Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > How to Test a PCB Board: Complete Guide to PCB Testing
Whether it is developing the early PCB prototype or conducting mass production of electronic products, PCB testing is an indispensable process. Through a scientific testing process, we can ensure the reliability, performance stability and long-term safety of the circuit board. The complete circuit board testing and validation can confirm that each printed circuit board complies with the design standards, and successfully passes the strict PCB electrical testing, while avoiding problems such as open circuits, short circuits, incorrect component installation or soldering defects.
Without a systematic PCB testing method, hidden defects may directly enter the finished product, ultimately leading to equipment failure, product recall, brand damage, and even posing safety risks in critical applications. Therefore, it is very important to establish a perfect PCB testing strategy in production. By combining functional testing (FCT), automated PCB testing and PCB reliability testing, it can not only significantly enhance the quality control capability, but also effectively reduce the risks in production and after-sales service.
In this guide, let's systematically learn how to test a PCB board, covering commonly used PCB testing tools, PCB testers, and PCB testing methods. Meanwhile, we will share the verified PCB analysis methods and the experience of print circuit board assembly testing, helping you complete PCB testing more efficiently to ensure product quality and reliability.
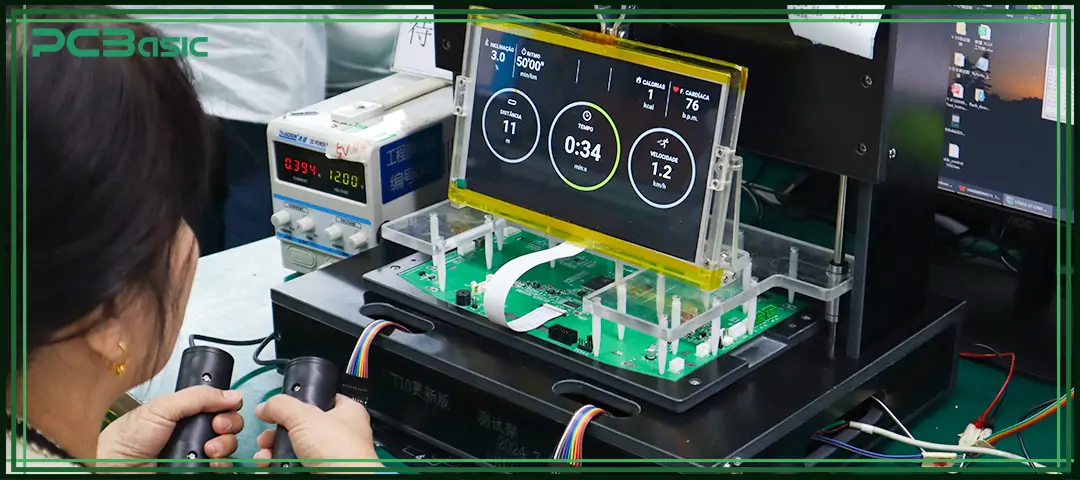

PCB testing refers to the process of comprehensively inspecting the functions, performance, quality and structural integrity of printed circuit boards (PCBs) before their mass production or formal use. Through systematic circuit board testing and validation, potential problems such as short circuits, open circuits, missing components, incorrect installation orientation, false soldering or thermal failure can be detected at an early stage, thereby preventing defective circuit boards from entering the market.
A perfect PCB board testing process can not only confirm whether the PCB functional testing meets the design requirements, but also the stability and durability of the circuit board in the actual working environment through means such as PCB electrical testing, FCT testing and PCB reliability testing. These PCB testing methods cover everything from simple conductivity checks to complex automated PCB testing and print circuit board assembly testing. Testing methods can be flexibly selected according to different product types and application scenarios.
With the stronger functions and more complex designs of electronic products, the role of PCB testing services in the entire product development and manufacturing process is becoming increasingly important. Only by using high-quality PCB testing tools and professional PCB testing solutions can it be ensured that each PCB meets design and industry standards, achieving high performance, high reliability and high-quality delivery.
The selection of an appropriate PCB testing method depends on multiple factors, including product complexity, production batch size, testing objectives and budget. Here’s a table of popular PCB testing methods:
|
Method |
Type |
Main Purpose |
Pros |
Best For |
|
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) |
Automated |
Electrical checks at the node level |
High accuracy, fast |
High-volume production |
|
Flying Probe Testing |
Automated |
Contactless node testing |
Cost-effective for low-volume |
Prototyping and small batches |
|
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) |
Automated |
Visual inspection |
Quick defect detection |
SMT inspection |
|
Burn-In Testing |
Functional |
Stress testing under load |
Ensures long-term durability |
Mission-critical applications |
|
X-Ray Inspection |
Non-Destructive |
Hidden joint inspection |
Checks BGA and internal layers |
Complex multilayer boards |
|
Functional Circuit Testing (FCT) |
Functional |
End-product functionality check |
Simulates real-world use |
Final quality control |
|
Environmental Testing |
Environmental |
Thermal, humidity, and shock tests |
Verifies robustness |
Harsh use-case scenarios |
Understanding how to test a PCB board is not as simple as powering on the circuit board. A standard PCB board testing process can ensure accurate results, efficient verification, and significantly reduce production risks.
