Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > IMS PCB – A Complete Guide to Insulated Metal Substrate PCB
Modern electronic products are becoming increasingly powerful and smaller in size. Under this trend, heat dissipation has always been a major challenge for electronic products. If the heat dissipation is not efficient enough, components may overheat, leading to a decline in product performance or even damage. To address this issue, IMS PCBs have emerged.
IMS boards, with their metal substrate and efficient heat conduction design, can significantly enhance the heat dissipation performance of products. They not only have excellent heat dissipation capabilities but also offer high mechanical strength, durability, and compact structure. They are widely applied. In this article, we will introduce IMS PCBs to you. After reading this article, you will understand what IMS PCBs are, why they are used and much more. Moreover, if you are looking for an excellent IMS PCB manufacturer, we will introduce some to you at the end of the article. So, let's first understand what an IMS PCB is!
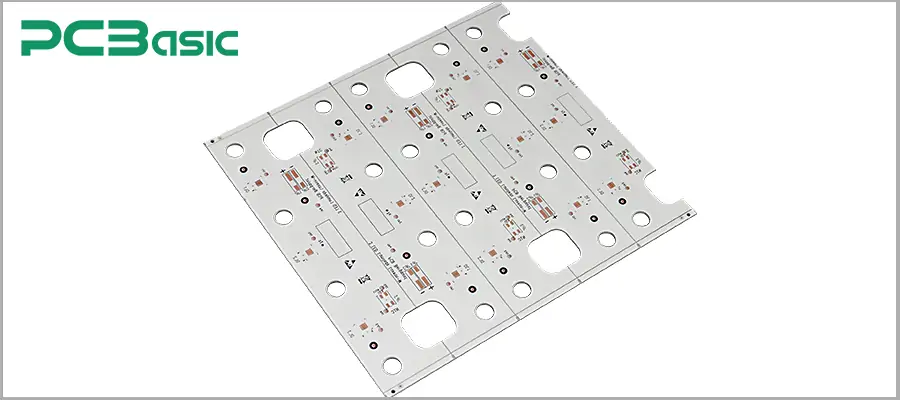

IMS PCB, also know as insulated metal substrate PCB, is a high-performance circuit board specifically designed for efficient heat dissipation in high-power and high-heat electronic devices. Unlike a traditional FR4 PCB, an IMS PCB adopts a structure of metal substrate and thermal insulating layer (In the following text, we will further elaborate on the differences between FR4 PCB and IMS PCB). This unique design enables the heat generated by electronic components to be quickly conducted through the insulating layer to the metal baseplate. Then, the baseplate transfers the heat to the surrounding environment or to external heat sinks.
Typically, an IMS PCB consists of three core layers:
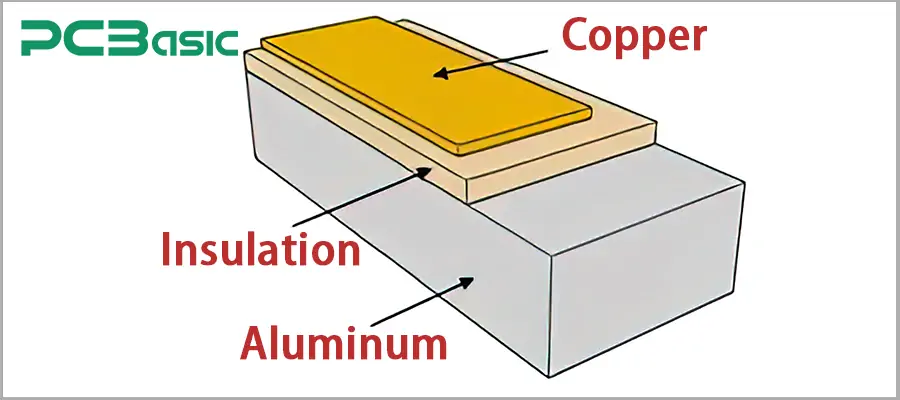
Copper circuit layer - Carries components and conducts current, while collecting heat
Insulating medium layer - Provides electrical isolation and transmits heat
Metal substrate (usually aluminum or copper) - Acts as an internal heat sink and provides mechanical support
This integrated heat dissipation structure gives IMS PCB the advantages of efficient heat dissipation, mechanical strength, and electrical stability. To fully understand the heat dissipation performance and durability of IMS PCB, we need to first understand its materials and layer structure.
The performance of IMS PCB depends on the selection of materials and the design of the stack-up structure. As mentioned earlier, IMS PCB consists of three layers: a copper circuit layer, a thermal insulating layer, and a metal substrate layer. Each layer has different functions. At the same time, they cooperate with each other to form a circuit board with efficient heat conduction, strong mechanical strength, and reliable electrical performance. Next, we will introduce the material characteristics and functions of each layer in sequence according to the structural order.
This layer is the top layer of the IMS PCB and is mainly responsible for electrical conduction and component mounting. The material used is high-purity copper foil. The common thickness ranges from 1 oz (35 μm) to 3 oz (105 μm). The thicker the copper layer, the stronger the current-carrying capacity and the more uniform the heat distribution. During the design process, we can enhance the heat conduction effect by widening the traces or using heat dissipation pads.

