Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > > Heat Sensor Circuit: Working Principle, Types, and Applications
Heat is a monitoring signal that can help us prevent fires, overheating, or premature damage to equipment. In modern home security, industrial production, and the operation of electronic devices, temperature monitoring has always been one of the most important aspects. Therefore, people have adopted heat sensors.
A heat sensor is an electronic component that detects temperature changes and converts them into electrical signals. The converted electrical signals can further trigger control logic, heat detector alarms, and achieve automatic control, protection, or warning. In simple terms, a heat sensor is a reliable, fast device that can convert temperature rise into executable signals.
In practical applications, there are different forms of heat sensors, and each has its own focus. Now, let's read this article together! We will discuss the working principle of heat sensors, common types of heat sensor circuits, and so on in the article.
Before delving into the heat sensor circuit, let's first understand what a heat sensor is!

Heat sensors, also known as temperature sensors (heat sensor) or heat detectors, are electronic components used to detect temperature changes and convert these changes into electrical signals. Their main function is to monitor the temperature of the surrounding environment or specific objects. When the temperature reaches or exceeds the preset threshold, the circuit will trigger the corresponding output through the sensor's signal, such as an alarm, starting the cooling system, or performing a safety shutdown.
Unlike smoke alarms that rely on smoke particles, heat detectors directly respond to the temperature in the air. This characteristic makes it more reliable in environments with a lot of dust, high humidity, or heavy cooking fumes. People often confuse smoke detectors with heat sensors. Below is a table that can help you better distinguish.
|
Feature |
Heat Sensor |
Smoke Detector |
|
Principle |
Detects air temperature rise |
Detects smoke particles |
|
Best Use |
Kitchens, garages, dusty or humid areas |
Homes, offices, clean spaces |
|
Reliability |
Few false alarms in harsh environments |
Early warning but prone to false alarms |
|
Response |
Slower (needs significant heat) |
Faster (detects smoldering fires) |
As a direct temperature-measuring electronic component, heat sensors are widely regarded as a reliable and low-maintenance method for heat detection. They are widely used in kitchens, garages, industrial workshops, and various electronic systems. Since different environments have different requirements, heat sensors are available in multiple types.
Depending on different working principles and application scenarios, Heat sensors come in various forms. The following are several common types:
Furnace heat sensors: This type of heat sensor is suitable for boilers, stoves, and industrial heating systems. It can withstand high temperatures and can cut off the power supply or trigger safety controls when overheating through the heat sensor switch.
Infrared heat sensor: This heat sensor measures temperature without physical contact by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects. It is commonly used in electronic devices, intelligent devices, and modern wireless heat sensors, and is of great value for IoT monitoring.
Constant-temperature heat detector: It only activates when the surrounding air reaches the preset temperature. Such sensors are often installed in kitchens, garages, or environments with a lot of dust as home heat sensors.
Rate-responsive heat detector: More sensitive to rapid temperature increases. Widely used in warehouses, factories, and other places. This type of heat sensor can trigger the heat detector alarm earlier when the fire is developing rapidly.
Wireless heat sensor: The wireless heat sensor combines a heat sensor with a wireless communication module. This type of sensor can directly transmit data to a smartphone or building control system. It is flexible to install and has low maintenance costs, and is an important component of advanced intelligent fire protection systems.
No matter which type of heat sensor it is, it functions within a circuit. So what are the components of a heat sensor circuit?
Typically, a typical heat sensor circuit consists of the following components:
1. Sensing Element: It is the core of the entire heat sensor circuit, used to sense the ambient temperature and convert it into an electrical signal. Common sensing elements include thermistors, thermocouples, and infrared sensors. The working principles of these three are different. For example, a thermistor will have its resistance value decrease as the temperature rises, while a thermocouple will generate a voltage difference at high temperatures. In fact, the role of the sensing element in the circuit is the "front-end sensor". It provides the circuit with a voltage or resistance signal proportional to the temperature, thereby providing the circuit with clear triggering conditions.
2. Comparator / Operational Amplifier: The comparator is a common analog circuit component used to compare the signal from the sensor with the set threshold. When the sensor voltage exceeds the threshold, the comparator outputs a high logic level; otherwise, it remains at a low level. If the sensor signal is too weak, an operational amplifier is needed to amplify it, enabling subsequent circuits to accurately identify. Its role in the heat sensor circuit is like a "judgment brain", determining whether to trigger an alarm or perform an action.
3. Relay or Switch: The relay is a switch device controlled by an electrical signal. It can control high voltage with low voltage and often exists as the execution part in the heat sensor circuit. When the comparator detects the over-temperature condition, it will send a triggering signal to the relay. Then the relay will immediately close or open the circuit, thereby controlling the operation of external devices.
