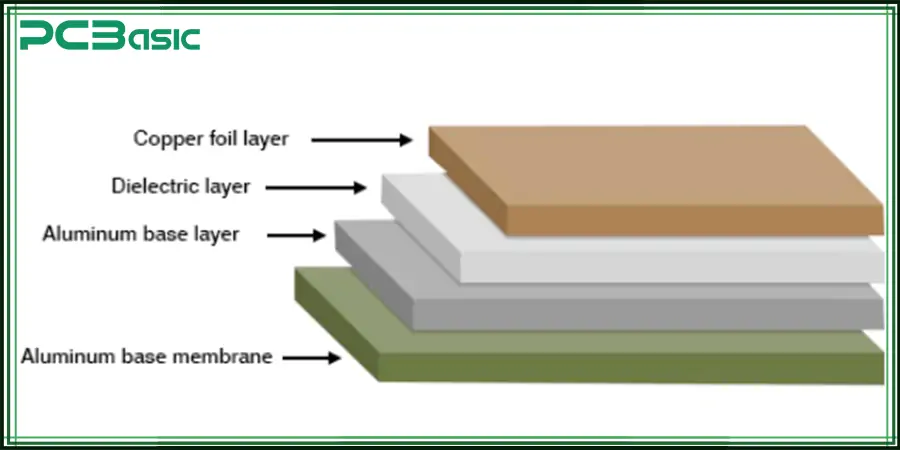
The typical structure of an aluminum PCB Board includes:
Circuit layer: A copper layer used to form electrical connections, typically with a copper thickness ranging from 1oz to 3oz, depending on design requirements.
Insulation layer: An intermediate layer with high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation performance, which is the key to heat conduction to the aluminum core.
Aluminum core layer: Thickened aluminum base PCB, providing excellent heat dissipation channels and mechanical support.
Back protective layer (optional) : Some aluminum backed PCBs are coated with a protective layer to prevent oxidation and enhance durability.
When designing an aluminum PCB structure, it is necessary to understand the specifications of aluminum-based copper-clad laminates. These copper clad laminates are specially designed for high thermal performance, with the thermal conductivity of the insulation layer typically ranging from 1W/mK to 3W/mK. In the process of aluminum PCB manufacturing, parameters such as thickness, surface treatment, and withstand voltage performance will directly affect the thermal performance and stability of the final board.
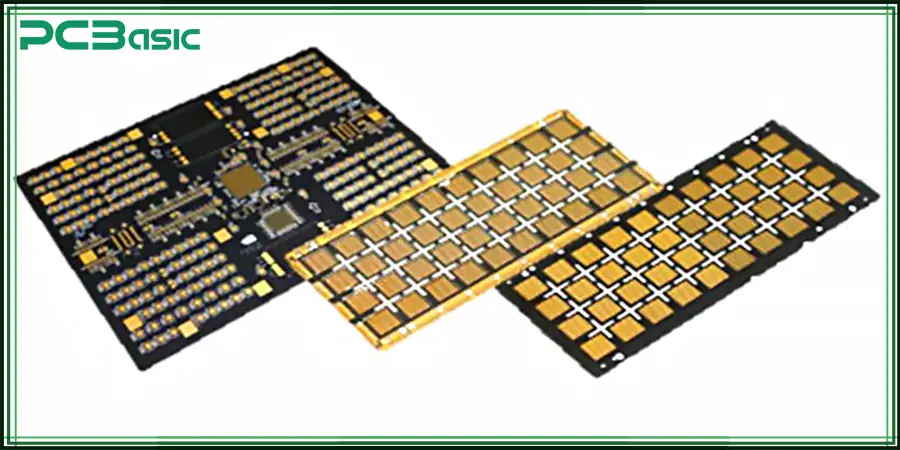
To meet the demands of various applications, there are several different types of aluminum PCBs:
A single-layer aluminum PCB is composed of a conductive copper foil layer, an insulating medium layer and an aluminum substrate layer. Its copper layer is usually on the top, directly connected to the external circuit, and the back is an aluminum heat dissipation base plate. The structure of single-layer aluminum PCB boards is simple, the manufacturing cost is low, and the production process is mature. It is mainly used for products with moderate heat generation, obvious heat dissipation requirements, but relatively simple circuit design.
Aluminum PCBs have a short manufacturing cycle, low cost and high reliability. However, it cannot support complex wiring or multi-functional integration and is limited to simple circuit design. Typical applications of aluminum PCB include: LED street lamps, LED modules, small power modules, audio power amplifier boards, etc.