Function:
Provides all the electrical wiring and component soldering positions
Collects and transmits the initial heat generated by the components
This layer is the core technology layer of IMS PCB, located between the copper circuit layer and the metal substrate. The commonly used material is ceramic-filled epoxy resin. Of course, for high-performance models, polyimide or special composite materials can be used. The thermal conductivity of this layer is usually 1 - 8 W/m·K. The higher the thermal conductivity, the faster the heat conduction and the better the heat dissipation performance. The thickness of this layer is different from that of the copper circuit layer. The thinner the thickness, the better the heat dissipation, but it must also meet the insulation safety requirements.

Function:
Provide electrical isolation between the copper layer and the metal substrate to prevent short circuits
Efficiently transfer heat from the copper layer to the metal base plate
The metal substrate is the bottom layer of IMS PCB, acting as an integrated heat sink and structural support.
Common materials are:

Aluminum: Lightweight, low cost, with a thermal conductivity of approximately 200 W/m·K, suitable for LEDs and automotive electronics
Copper: With a thermal conductivity of up to 400 W/m·K, suitable for high-power, high-density designs, but heavy and expensive
Steel or alloy: Rare, used in special scenarios with extremely high mechanical strength requirements
Function
Absorbing the heat transferred by the insulating layer
Spreading it rapidly across the entire surface and dissipating it to the environment
Providing overall mechanical support and enhancing seismic resistance
The three-layer materials of the IMS PCB are closely integrated, forming a complete heat conduction path.
The greatest advantage of IMS PCB lies in its efficient heat management capability. This feature is of vital importance for the reliability of components and the lifespan of the product.
1. Thermal resistance (Rθ) is a key parameter that reflects how efficiently heat can be transferred from components to the environment. The lower the Rθ value, the faster the heat conduction, resulting in a lower component temperature and longer lifespan. The higher the Rθ value, the more heat accumulates, which can easily cause the component to overheat or fail.
2. The heat dissipation efficiency of IMS PCB is mainly determined by the thermal conductivity of the insulating layer material. The higher the thermal conductivity, the faster the heat can travel through the insulating layer to reach the metal substrate.
|
Dielectric Material Type |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Typical Applications |
|
Standard Type |
1–2 |
Low-power LEDs, General Lighting |
|
High-Performance Type |
3–5 |
Automotive ECUs, Motor Drivers |
|
Advanced Ceramic-Filled Type |
6–8+ |
Power Modules, Inverters, Industrial Control |
3. To fully leverage the thermal management advantages of IMS PCB, the following points can be taken into consideration during the design process:
Component layout: Place the main heat-generating components as close as possible to the metal core heat dissipation area.
Material selection: Use high thermal conductivity insulating layer materials in high-power areas.
Heat path optimization: Utilize thermal vias or thermal pads to provide a direct path for heat dissipation.
Avoid thermal interference: Place heat-sensitive components away from hotspots.
Auxiliary cooling: If necessary, install external heat sinks to enhance the cooling efficiency.
By combining the copper circuit layer, high thermal conductivity insulating layer and sturdy metal substrate, IMS PCB achieves outstanding heat dissipation performance and mechanical stability. Besides, IMS PCB also has many other advantages. Next, we will introduce the core advantages of IMS PCB in detail.
1. The greatest advantage of IMS PCB is its efficient thermal management capability, which has also been mentioned earlier. The combination of the metal substrate and the high thermal conductivity insulating layer enables the heat generated by components to be quickly conducted to the metal baseplate and then diffused into the environment. This process effectively reduces hotspots and prevents high-power electronic products from overheating.
2. Due to the efficient thermal management capability of IMS PCB, the equipment can maintain a lower operating temperature, thereby significantly reducing the thermal stress of components. This is very important for improving the reliability of the equipment and extending its service life.
3. The metal substrate of an IMS PCB provides strong mechanical support and significantly reduces the risk of bending.
4. Due to the high heat dissipation efficiency, many designs do not require additional large heat sinks, thus enabling a more compact and lightweight structure for the product.
5. IMS PCB can safely carry higher currents through its thick copper foil layer and efficient heat conduction channels.
IMS PCB also comes in various types. Below, we will mainly classify and explain it based on the type of metal substrate. According to the metal substrate, IMS PCB can be divided into three types: aluminum-based, copper-based, and steel/alloy-based.
Aluminum-based is the most commonly used metal substrate, featuring light weight, low cost, and moderate thermal conductivity (approximately 200 W/m·K). This type of PCB is widely used in LED lighting, automotive lamps, and consumer power modules, achieving a balance between cost and heat dissipation performance.
Copper substrates possess excellent thermal conductivity (approximately 400 W/m·K) and outstanding electrical properties, making them highly suitable for applications involving large currents and high power. However, copper-based IMS PCBs are relatively expensive and require corrosion protection to ensure durability.
Steel or alloy substrates have excellent mechanical strength and rigidity, but their thermal and electrical properties are inferior to those of aluminum and copper. Such PCBs are often used in industrial equipment with high vibration or high mechanical strength requirements, as well as in special scenarios.
|
Feature |
IMS PCB (Insulated Metal Substrate PCB) |
FR4 PCB (Traditional Fiberglass PCB) |
|
Structure |
Copper circuit layer + Thermal insulating layer + Metal substrate (Aluminum/Copper/Steel) |
Copper circuit layers + Fiberglass epoxy resin layers (multi-layer) |
|
Thermal Management |
High thermal conductivity (1–8 W/m·K), low thermal resistance, excellent heat dissipation |
Low thermal conductivity (~0.3 W/m·K), heat relies on air and external heat sinks |
|
Mechanical Strength |
High rigidity and vibration resistance from metal substrate |
Lower rigidity, more susceptible to mechanical stress |
|
Operating Temperature Range |
Suitable for high-power and high-temperature environments |
Mainly used for low-to-medium power applications |
|
Typical Applications |
LED lighting, motor drivers, automotive electronics, power modules, inverters |
Consumer electronics, computer motherboards, low-power circuits |
|
Cost |
Higher (depends on metal materials and manufacturing complexity) |
Lower, with mature and cost-effective processes |
|
Layer Design |
Commonly single-layer, double-layer, or limited multi-layer |
Flexible multi-layer designs, can exceed 10 layers |
|
Weight |
Heavier (due to metal core) |
Lighter (mainly fiberglass material) |
|
Key Advantage |
Efficient heat dissipation, high reliability, ideal for high-power and high-density designs |
Low cost, flexible design, ideal for general electronics |
IMS PCB is widely used in various high-power and high-heat dissipation electronic products. With its excellent heat dissipation performance, mechanical strength and reliability, IMS PCB plays an important role in the following fields:
1. LED Lighting and Display
IMS PCB is commonly used in LED modules, high-power lamps and display backlights because LEDs generate a lot of heat during operation. Metal substrates can quickly conduct the heat away from the LED chip, preventing brightness degradation and extending the lifespan of the lamps. Common applications include automotive headlights, street lamps, spotlights, indoor LED panels, etc.
2. Automotive Electronics
There are a large number of high-power electronic modules in modern automobiles, such as engine control units (ECUs), motor drivers and power converters. IMS PCB provides durability and thermal stability, and can adapt to the harsh automotive environment. It is commonly used in electric vehicle inverters, battery management systems (BMS) and on-board lighting systems.