Before starting to test the PCB, a complete test plan needs to be formulated, including:
• Test coverage goals: Clarify whether to conduct component-level testing or full-board functional testing.
• Acceptable failure criteria: Determine which defects (such as open circuits, short circuits, and solder joint defects) must be scrapped or reworked.
• Required PCB testing tools and fixtures: Select appropriate PCB testers, probes, fixtures or automated PCB testing equipment.
• Safety protocols: When conducting PCB electrical testing, ensure the safety of operators and equipment.
A complete test plan can reduce repetitive rework, accelerate production progress, and ensure the consistency and traceability of PCB testing results.
After the test plan is prepared, the PCB tester can be used to perform the test according to the selected PCB testing methods. The testing process may include automatic probe detection, running functional routines or signal scanning, and the following indicators are recorded and analyzed:
• Electrical performance (voltage, current, impedance, etc.)
• Signal integrity (interference, noise, delay)
• Functional performance (whether the components work normally and whether the FCT test is passed)
All data will undergo PCB analysis and be compared with the design standards. If abnormalities such as short circuits, open circuits or functional failures are found during PCB testing, the circuit board will be marked for repair or scrapping to ensure that defective products do not enter the next stage of production or the market.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
To conduct accurate and reliable PCB analysis and circuit board testing, it is necessary to be equipped with appropriate PCB testing equipment and tools. These tools can help engineers quickly locate defects, verify designs and ensure that products meet quality standards
PCB testers are the core equipment for achieving efficient and standardized printed circuit board testing. They can automatically perform various electrical tests, provide consistent and repeatable test results, and avoid errors caused by manual operation.
Common types of PCB testers include ICT (In-Circuit Test) machines, which directly detect the soldering quality, resistance, capacitance and circuit connectivity of components through a bed-of-nails or probe, and are suitable for mass production.
In addition, there are also the flying probe testers. It uses high-speed moving probes to test the circuit board point-by-point. It is highly flexible and does not require custom fixtures. It is suitable for small-batch and prototype PCB board testing.
Common PCB testers also include ATE systems (Automated Test Equipment), which can comprehensively use hardware, software and automatic probes to complete high-precision PCB testing. Covering a wide range of requirements from FCT testing to PCB electrical testing.
Each type of PCB tester is designed for different production scales and test coverage requirements. A reasonable selection can enhance production efficiency and reduce test costs.
Test fixtures and probes are indispensable tools for achieving precise automated PCB testing.
Fixtures are custom-made according to the layout of test points on a PCB, used to fix the circuit board and ensure that each test point can be accurately touched. Spring-loaded pins or bed-of-nails come into contact with the circuit board in PCB electrical testing and are used to quickly detect open circuits, short circuits and soldering defects.
In a large-scale production environment, these tools can significantly improve the testing speed and stability, and are the key to achieving efficient PCB testing services.
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) provides complete PCB test solutions, integrating software control, hardware modules and automatic probe systems. Realize full-process PCB functional testing, circuit board testing, and validation.
Automated testing equipment features high throughput and can complete the testing of a large number of PCB boards in a short time. Moreover, it can also conduct real-time diagnostics, quickly identify faults during the testing process and record detailed data for subsequent PCB analysis. Meanwhile, the automated test equipment can conduct complex signal analysis, supporting multi-channel and high-frequency signal testing to ensure that the products meet the design specifications and reliability requirements.
Whether it is FCT testing or ICT, ATE can significantly improve production efficiency, reduce manual intervention, and enhance the accuracy of PCB reliability testing.
