Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PWB vs PCB: What’s the Real Difference in Electronics?
In electronic manufacturing, the terms PWB and PCB frequently appear. They all refer to circuit boards, which are used to connect and support electronic components. But are they really the same? Is there still an essential difference?
Understanding the differences between PWB and PCB is of great significance to engineers, OEM manufacturers, purchasers, and those involved in PWB design, assembly or procurement. This article will explain the sources, definitions and practical uses of these two terms, helping you figure out whether they are different concepts or just two different names.
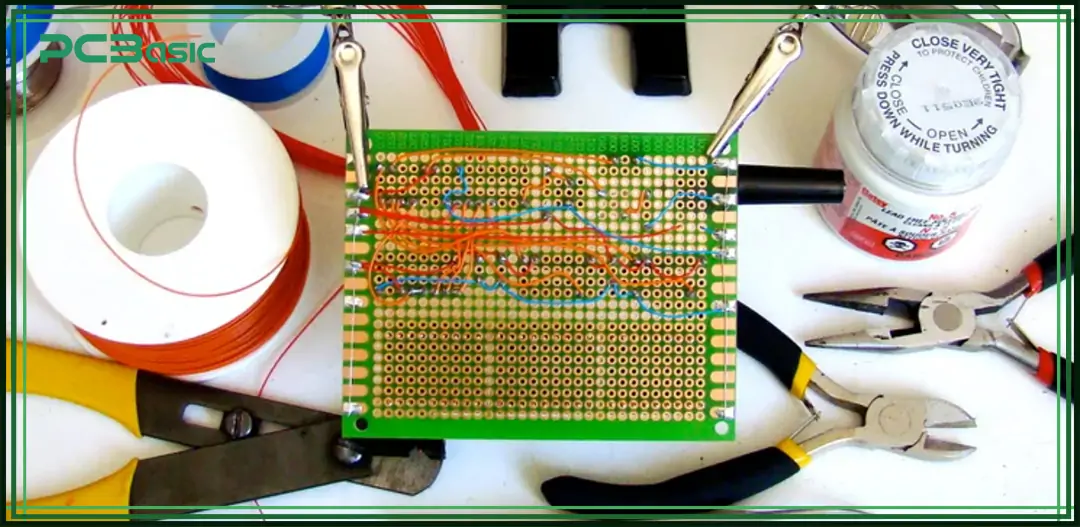
PWB is the abbreviation of Printed Wiring Board. It refers to a circuit board where conductive traces have been fabricated but no electronic components have been mounted yet. In simple terms, PWB is a bare board that has not yet started assembly.
The term PWB originated from the early days of the electronics industry. At that time, people paid more attention to the layout of the wires on the circuit board, that is, wiring, rather than the complete circuit functionality. Therefore, the meaning of PWB has always referred to a board with only copper traces and no components.
So, what does PWB stand for? Its full name is Printed Wiring Board, which means a circuit board with a wiring structure formed through a printing process. Its focus lies in carrying the wiring rather than the electronic components.
To this day, the term printed wiring board is still in use in some industries that have strict requirements for terminology, such as aerospace, medical equipment, military industry and other fields. Especially in the manufacturing industry of Japan, this term is still widely used in technical documents and production files.
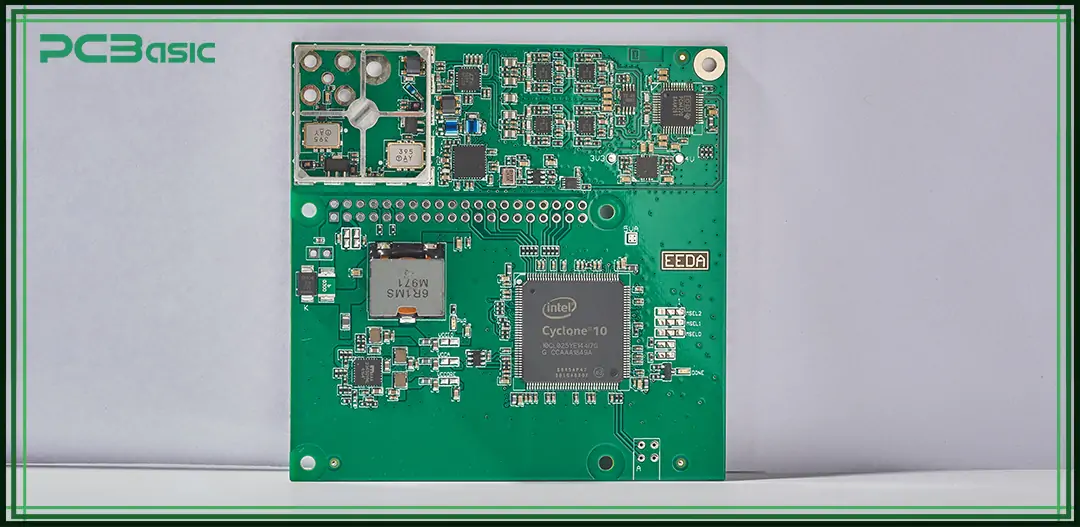
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It is a circuit board used for connecting and supporting electronic components and is one of the most common basic components in modern electronic products.
Unlike PWB, PCB is a more commonly used and widely applied term. In practical usage, PCB can refer to either a bare board without any components installed or a complete board that has been assembled and is ready for direct use.