3. Power Electronics and Industrial Control
IMS PCB is also widely used in power electronics and industrial control. Its low thermal resistance structure enables stable operation under continuous high loads. Its metal core design significantly enhances the reliability of the equipment, meeting the requirements of industrial applications for long lifespan and high performance.
4. Consumer Electronics and Computing Devices
IMS PCB can efficiently manage heat in limited spaces and is widely used in compact devices such as power adapters and audio amplifiers.
In summary, IMS PCB is widely applied in LED lighting, automotive electronics, power modules, and high-density consumer electronics. It combines efficient heat dissipation performance with structural strength, making it the preferred solution for modern high-power electronic design.
PCBasic is a professional PCB and PCBA manufacturing enterprise. It has rich experience and advanced production capabilities in the IMS PCB field. PCBasic is a reliable IMS PCB manufacturer for global customers, offering efficient thermal management solutions, strict quality control, and flexible customization services.
1. PCBasic is equipped with automated SMT production lines, precision drilling and laser cutting equipment, AOI, flying probe testing and X-ray inspection. They can meet the production needs of single-sided, double-sided and multi-layer IMS PCBs. Whether it is aluminum substrate, copper substrate or steel/alloy substrate, PCBasic can provide products with high thermal conductivity and high reliability.
2. PCBasic can provide insulation layer materials with thermal conductivity ranging from 1 to 8 W/m·K. Moreover, they support customized copper thickness, metal thickness, thermal via design and special surface treatment. Customers can choose single-sided, double-sided or multi-layer IMS PCBs according to project requirements to achieve the best thermal management and mechanical strength.
3. PCBasic has passed multiple international certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, UL, RoHS, REACH, etc. During the production process, they will implement full-process quality traceability and reliability testing. They can ensure that each IMS PCB meets the usage standards of high-power electronic products.
If you are looking for a reliable IMS PCB manufacturer, PCBasic will be an ideal partner to help your products achieve higher performance and longer lifespan.
This article is coming to an end now. In summary, IMS PCB is a high-performance circuit board with excellent heat-conducting properties. It is specially designed for high heat demands and harsh environments. The unique combination of its durability, electrical reliability, and thermal efficiency makes it a powerful solution for modern electronic devices.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