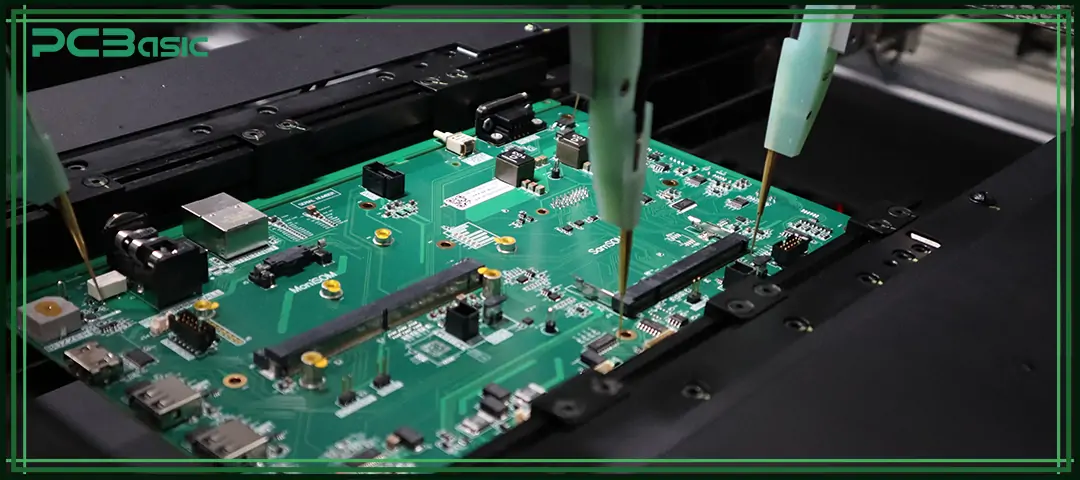
Automated PCB Testing has the advantages of high speed, high precision and consistent results. Through ICT, flying probe testing and automated test equipment (ATE), it can efficiently complete PCB functional testing and circuit board testing and validation, quickly detect problems such as open circuits and short circuits, and is very suitable for mass production.
Manual PCB testing is more suitable for prototype development, small-batch production or verification of special functions. It enables engineers to flexibly conduct PCB analysis, adjust parameters and identify details that are not covered by automated testing.
|
Feature |
Automated PCB Testing |
Manual PCB Testing |
|
Speed |
Very fast |
Slower and labor-intensive |
|
Accuracy |
High |
Subject to human error |
|
Initial Cost |
Expensive due to fixtures |
Lower initial cost |
|
Best For |
High-volume manufacturing |
Prototypes and small batches |
In actual production, two methods are usually combined: manual testing is used in the small-batch stage, and automated PCB testing is adopted in the large-batch stage, which not only ensures efficiency but also guarantees the reliability of PCB testing.
PCBasic is a professional company located in Shenzhen, specializing in PCB manufacturing & assembly and full-process PCB testing services. Its core businesses include PCB production and assembly, PCB testing and validation, etc.
Equipped with complete PCB testers and Automated Test Equipment (ATE), capable of performing various PCB testing methods, PCBasic provides reliable quality assurance for industries such as consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial control.
PCBasic can cover the entire process of PCB board testing and PCB reliability testing from prototype boards to mass production. Its testing methods include In-Circuit testing (ICT), flying probe testing, and functional circuit testing (FCT). X-Ray inspection, environmental stress & aging test, and AOI, etc.
Additionally, PCBasic strictly adheres to international standards and has passed certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, and IATF 16949, and complies with IPC test process standards.
Through professional PCB testing tools and complete PCB test solutions, PCBasic can ensure that the PCBs and PCBA products it produces meet design and regulatory requirements, achieving high performance, high reliability and stable delivery.
PCB testing is not an option but a necessary guarantee for product quality. With the increase in the complexity of electronic products, reliable PCB testing tools and mature PCB testing methods need to be used. And it is necessary to rely on professional PCB testing services to ensure stability and safety.
If you are looking for reliable PCB and PCBA products that have undergone strict PCB testing, PCBasic is a trustworthy choice. It not only provides customers with the full-process circuit board testing and validation from prototype boards to mass production, but is also equipped with complete PCB testing tools and Automated Test Equipment (ATE). Through various PCB testing methods, PCBasic can ensure that each circuit board meets the design specifications and international quality standards.
How to test a PCB board without equipment?
You can visually inspect the board for burnt components, incorrect placements, or broken traces. A multimeter can be used for continuity checks, though this is limited and not a replacement for full PCB testing.
What are the most reliable PCB testing tools?
Top tools include automated test equipment (ATE), ICT testers, flying probe machines, and AOI systems. These offer precise PCB analysis and defect detection.
Can I reuse test fixtures for different PCBs?
Generally, no. Each fixture is custom-made. However, modular test fixtures exist for similar board layouts. Customization still ensures more accurate printed circuit board testing.
What’s the difference between FCT and ICT?
ICT checks individual components and connections on the board, ideal for detecting basic defects. FCT testing, on the other hand, simulates real-world usage to verify that the entire board functions properly. Both are vital in PCB functional testing strategies.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