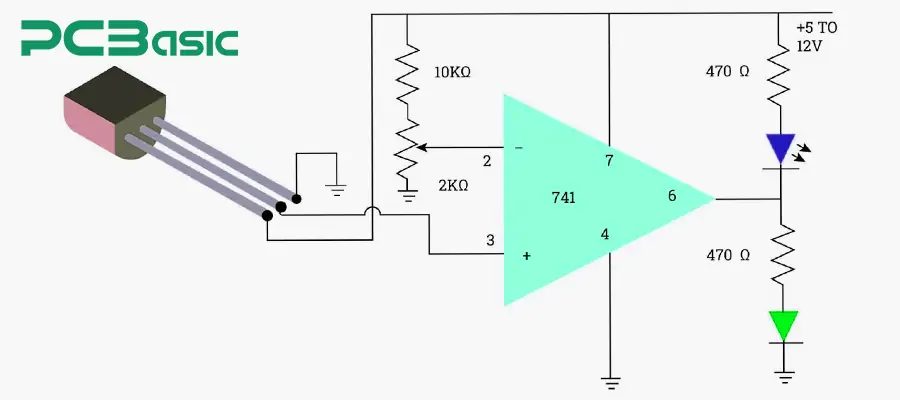
4. Alarm / Indicator: They are the user-facing output part of the heat sensor circuit. Common forms include buzzers, alarm bells, or indicator lights. They can convert the electrical signals of the circuit into sound or light signals, thereby alerting the user to take notice. For example, in a household fire alarm circuit, when the temperature exceeds 70°C, the circuit not only cuts off the power supply but also drives the buzzer to emit a sharp alarm and lights up the red LED, ensuring that the user can receive the prompt in time.
5. Power Supply: A stable power supply is a necessary condition for the operation of any heat sensor circuit. Usually, the size of the used direct current power supply depends on the specifications of the sensor, amplifier, and relay. The stability of the power supply is crucial for the reliability of the entire circuit, as voltage fluctuations may cause the comparator to misjudge or the relay to fail.
It is because of the joint collaboration of these components that the heat sensor circuit can complete the entire process from temperature detection to signal processing, to action execution and warning issuance.
Earlier, we mentioned that the heat sensing circuit functions through the joint efforts of multiple components. So, how do these components collaborate with each other? Next, we will explain this to you.
1. First of all, when the environmental temperature changes, the sensing element in the circuit will respond first. Take the thermistor as an example. When the environmental temperature changes, its resistance value will decrease as the temperature rises; during this process, the sensing element converts the temperature change into an electrical signal. This can be called the initial "input" of the circuit.
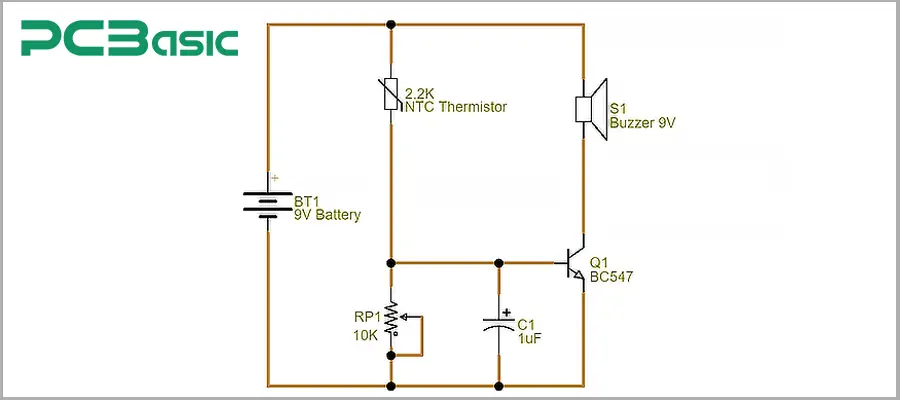
2. Then, the modified signal will be sent to a comparator or an operational amplifier. When the sensor signal is lower than the threshold, the circuit remains in a static state; once the temperature rises above the threshold, the corresponding voltage signal will cross the reference point, and the comparator will quickly reverse the output state. This "threshold judgment" mechanism ensures that the circuit operates stably at normal temperatures and can respond immediately in case of overheating.
3. After the comparator outputs the trigger signal, it will drive the relay or electronic switch. At this point, the temperature change detected by the sensor is converted into a real execution action.
4. Finally, when the relay is triggered, the alarm device equipped in the circuit will start simultaneously, providing users with audible or visual cues as a prompt. Thus, even if the user is not directly monitoring the equipment, they can detect abnormalities immediately and take appropriate measures.
In summary, the heat sensor plays a central role in this circuit. This closed-loop process of "perception - judgment - execution - prompt" constitutes the basis of most heat detection devices.
