Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > IC Reballing: A Complete Guide
IC reballing plays a crucial role in the maintenance, rework and manufacturing of modern electronic products. Reballing can help save expensive or hard-to-replace integrated circuits (ICs) in many devices. Successful IC reballing requires not only experience but also high-quality tools and kits. These tools usually include IC reballing paste, hot air guns or infrared heating devices, solder balls and PCB cleaners, etc. Only by being equipped with the appropriate reballing equipment and mastering the standardized operation procedures can each solder joint be ensured to be firm and reliable, and the failure of rework or the secondary damage of electronic equipment be avoided.
So, what is IC reballing? How to reball IC? Today, we will discuss the topic of IC reballing. First of all, let's understand the definition of IC reballing first.
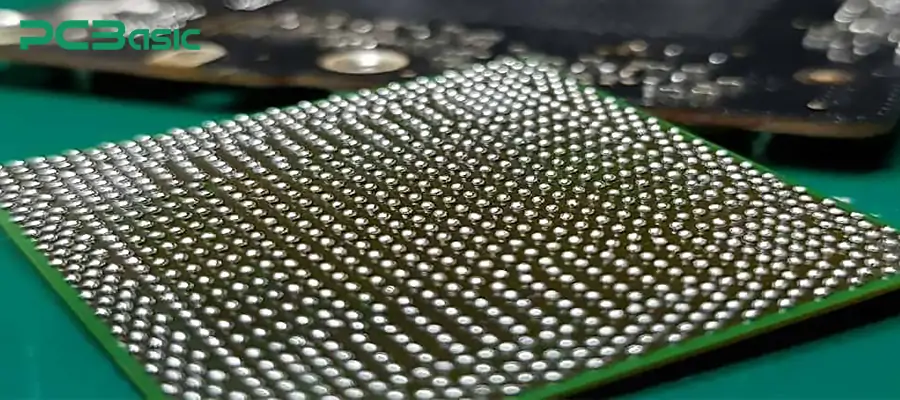
IC reballing refers to the process of removing integrated circuits from the circuit board, cleaning them thoroughly, re-implanting solder balls, and then reinstalling them onto the circuit board. Simply put, IC reballing involves safely removing the integrated circuit from the circuit board, then cleaning up the original solder residue, using a dedicated IC reballing stencil and solder balls to re-balling the chip, and finally re-soldering the IC onto the circuit board.
The IC reballing meaning lies in restoring the electrical connection between the IC and the circuit board. Finally, achieve the repair of circuit faults caused by solder joint breakage, false soldering or corrosion. IC reballing is particularly common in mobile IC reballing, BGA chip rework and various high-precision electronic assemblies. It is a common method for the maintenance and remanufacturing of smartphones, laptops, game consoles, automotive electronics and industrial control equipment.
IC is the core of modern electronic devices. Throughout the entire service life of electronic products, ICs may malfunction for various reasons. When the IC malfunctions, IC reballing becomes particularly important. Because it can restore the function of the device without replacing expensive chips. Understanding the root cause of IC failure helps us determine whether it is suitable for reballing IC. Common causes leading to IC failure and the need to reballing include:

Excessively high temperatures are one of the main causes of IC problems, especially for chips packaged in BGA (Ball Grid Array). Long-term high temperatures can cause fatigue, cracking or failure of the solder joints at the bottom of the IC, resulting in poor electrical connections. At this point, appropriate IC reballing tools can be used, such as a hot air station or IC reballing stencil, to reball and restore the connection.
ICs in industrial equipment, automotive electronics or mobile devices are often subject to continuous vibration or shock. In such an environment, ICs are prone to solder ball cracking and breaking, which in turn can cause intermittent or permanent faults. Rather than replacing the entire chip, it is more economical and efficient to repair it by reballing IC. Technicians usually use dedicated mobile IC reballing tools and IC reballing kits to remove damaged solder balls and perform precise mobile IC reballing.

