Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > The Complete Guide to Electronics Prototyping
In modern hardware development, the ability to rapidly transform products from design to functional hardware has become one of the most important competitive advantages for enterprises. The pace of the global market is getting faster and faster - according to McKinsey's statistics, average hardware time-to-market has shortened by 35%, and teams that can launch reliable prototypes are 2-3 times more likely to succeed than their competitors. Whether you are designing IoT devices, robot controllers, wearable products, or industrial-grade sensors, the entire development journey must start with electronics prototyping.
In recent years, with the popularity of rapid prototyping, custom fabrication and professional electronics prototyping services, the development efficiency of hardware teams has also improved significantly. The 2024 industry report indicates that enterprises using professional prototyping services can, on average, shorten the development cycle by 30-50% and significantly reduce error costs through rapid iteration.
This guide will start from scratch and take you to have a comprehensive understanding of the complete process of electronics prototyping or the core differences between rapid prototyping and traditional prototyping, and introduce an outstanding manufacturing partner that can help you achieve rapid and reliable PCB/PCBA prototype development.
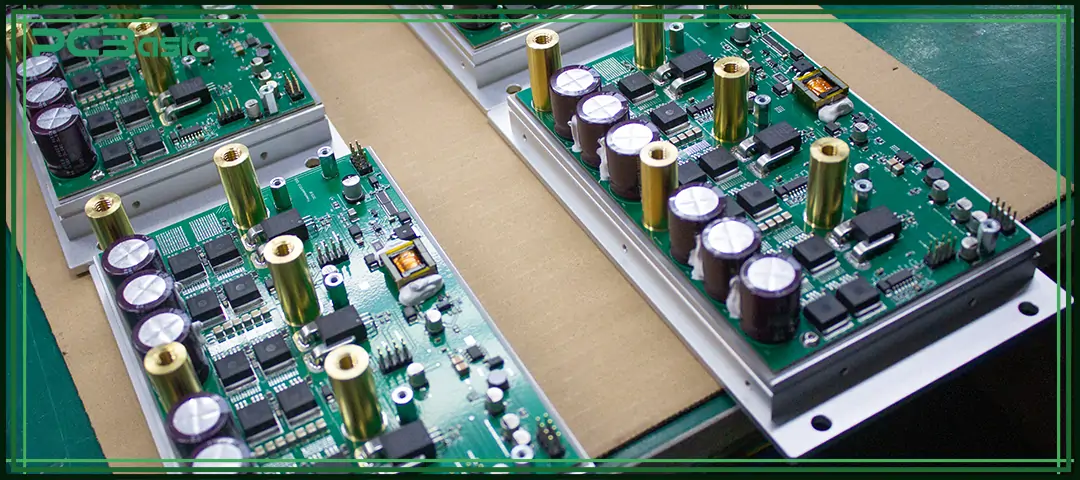
Electronics prototyping refers to the entire process of transforming an electronic design into a truly functional hardware device. This step is far more realistic and crucial than running simulations or drawing CAD models on a computer, because only by making the circuit a physical entity can we see its performance under real conditions, for example, how signals change inside the circuit, how power is distributed, how components heat up under load, and whether the system is reliable enough in actual operating conditions. All of these cannot be fully revealed by digital models.
In actual product research and development, electronics prototyping is usually not completed in one go but is a process of repeated iterations. Most hardware teams will first conduct several rounds of rapid prototypes to verify the core functions, and then continuously improve the PCB layout, correct problems, optimize the structure, and eventually form PCBs that can be used for mass production. Prototypes can be implemented in various ways: using a prototype board to wire temporary circuits, hand-wiring components with jumpers, or directly fabricating a prototype PCB. No matter which one it is, each prototype is an experiment, an experience and a test of the design.
With the continuous increase in hardware complexity, modern electronics prototyping companies no longer merely offer PCB prototyping or soldering services but integrate all the necessary stages for research and development together, such as firmware programming, enclosure design, functional testing, reliability testing, certification support, BOM optimization, and DFM (Design for Manufacturing) review. This type of professional electronic prototyping service helps teams identify problems and iterate more quickly, thereby reducing development costs. It also enables both start-ups and large OEMs to advance their products to the verification, trial production and mass production stages in a shorter period of time.
The main purposes of electronics prototyping include:
The primary purpose of electronics prototyping is to confirm whether the circuit is truly working as expected. Through the prototype, engineers can directly evaluate power stability, signal integrity, component compatibility, thermal behavior under load, and whether the firmware and hardware can cooperate normally.
Every round of prototyping, potential problems can be identified in advance before mass production. Verifying the design in advance can reduce rework costs, prevent failures in compliance tests, and also lower the risk of encountering serious problems when entering mass manufacturing.
Prototypes give engineers the opportunity to continuously optimize the design, such as adjusting component placement, improving PCB routing, choosing more suitable components, or modifying firmware logic, making the entire system more stable and reliable.
Gradually moving from rapid prototyping to the more mature prototype manufacturing can make the product closer to the actual mass production requirements. Through the inspection of DFM (Design for Manufacturing) and DFT (Design for Test), it is ensured that the design can be smoothly produced, assembled and tested in the factory.
A physical prototype is very important for team communication and external presentation. It can help founders present product concepts to investors, enable the team to have discussions around real prototypes, and allow customers to understand the product value more intuitively.
From an initial idea to the final mass-producible finished hardware, the entire electronics prototyping process generally goes through the following key stages.
