Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
PCB Cost
$0.00
BOM Cost
--
SMT Cost
$0.00
| TG Value | Build Time | Price/Pcs | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| You can select different parammeters to estimate the cost of the board |

 DHL
DHL
|
0 days | $0.00 |

 UPS
UPS
|
0 days | $0.00 |

|
0 days | $0.00 |
New User Discount
-$10.00

How to Order (3 steps)
✖

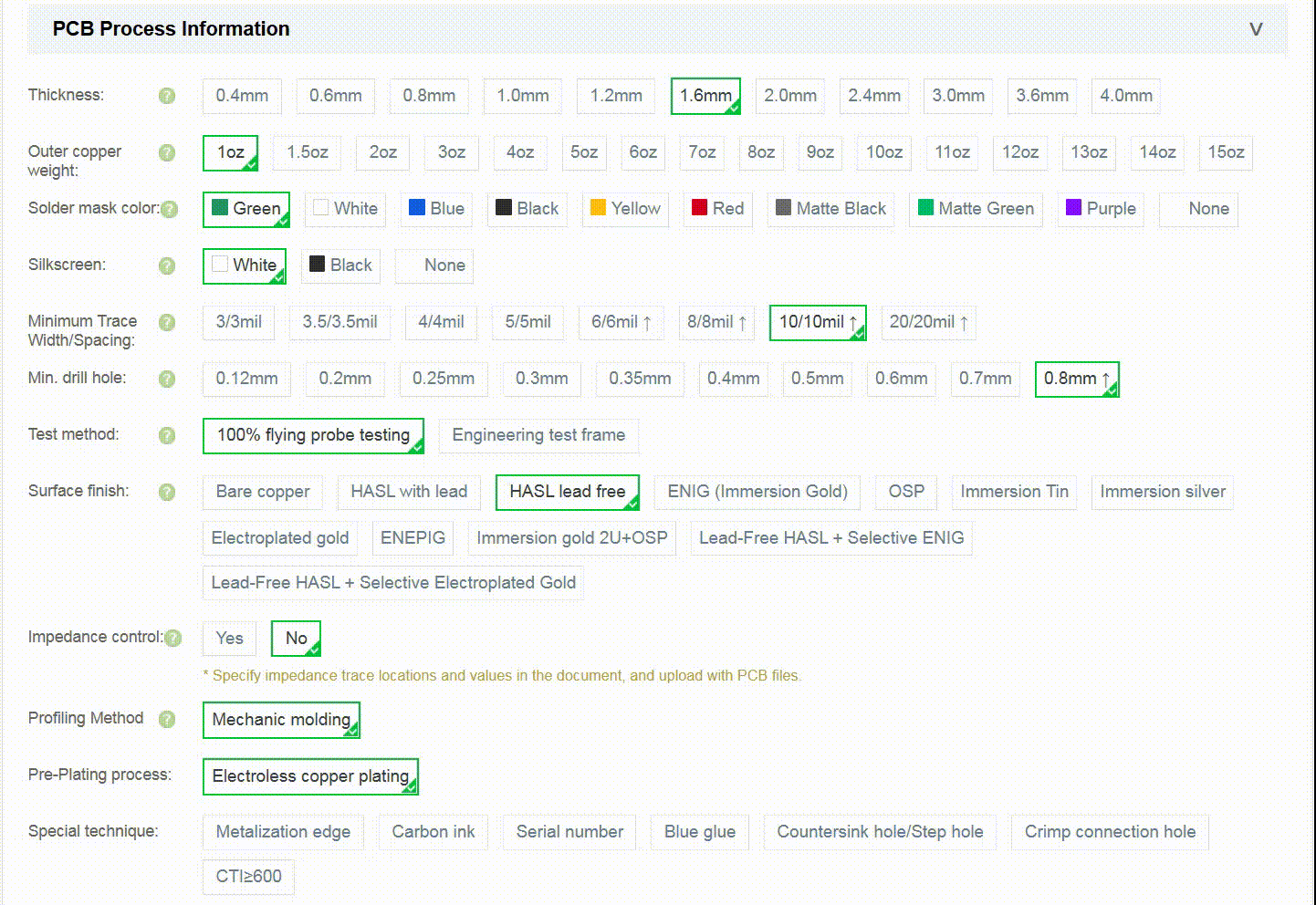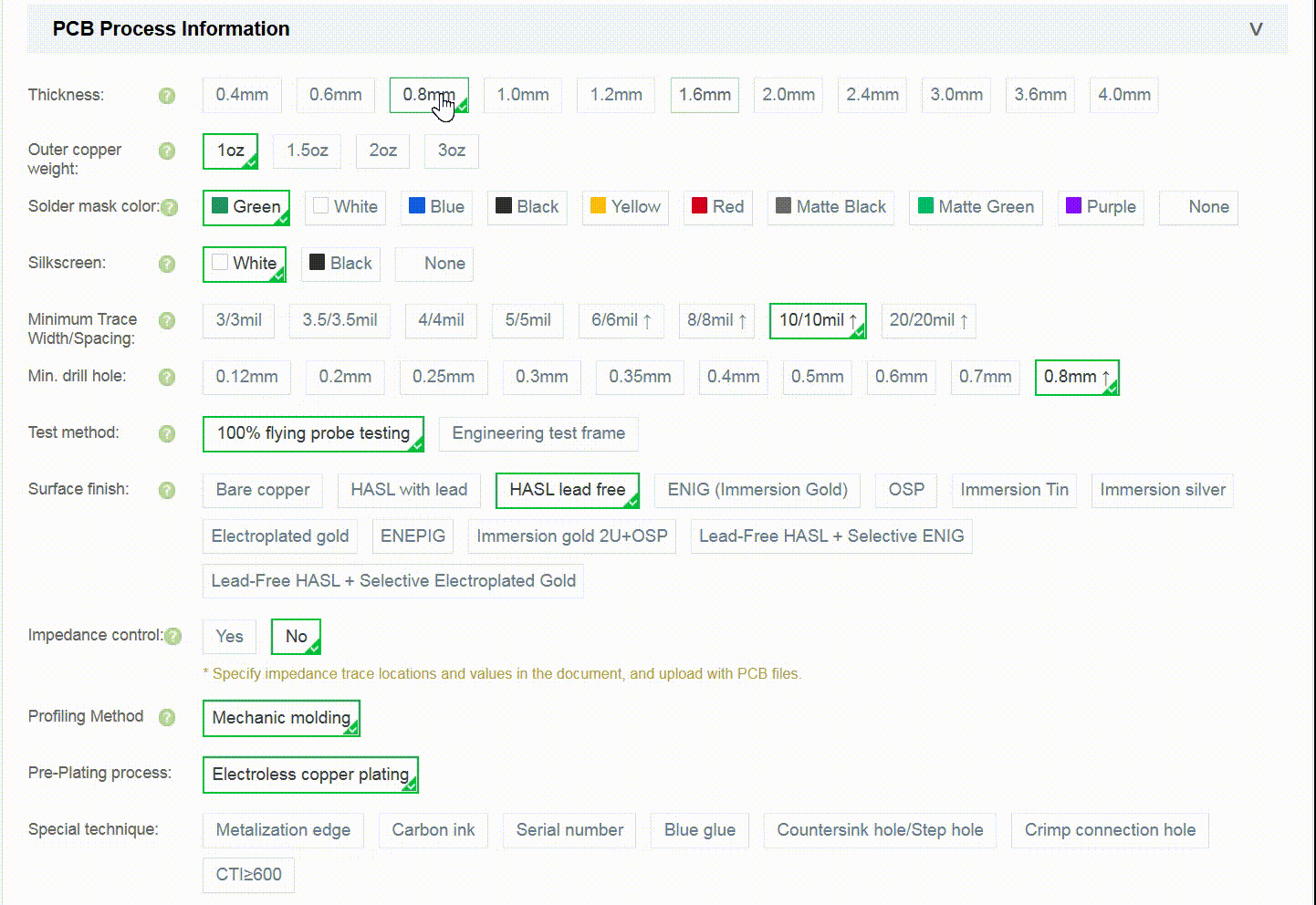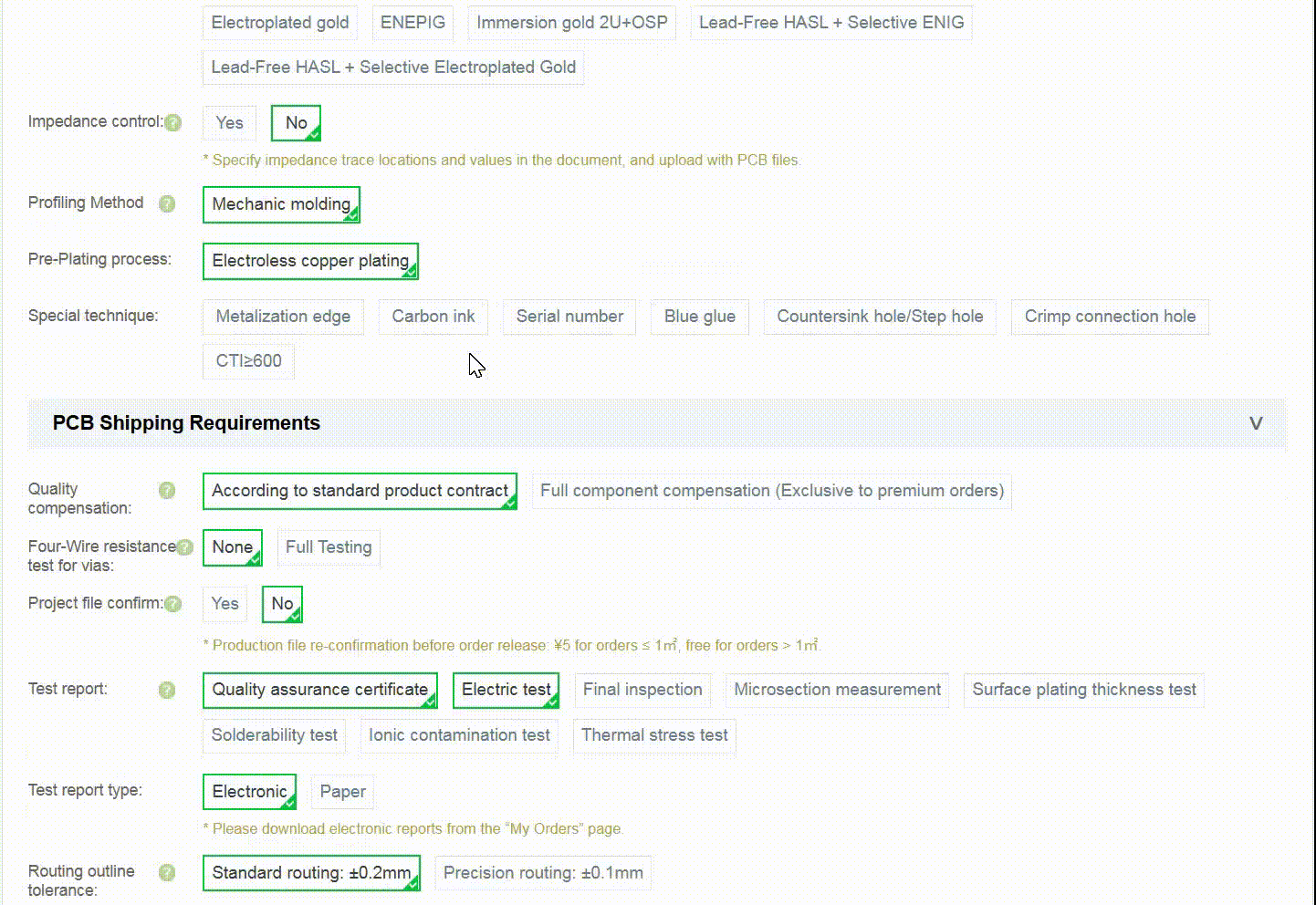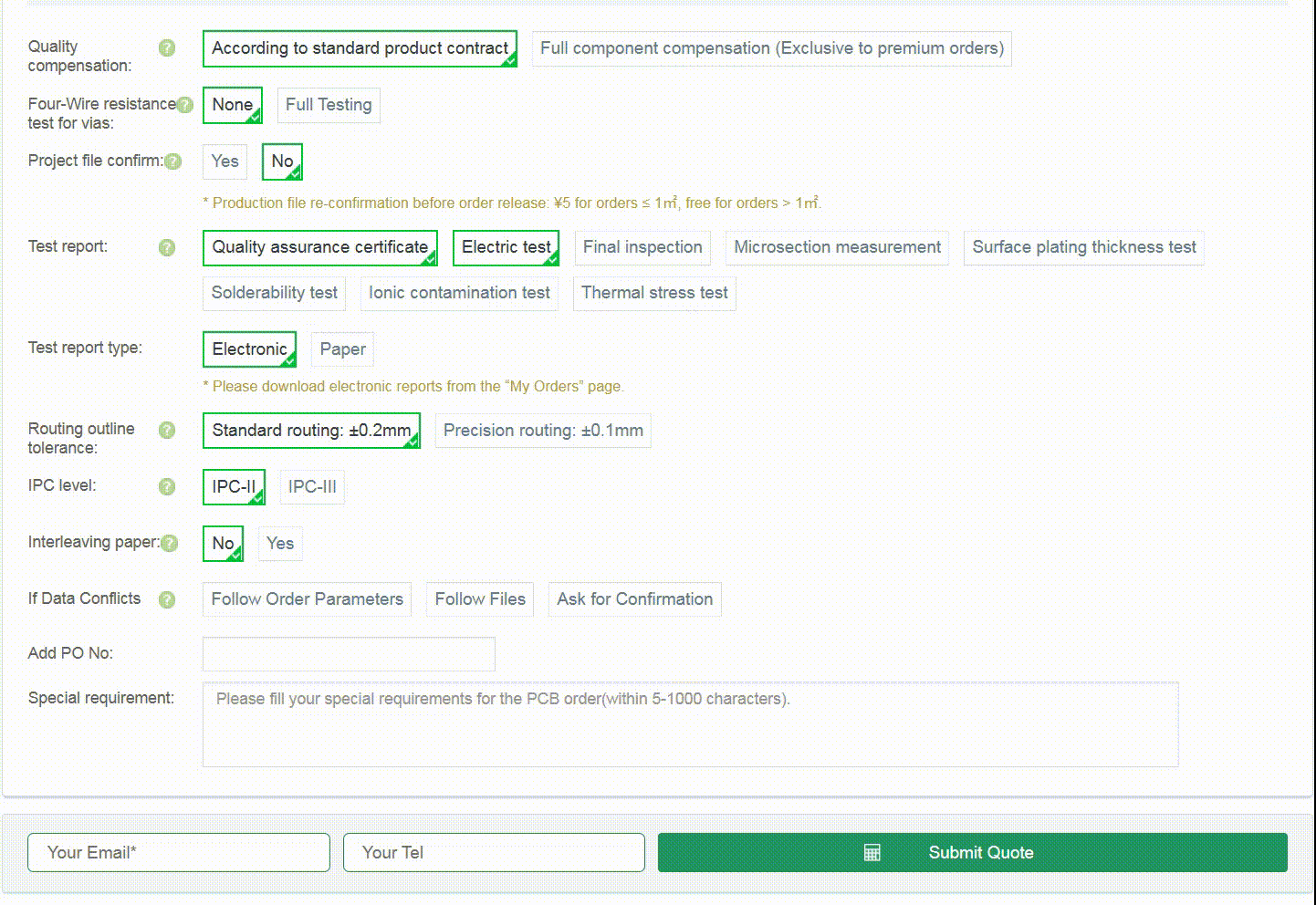
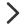
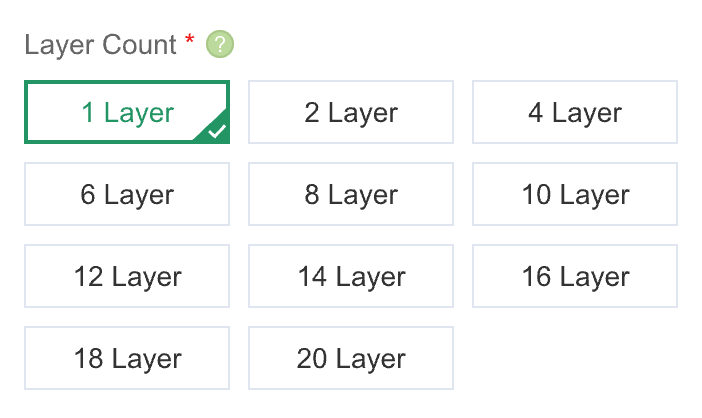
Step 1: Enter Basic PCB Parameters
Step 2: Confirm Additional Parameters
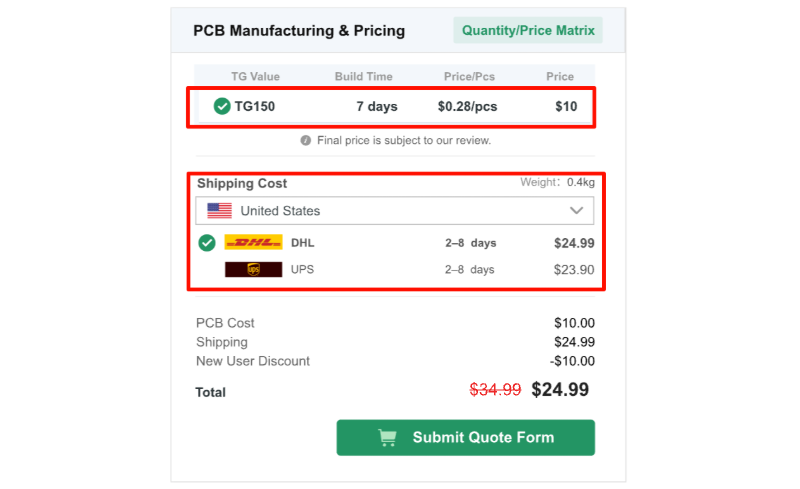
Step 3: Confirm Order Price and Choose a Carrier
1. Upload the correct Gerber file (optional)
2. Select the PCB layer count that matches your Gerber file
3. Enter the finished PCB length and width
4. Enter the PCB order quantity
Default parameters are pre-selected, and you may click “Submit Quote” to proceed.
If needed, you may also adjust parameters such as base material, surface finish,
special processes, and order notes.
After confirming the price and lead time, click “Submit Quote Form” to add the
quotation to your account.
You can upload the Gerber file in your account dashboard.
Step 1/3
The PCB layer count, dimensions, and order quantity are mandatory fileds and must be provided

Step 2/3
Default parameters are preselected. You may adjust them as needed (e.g., PCB Thickness)


Step 3/3
After confirming the order price, click Submit Quote to add it to your account.



Registration Successful!
Temporary Default Password
123456
For your account security, please click here to change your password.
New User Benefit: $10 USD coupon has been credited.
Change Password

Password changed successfully!
New User $10 Coupon
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