When exposed to air, moisture or chemicals for a long time, solder joints are prone to oxidation and corrosion, resulting in poor contact. At this point, reliable electrical connections can also be restored through IC reballing without the need to replace the entire IC.
In conclusion, IC faults caused by overheating, mechanical stress and oxidation can all be effectively repaired by selecting appropriate tools and materials for IC reballing. Whether using the complete IC reballing kit or the dedicated mobile IC reballing tools, understanding the root cause of IC faults is the first step to achieving efficient maintenance.
Before deciding whether to perform IC reballing, it is crucial to accurately identify faults in integrated circuits. The common causes of IC failure have been understood before. So how to determine whether the equipment needs to reballing? The following are common methods for detecting IC damage:
1. The device cannot be turned on
If electronic devices fail to start or frequently shut down automatically, it is usually due to the breakage of the solder joints beneath the key IC. At this point, we can utilize the IC reballing kit or the mobile IC reballing tools. Cooperate with professional reballing equipment for inspection, disassembly and restoration of IC connections.
2. No signal or functional abnormality
If the device has no network signal, the mobile phone cannot connect to the Internet, or there are random restarts or crashes and other abnormalities, it is often caused by damage or oxidation of the solder balls under the IC. The electrical connection can also be restored by reballing and soldering.
3. Local overheating of the IC
Abnormal heating found in a local area of a PCB or IC is usually a typical manifestation of a short circuit or an open solder joint. We perform positioning and repair through mobile IC reballing, and with the aid of thermal imagers and dedicated reballing equipment.
4. Visual inspection and microscopic examination
Inspect the IC and its surrounding solder joints through a magnifying glass or microscope to observe if there are any cracks, pad lifting, oxidation or other phenomena. If the above situation exists, reballing can be carried out to repair the faulty solder joint.
5. Electrical testing
The connection between each pin of the IC and the PCB can be detected by using a multimeter or a continuity tester. If the reading is abnormal, it often indicates that a reballing IC is needed.
The above are the common methods for determining whether an IC is faulty and whether the ball needs to be replanted. By carefully observing the performance of the equipment and combining it with the appropriate reballing equipment and technological means, it is possible to accurately determine whether the IC is damaged. Early detection and precise repair not only save time and costs but also extend the service life of electronic products.
Successful IC reballing relies on professional tools and materials to ensure an accurate and reliable process. Whether you are using standard chips or performing mobile IC reballing, using the right IC reballing tools and equipment will significantly enhance your efficiency and maintenance quality. The following table summarizes the basic tools and equipment used for IC reballing in general and mobile maintenance scenarios.
|
Tool / Equipment |
Description & Function |
ApplicationNotes |
|
IC Reballing Kit |
Complete set including reballing tools, stencils, solder balls, paste, tweezers, etc. |
For beginners and professionals |
|
IC Reballing Tools |
Includes tweezers, scrapers, spatulas, and cleaning brushes |
General reballing IC process |
|
Mobile IC Reballing Tools |
Mini hot air guns, compact stencils, and fine-point tweezers for small devices |
Optimized for smartphones and tablets |
|
Reballing Equipment |
Hot air station, reflow oven, or infrared rework station |
Provides controlled heating for soldering |
|
IC Reballing Stencil |
Precision template for aligning and placing solder balls on the IC |
Ensures accurate ball placement |
|
IC Reballing Paste |
Special solder paste used for holding and bonding solder balls during reballing |
Improves reballing yield |
|
Solder Balls |
Tiny spheres of solder used to re-establish connections |
Available in different diameters |
|
Flux |
Chemical cleaning agent to improve solder flow and adhesion |
Essential for reliable solder joints |
|
Cleaning Agents |
Solvents and wipes for removing old solder and flux residues |
Keeps IC and PCB clean before reballing |
After preparing the tools needed for reballing, the process of reballing can be carried out. The reballing process is an accurate and crucial maintenance method, mainly used to repair ICs in packages such as BGA. The following is a typical reballing IC process:
1. IC disassembly
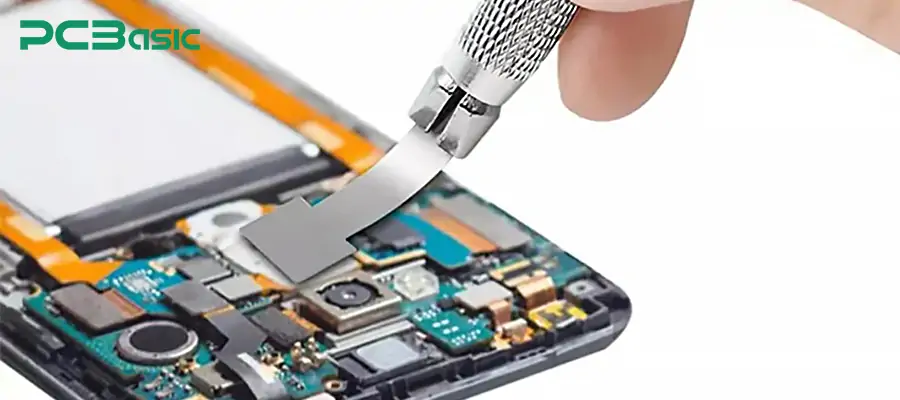