At this stage, engineers usually use development boards such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi to quickly build a prototype that can demonstrate the core functions, which is to prove whether the product idea is feasible.
After completing the POC, we can start making the first real prototype PCB. This version generally uses a basic routing layout, with the core objective of transforming the schematic diagram into an operational physical circuit.
After the first round of testing, the design team will fix the issues, optimize the layout and enter the second round of prototyping. The focus of this stage is to improve the routing, adjust the power path, optimize the thermal design and EMI performance, while enabling the firmware to run on more stable hardware.
This stage marks the first time the product starts to resemble a "near-production" version. The engineering prototype is a fully functional PCBA with a structure close to the final version, while the component packaging, layout, and mechanical dimensions are all closer to the requirements of mass production. The prototypes at this stage will be used for EVT (Engineering Verification Testing) to determine whether the product is ready to enter a more rigorous testing process.
The prototype at this stage has undergone comprehensive inspections by DFM (Design for Manufacturing) and DFA (Design for Assembly) to ensure that the product can be smoothly assembled, soldered, tested and controlled in the factory.
• EVT (Engineering Validation Test): Confirms electrical performance and functional stability of the hardware.
• DVT (Design Validation Test): Verifies design reliability, structural durability, and regulatory compliance.
• PVT (Production Validation Test): Sets up a pilot production line and completes a small-batch trial run to validate the full manufacturing process.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
The following are common prototype development methods in the industry.
|
Prototyping Method |
Description |
Applicability |
Limitations |
Professional Level |
|
Point-to-Point Wiring / Space Wiring |
Components are connected directly using wires; commonly used by hobbyists in the early stages. |
Very early and simple circuit verification. |
Messy wiring, low reliability, not suitable for complex designs. |
Rarely used in professional prototype development services. |
|
Wire-Wrap |
Wiring is done by wrapping wires around connector posts; used in older digital circuits. |
Small-scale digital logic or training purposes. |
Not compatible with high-density SMD designs; outdated for modern electronics. |
Mostly obsolete in the industry. |
|
CNC-Milled PCBs vs Home-Etched PCBs |
DIY approaches such as CNC milling or chemical etching to make rough prototype PCBs. |
Educational use, hobby projects, simple 2-layer PCBs. |
Limited to two layers, low precision, cannot support fine-pitch ICs. |
Most companies now prefer higher-quality rapid prototyping service providers instead. |
|
Professional PCB Prototyping (Industry Standard) |
Industrial-grade PCB prototyping suitable for all serious hardware projects. |
Commercial products and professional hardware development. |
Higher cost than DIY, but much better performance and reliability. |
Core method for modern prototype manufacturing, supporting: high precision, multi-layer stack-ups, HDI structures, fine-pitch ICs, and fast turnaround. |
PCBasic is a professional electronics prototyping company that has long been dedicated to prototype PCBs, PCBA, and small-batch rapid manufacturing. With advanced SMT production lines, experienced engineering teams and flexible and efficient production systems, PCBasic can provide rapid and stable prototype support for start-up teams and mature hardware enterprises.
PCBasic can complete PCB fabrication, PCB assembly, DFM/DFA checks, functional testing (AOI, SPI, X-ray, ICT, FCT), component sourcing, prototype rework, and rapid iteration all within the same factory. The entire process does not require coordination among multiple suppliers.
PCBasic can offer expedited PCB production within 24-72 hours and complete PCB assembly within the same week. The minimum order quantity is flexible, making it an ideal choice for hardware teams to conduct rapid prototypes and short-cycle verifications.
PCBasic is equipped with a full set of inspection equipment, such as nitrogen reflow soldering, 3D SPI inspection, fully automatic AOI, and X-ray (suitable for BGA/QFN), ensuring that the soldering quality and the prototype performance can approach the mass production effect and avoiding hidden quality problems in the prototype stage.
The engineering team of PCBasic can provide early-stage guidance on signal integrity and power design, and also assist in optimizing high-speed traces, thermal design, device layout, and BOM lifecycle management.
PCBasic can not only produce early prototypes but also accompany customers through each stage of EVT, DVT and PVT, including trial production, verification and manufacturability validation.
Whether you need rapid prototyping services, prototype development services, or are looking for a long-term stable prototype manufacturer, PCBasic can provide you with high-quality and fast-response hardware prototype solutions.
Electronic prototyping is the core foundation of modern hardware innovation. From proof of concept (POC) to engineering prototypes and then to pre-production prototypes, each iteration brings the product closer to a truly manufacturable, testable, reliable and standard-compliant electronic device.
When you combine a clear development process, the right prototyping strategy, and a reliable electronics prototyping company like PCBasic, the hardware team can significantly reduce R&D risks, accelerate the time to market for products, and achieve higher-quality final results.
If you are preparing to develop your next product, please choose your rapid prototyping partner carefully - it will directly affect your project cycle and market competitiveness.
1. What is the difference between PCB prototyping and product prototyping?
PCB prototyping focuses on the electronic circuit, while product prototyping includes enclosure, firmware, and overall functionality.
2. How many PCB prototypes do I need before production?
Most teams need 3–5 PCB revisions before EVT/DVT/PVT.
3. What is the difference between PCB prototyping and PCBA prototyping?
PCB = bare board
PCBA = board + components soldered (fully functional)
4. How long does PCB prototyping take?
With rapid prototyping companies, PCB fabrication can take 24–72 hours.
5. What is the cost of a prototype PCB?
Prices vary, but range from $10 to $100+ depending on layers, materials, and turnaround speed.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
