Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > A Complete Guide to Soldering Machine: Types, Functions, Applications
Precise, reliable and efficient soldering is of great significance in the field of modern electronic manufacturing. Whether it is assembling smartphones, automotive control units, or industrial sensors, soldering machines play a crucial role in ensuring a firm electrical connection and the long-term reliability of products. With the increasing miniaturization and high density of electronic products, the soldering process has become particularly crucial in the manufacturing of PCBs and PCBA.
In this article, we will comprehensively introduce the types, functions, application fields of soldering machines as well as common manual soldering tools. This article can help you choose the most suitable soldering solution according to the project requirements. Whether you are an electronics manufacturer, an engineer, or a DIY technician, this guide can provide practical references for your soldering process.
A soldering machine is a device specifically designed for soldering electronic components onto printed circuit boards. It achieves a strong electrical and mechanical connection between metals by melting solder (a fusible alloy), and this process can be completed automatically or with assistance. According to the production scale and application requirements, soldering machines can be classified into manual, semi-automatic and fully automatic types.
Unlike traditional manual soldering with a handheld soldering iron, soldering machines increase the speed, consistency and precision of soldering through automated operation. The automatic soldering machine is particularly suitable for the production of large quantities of electronic products. Automatic soldering machines such as wave soldering machines, reflow soldering machines and selective soldering machines are widely used in SMT and THT processes. The application of these soldering machines has significantly enhanced production efficiency and can meet lead-free environmental protection standards.
For complex or hybrid technology PCBs, selective wave soldering machines and surface mount soldering integrated machines can provide higher precision. However, in sample making or maintenance, soldering irons, soldering tool kits and professional soldering stations remain indispensable. The selection of appropriate soldering equipment not only affects production capacity, but also directly determines the soldering quality and cost control. So, what types of soldering machines are applied in PCB assembly?
In PCB and PCBA manufacturing, choosing the right soldering machine is crucial for ensuring product quality, improving production efficiency and achieving large-scale manufacturing. According to different production needs - whether it is mass assembly, precision surface mount or prototype repair - a wide range of soldering equipment is available on the market, from fully automated systems to manual soldering tools. Below, we have summarized some commonly used and high-end types of soldering machines.
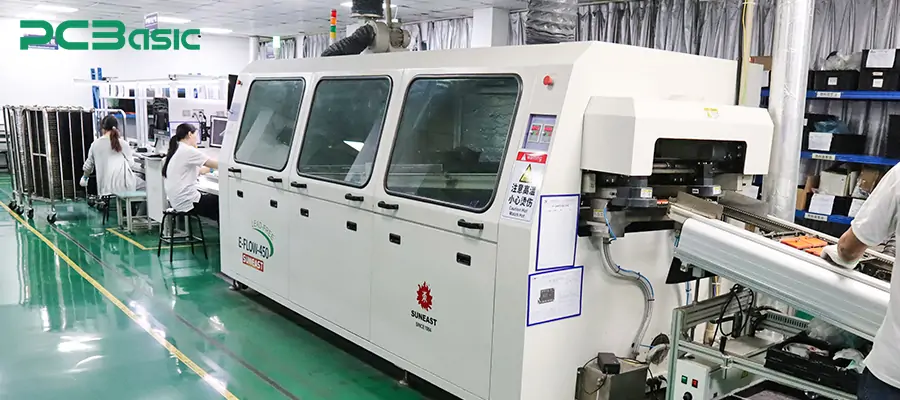

A wave soldering machine is a common automatic soldering machine, which is mainly used for soldering through-hole components. It achieves simultaneous soldering of all pins by allowing the PCB to pass through a layer of molten solder waves. Its process includes flux coating, preheating, passing through the peak of molten soldering and cooling. It is the preferred choice for mass production of through-hole component soldering, especially suitable for the large-scale production of consumer electronics, power boards, etc.

Reflow soldering machines are indispensable equipment in surface mount technology. It heats the solder paste through multiple precise temperature control zones (preheating, constant temperature, reflow, cooling), enabling SMD components to be firmly soldered onto the PCB. This machine is mainly used for surface mount components. This ensures precise soldering of small and high-density components. As an automatic soldering machine, it ensures the soldering accuracy and repeatability of high-density boards.

Selective soldering machines are ideal alternatives to wave soldering. It can provide more precise and flexible soldering solutions. For hybrid technology circuit boards (i.e., boards that contain both SMT and THT components), selective soldering machines can perform local soldering on specific through-hole components. This can prevent thermal damage to adjacent sensitive components and is suitable for complex PCB designs.
The above lists three common types of soldering machines. Besides, not all soldering tasks need to be automated. Manual soldering tools are still widely used in sample making, rework and small-batch production. Commonly used manual soldering tools include:
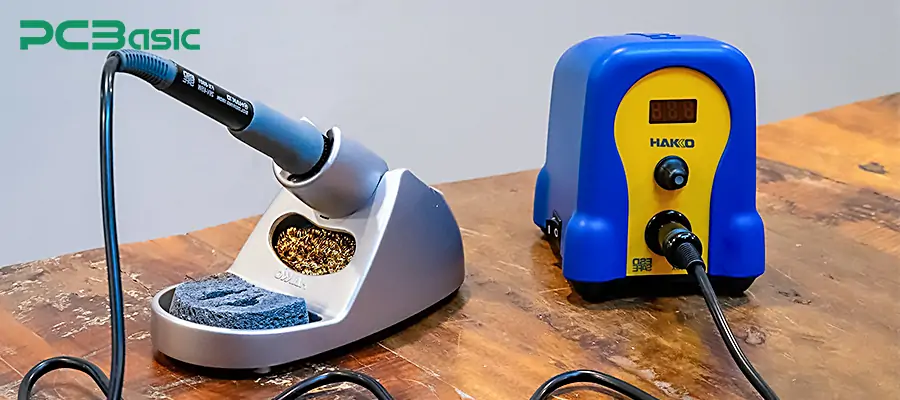