In practical applications, based on different working principles, there are two different designs of heat sensor circuits, namely the constant-temperature type heat sensor circuit and the temperature-rise type heat sensor circuit. Although they both belong to heat detection devices, they differ in triggering conditions and application scenarios.
As shown in the figure, a fixed temperature type heat sensor circuit works as follows:
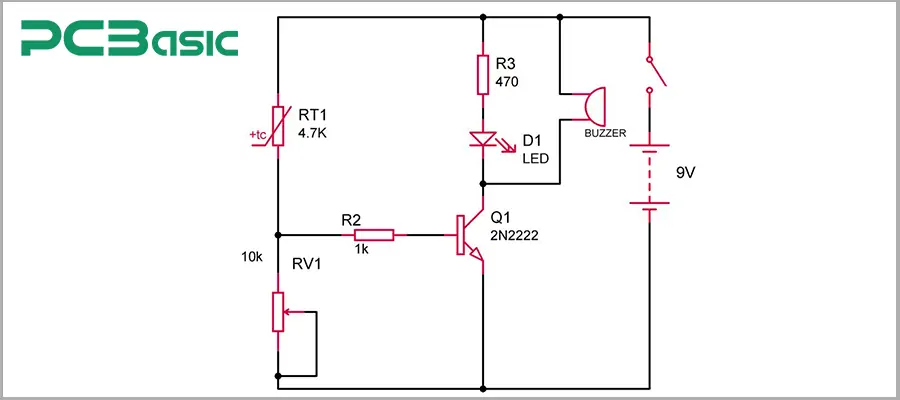
When the temperature reaches the preset threshold, the circuit will be activated. For instance, a furnace heat sensor can be set to respond at 60℃. Once the temperature of the furnace exceeds this critical point, the heat sensor switch will act, sending a signal to the circuit, either cutting off the power supply or activating the heat detector alarm. This mechanism ensures that overheating situations can be detected in time, reducing the risk of fire and protecting the equipment.
In other words, these heat detectors only respond to "absolute temperature values", rather than the rate of temperature increase.
Unlike the constant-temperature type, the rate-of-rise heat sensor circuit focuses on the "speed" of temperature changes. It does not wait until a fixed temperature (such as 60℃) is reached, but continuously monitors the rate of temperature increase. For example, if the room temperature rises by more than 10℃ within one minute, the heat sensor will trigger an alarm.
This type of heat sensor is particularly suitable for environments where flames or the development of overheating occurs very rapidly, because simply waiting to reach a fixed threshold might be too late.
Heat sensor circuits offer significant advantages in modern households, industries and electronic systems. For example,
1. The heat sensing circuit remains reliable even in dusty, humid or smoky environments and is often installed in high-risk areas. Compared to traditional smoke detectors, it does not fail due to dust or steam. In industrial plants, kitchens or boiler rooms, using heat detectors is safer than relying solely on optical smoke alarms.
2. Compared with optical smoke alarms, heat sensor circuits require less maintenance. Since they do not rely on the optical reflection principle, they are less likely to give false alarms, which significantly reduces the need for regular cleaning and maintenance. The low maintenance characteristic of heat sensor circuits makes them an ideal choice for home heat sensors and industrial heat detection devices.
3. Compatibility: Modern heat sensors can be connected either via wired connection or through wireless heat sensors to smart home or industrial Internet of Things systems. The wireless version of the heat detector can directly transmit abnormal temperature readings to mobile phones or control centers, significantly enhancing the system's compatibility and convenience.
Heat sensors have extensive applications in both daily life and industrial fields. They play a crucial role in many application areas.
1. Home Safety
In the home environment, heat sensors are used in kitchens, garages and bedrooms to ensure the safety of family members. For instance, wireless sensors installed in the kitchen and garage; heat detection alarms integrated with smart home systems play a crucial role in maintaining the safety of the household.

2. Industrial Machines
In the industrial field, heat sensor circuits are often installed in high-temperature or high-power equipment. For instance, there are furnace heat sensors which can automatically cut off the power supply when the boiler or industrial furnace overheats, thus preventing accidents. Moreover, heat sensors are frequently incorporated into motors and transformers to monitor the temperature in real time and avoid overload damage.
3. Electronics Overheating Protection
In modern electronic devices, heat sensor circuits are also indispensable. For instance, the heat sensors in the mainboards of computers and mobile phones can monitor the temperature of the chips in real time to prevent hardware damage caused by overheating.
Thermal sensors play a crucial role in preventing overheating and fire risks in households, industries, and electronic devices. The realization of this role is inseparable from the design and implementation of thermal sensing circuits. A stable and reliable thermal sensor circuit is no longer an optional choice but a necessary requirement for ensuring safety and efficiency.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