The key points of a PCB are not only the conductive wiring but also the layout of components and the integration of the entire circuit system. In other words, a PCB describes a complete circuit structure, not just the wiring. Therefore, in some cases, the meanings of PCB and PWB are the same, but in other situations, the PCB specifically refers to a product that has already been assembled.
With the advancement of electronic technology, PCB has gradually become an industry-standard term. It is widely used in technical documents, industry specifications, product descriptions and global supply chains.
Nevertheless, in some technical subfields or international manufacturing cooperation, the discussion of PWB vs PCB still exists, especially in scenarios where it is necessary to clearly distinguish between bare boards and assembled boards.
The discussion on PWB vs PCB often depends on the context in which the terms are used and regional differences. The following is a detailed comparison:
|
Feature |
PWB (Printed Wiring Board) |
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) |
|
Definition |
Bare board with copper traces |
Bare or assembled board |
|
Includes Components? |
No |
Sometimes (depending on usage) |
|
Common Usage Region |
Japan, aerospace, defense |
Global (especially Western countries) |
|
Term Focus |
Wiring layout |
Circuit integration |
|
Relevance Today |
Still used in documentation & specific contexts |
Dominant term across industries |
Overall, although PWB vs PCB have differences in strict definitions, in practical applications, the two can often be interchanged. However, in precision industries such as PWB electronics, the accuracy of terms is still very important.
Another common point of confusion is the difference between PWB assembly and PCB assembly. They look similar, but in some industries, their meanings and uses are different.
PWB assembly refers to the process of mounting electronic components onto the printed wiring board. After the assembly is completed, the board becomes a printed wiring assembly. This term often appears in the military industry, aerospace and medical electronics industries. These industries require the precise distinction between bare boards and assembled boards in technical documents.
In contrast, PCB assembly is a broader term. It not only includes PWB assembly but also other types of electronic assembly processes applicable to various products such as consumer electronics, industrial control, and communication equipment. For most ordinary users and manufacturers, PCB assembly refers to the entire process of a circuit board from a bare board to a complete finished product.
After the completion of PWB manufacturing, the bare board will undergo PWB assembly through methods such as SMT surface mount or THT through-hole. After the assembly is completed, it becomes a complete printed wiring board assembly and can be directly used in the equipment.
Therefore, in different industries or contexts, PWB vs PCB may represent different meanings at the assembly stage. Understanding these differences helps to avoid misunderstandings in technical communication.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
PWB design is a key step to ensure the performance and reliability of electronic products. Engineers must define copper trace widths, routing paths, insulation layer structures, and via layouts. At the same time, they need to consider manufacturing feasibility and heat management.
After the design is complete, the board enters the PWB manufacturing process, which includes:
• Base material preparation
• Copper etching to form traces
• Multilayer lamination
• Drilling and plating
• Solder mask and silkscreen application
The entire PWB manufacturing process requires high-precision equipment and strict tolerance control. This ensures that the final printed wiring board assembly meets all functional requirements.
Although these steps are the same as in PCB manufacturing, industries that still use the PWB term may also require special certifications or more detailed documentation standards.
Why do some industries still use the term PWB today? There are two main reasons: regional habits and different standards in each industry.
• Japan: In Japan, electronics manufacturers commonly use PWB to refer to a bare board and PWA for an assembled board. This usage has become an industry norm. Clear separation between the two helps improve documentation and avoid confusion.
• Aerospace and Military: These industries have strict requirements for process control. It is important to clearly distinguish between a printed wiring board and a fully assembled board. Using PWB helps reduce misunderstandings and ensures accurate manufacturing and inspection.
• Medical Devices: The medical industry is very sensitive to compliance and traceability. The design, manufacturing, and assembly stages must be documented separately. Using terms like PWB design, PWB manufacturing, and PWB assembly helps ensure each step meets industry regulations.
In contrast, consumer electronics and most Western countries use PCB as a general term. They usually do not make a strong distinction between bare and assembled boards. In these fields, exact terminology is not a top priority in daily communication or documentation.
This is why the PWB vs PCB discussion still exists. In industries where accurate terminology is critical, using the wrong term may lead to confusion in documentation, incorrect purchasing, or even compliance failures. Understanding and using the correct terms is essential for clear communication and successful product delivery.
Although the terms PWB and PCB seem similar, their usage varies depending on the industry and region. Although PCB has become a mainstream term, PWB remains indispensable in specific fields where it is necessary to clearly distinguish between bare boards and assembly boards.
Whether you are engaged in PWB design, looking for a PWB manufacturer, or reviewing a document for the assembly of a printed circuit board, understanding and correctly using these two terms will greatly enhance professionalism and communication efficiency.
With the development of technology, the boundary between PWB and PCB may become further blurred. However, at present, understanding their differences remains a basic quality for every electronic engineering professional.
What does PWB stand for in electronics?
PWB stands for Printed Wiring Board, referring to a bare circuit board without any components mounted on it.
Is a PWB the same as a PCB?
Not exactly. In practice, they are often used interchangeably, but PWB refers to the bare board, while PCB may refer to either the bare or the assembled board.
Are PWB and PCB assemblies different?
The assembly processes are similar, but PWB assembly usually emphasizes regulatory clarity, especially in industries where the distinction between board and assembly is critical.
Which industries still use “printed wiring board” terminology?
Industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical electronics, as well as many Japanese manufacturers, still use printed wiring boards and printed wiring board assembly for documentation and compliance.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