The double-layer aluminum PCB has two conductive copper layers on the top and bottom, with an insulating medium in between. It achieves double-layer interconnection Through Plated Through Holes (PTH). Beneath it is still an aluminum base material, providing heat dissipation and support.
Double-layer aluminum PCBs support more complex circuit layouts, such as cross-routing and more component layouts. It has both heat dissipation function and a good balance of electrical performance. Double-layer aluminum PCBs offer higher design freedom, more complex manufacturing processes, are suitable for more complex applications, and have a higher manufacturing cost than single-sided aluminum substrates. Typical applications include: medium-complexity power modules, automotive electronics, power tool control boards, etc.
Multi-layer aluminum PCBs are composed of three or more copper layers, insulating layers and aluminum substrate layers stacked multiple times. Usually, there is one or more layers of aluminum base materials in the middle. Some designs also use composite materials as the central heat dissipation core. Interlayer interconnection needs to be achieved through complex lamination and metallized hole techniques.
Multi-layer aluminum PCBs are suitable for systems with high functional integration, high-density wiring, high current carrying capacity, and high heat intensity. It is powerful and can meet higher-level system integration and heat dissipation requirements. However, it is difficult to manufacture, has a long production cycle and high costs.
Flexible aluminum PCB combines a hybrid design of local flexible circuits (such as FPC) and aluminum substrates. Its flexible part adopts flexible materials such as polyimide, which can achieve bending within a limited range. The rigid part is an aluminum-based structure, providing heat dissipation and mechanical support.
Flexible aluminum PCBs are particularly suitable for compact devices that require spatial flexibility but have high requirements for thermal management. The flexible aluminum PCB features a bendable structure. It can be bent and dissipate heat, combining the advantages of both materials. It is usually used in portable medical devices, smart wearable devices, micro lighting modules, aerospace electronic components, etc.
The most prominent advantage of aluminum PCBs is their excellent heat dissipation performance. The aluminum base layer can quickly conduct heat, which is particularly suitable for fields such as LED lighting, power converters, and automotive systems that have extremely high requirements for temperature rise control. In addition to thermal performance, aluminum substrate PCBs also have excellent mechanical stability. Its metal core structure is more resistant to vibration, impact, and temperature changes than traditional fiberglass boards.
In addition, a notable feature of aluminum substrate PCBs is their lightweight design-although it is made of metal, its overall weight is lower than other metal substrate options, making it suitable for use in scenarios that require both heat dissipation and weight reduction. More importantly, aluminum materials are recyclable, making aluminum substrates more environmentally friendly than other types of PCBs, in line with the current development trend of green manufacturing.
The performance of aluminum PCBs depends on their thermal management properties. In high-power applications, heat can cause problems for electronic components and circuits, accelerating component aging and causing overall system performance degradation. In the worst case, it can even cause the entire system to crash. While aluminum substrates can often solve these problems because they can absorb more heat than fiberglass substrates.
In addition, aluminum substrates have superior mechanical properties that can enhance the physical properties and environmental adaptability of printed circuits. This is very beneficial for applications that are susceptible to vibration and temperature changes, such as automotive electronics.
From an electrical perspective, aluminum PCBs have a conductive layer made of copper for signal transmission; and a dielectric layer to prevent short circuits. All in all, aluminum substrates are an excellent thermoelectric composite material with strong mechanical properties that allow them to withstand high durability.
As a leading metal core PCB Manufacturer, PCBasic focuses on providing high-quality aluminum PCB manufacturing services to meet the diverse needs of customers in different industries.
The aluminum substrate services of PCBasic include:
Whether you need aluminum PCB boards for developing innovative LED products or aluminum core PCBs for complex industrial equipment, PCBasic can provide flexible and reliable delivery support.
As a reliable aluminum PCB supplier, PCBasic services cover multiple fields such as automobiles, new energy, medical electronics and consumer electronics, helping customers successfully capture the market.
The continuous demand for reliability, thermal management and high performance is driving the rapid growth of the aluminum substrate market. With its robust structure, diverse types and wide range of applications, aluminum substrates are reshaping various industries that require excellent heat dissipation and durability.
By leveraging PCBasic’s expertise, you can ensure faster project turnaround and superior product reliability.By choosing to cooperate with an experienced aluminum substrate PCB manufacturer like PCBasic, enterprises can accelerate the pace of innovation, improve product quality, and gain an advantage in the increasingly competitive market. Learn about the aluminum PCB prototyping services of PCBasic and let us help your product achieve a breakthrough faster!
Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