First of all, use a hot air table or a dedicated reballing equipment to heat the IC to melt the solder joints. Safely remove the damaged IC from the circuit board to avoid damaging the PCB.
2. Clean Up
Use solder tape, cleaning agents and various IC reballing tools (such as brushes, scrapers, etc.) to thoroughly remove the residual solder and flux on the IC and PCB. This step is to prepare the surface for the implantation of the new soldering balls.
3. Apply the template
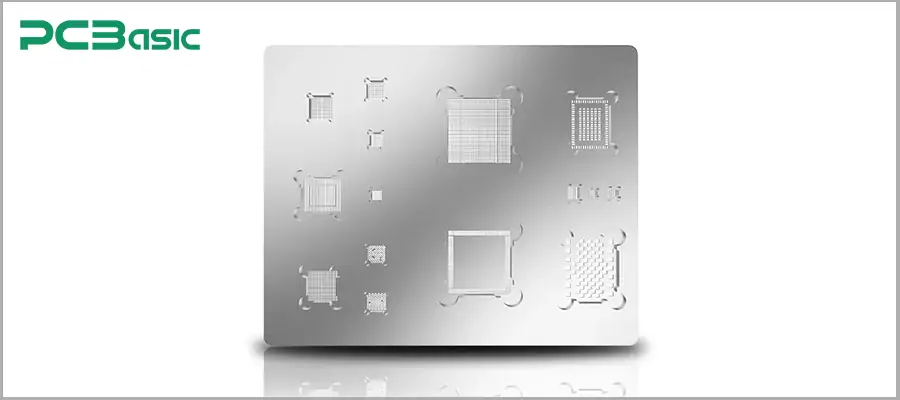
Align the high-precision IC reballing stencil with the bottom of the IC to ensure that each solder ball can be precisely placed in the designated position.
4. Add soldering balls

Evenly sprinkle the soldering balls of appropriate diameters on the formwork. Sometimes, a layer of IC reballing paste is applied first, which helps to fix the solder balls and improve the subsequent soldering quality.
5. Reflow soldering
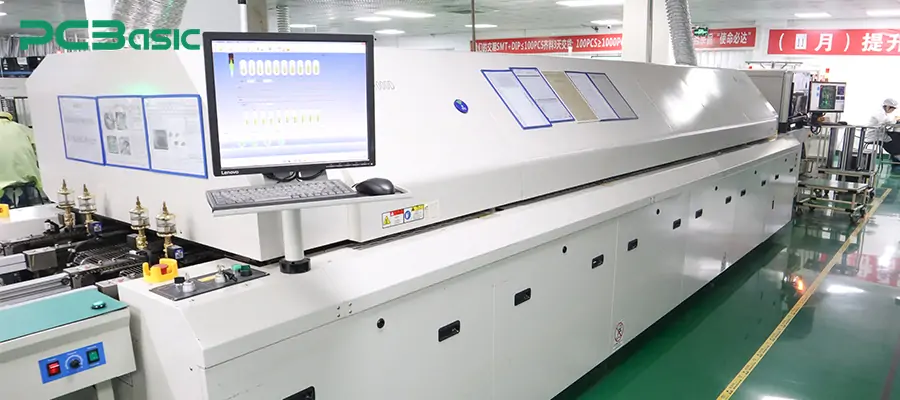

Place the IC with solder balls (after stencil removal) into a reflow oven or apply heat using a hot air rework station.
6. Formwork removal and inspection
After the soldering is completed, remove the IC reballing stencil. Carefully inspect all the solder balls at the bottom of the IC with a microscope again to ensure that the solder joints are firm, without false soldering or short circuits.
7. Reinstall
ICs that have undergone reballing ball treatment can be re-soldered back to the PCB using the "mobile IC reballing tools" or reflow soldering equipment. Sometimes, flux needs to be reapplied to ensure reliable connections.
✅ Excessive heat may damage the IC or PCB. When using a reflux furnace or a hot air gun, it is necessary to operate in accordance with the recommended temperature curve.
✅ Residual solder, flux or contaminants may cause poor contact, short circuit or later corrosion. Be sure to clean thoroughly before replanting the balls.
✅ Even a slight deviation can cause functional malfunctions or subsequent assembly problems.
✅ IC reballing is a high-precision process, and haste often leads to the failure of expensive components due to operational errors.
This summarizes the complete IC reballing process. Throughout the entire reballing IC process, whether it is conventional or mobile IC reballing, choosing high-quality IC reballing kits, templates and solder paste is the key to ensuring the success of maintenance.
IC reballing is an important process for extending the service life of electronic devices and reducing maintenance costs. It provides an efficient solution for restoring the functionality of expensive integrated circuits without the need to replace chips. By understanding the common causes of IC faults such as overheating, vibration and oxidation, and mastering the correct detection and replanting methods, we can significantly improve maintenance efficiency and reduce costs. Whether used in smartphones, automotive electronics or industrial equipment, the success of IC reballing depends on choosing the right tools, following standardized operation procedures and ensuring accuracy at every stage. However, for complex circuits or important equipment, choosing professional services is the safest solution.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
1. What is the most common reason for the failure of replanting balls?
These are all possible reasons that may cause the IC to need to replant the ball.
2. How to prevent the occurrence of tin ball bridging when replanting the balls?
These are all effective methods to avoid the occurrence of tin ball bridging when replanting the balls.
3. Can beginners replant IC balls at home by themselves?
Theoretically, it is possible. However, it is not recommended without suitable equipment (such as temperature-controlled hot air tables, re-planting ball templates, microscopes). Because the replanted balls require high-precision alignment and temperature control. However, beginners can practice more on used boards before attempting to deal with valuable ICs.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