Soldering iron - a handheld heating tool for local soldering;
Soldering kit - includes complete accessories such as soldering iron, soldering tip, solder wire and flux;
Soldering stations - with temperature control platforms; More stable and precise operation;
Professional soldering station - with digital display; High-end equipment for ESD anti-static protection;
Although these tools are not classified as soldering machines, they play an indispensable role in the overall soldering equipment. So, how to solder a PCB without a soldering machine?
For sample making, small-batch circuit boards or DIY projects, mastering how to solder PCBs without a soldering machine is a very practical skill. Although large-scale electronic manufacturing mainly relies on automatic soldering machines such as wave soldering machines, reflow soldering machines, and selective soldering machines, learning manual soldering skills remains essential. The steps for manually soldering PCBs are as follows:
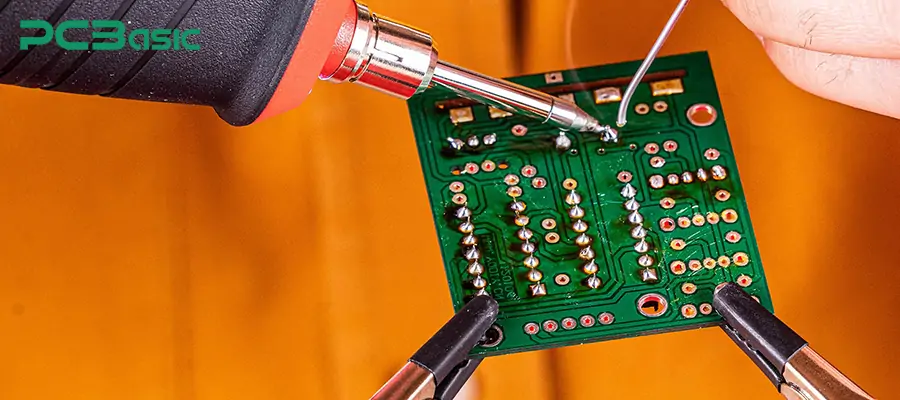
1. Prepare the tools needed for soldering and a professional soldering work area.
Before starting the soldering, we should prepare the following soldering tools:
A soldering iron or a professional soldering station with temperature control;
A soldering kit including lead-free solder wire, flux, tweezers, cleaning sponge, etc.
Protective glasses and a well-ventilated environment.
2. Prepare the PCBs and electronic components to be soldered.
First of all, we clean the surface of the PCB to remove oxides or dust. Then insert the component into the through-hole or gently place the SMD components on the pad. In industrial production, a pick-and-place machine is usually used for placement. In manual operation, you can use tweezers to do it.
3. Apply flux (if necessary)
Flux can remove oxides from the surface of metals, promote solder wetting and improve the quality of soldering. Flux is included in the wire of some soldering kits. If the solder joint is difficult to wet, an appropriate amount of external flux can be added.
4. Heat the solder joint
Open the soldering iron or the soldering station. Then set the temperature to an appropriate range (usually 300 to 350°C for lead-free soldering), and at the same time, make the soldering iron tip touch the component pins and pads.
5. Send in the solder
Sending in the solder means bringing the solder wire close to the heated area (not directly to the soldering iron tip) and letting the solder flow naturally. Then a firm and smooth solder joint will be formed. Be careful to avoid cold soldering or excessive tin stacking when soldering.
6. Inspection and cleaning
After the soldering is completed, please visually inspect all the weld points to ensure they are full and free of false soldering and solder connection. Then use alcohol and a brush to remove the residual flux to ensure the circuit board is clean and reliable.
|
Category |
Manual Soldering |
Automated Soldering |
|
Equipment Used |
Soldering iron, soldering kit, professional soldering station |
Wave soldering machine, reflow soldering machine, selective soldering machine |
|
Best For |
Prototyping, repairs, small-batch production |
High-volume production, standardized assembly |
|
Flexibility |
High — allows real-time adjustments and custom work |
Low — requires pre-set parameters, suitable for repetitive tasks |
|
Skill Requirement |
High — depends on operator expertise |
Low — machine-operated, less dependent on human skill |
|
Soldering Consistency |
Variable — affected by human error |
High — consistent and repeatable solder joints |
|
Speed & Efficiency |
Slower — ideal for one-off boards |
Fast — optimized for throughput and assembly lines |
|
Compatible Components |
Both SMD and THT components |
SMD (reflow soldering), THT (wave/selective soldering) |
|
Initial Cost |
Low — minimal investment in tools |
High — requires full automation setup |
|
Maintenance & Operating Cost |
Low — occasional tip cleaning, tool calibration |
High — includes machine maintenance, part replacement, software updates |
|
Typical Applications |
DIY projects, R&D labs, prototyping, electronic repair shops |
Consumer electronics, automotive PCBs, industrial control boards, medical electronics manufacturing |
After learning how to manually solder PCBs and differences between manual soldering and automated soldering, let's continue to learn about the functions and features of soldering machines! Understanding these key capabilities can also help us achieve high-quality solder joints.
Whether it is a fully automatic soldering system or a manual soldering tool, modern soldering machines and soldering equipment typically have the following key features to support high-quality PCB assembly:
From basic soldering iron to advanced automatic soldering machines, accurate and stable temperature control is key to preventing false soldering and component damage. Professional soldering stations or the best soldering iron for electronics can achieve precise temperature control, while reflow soldering machines and wave soldering machines rely on programmed thermal curves to ensure batch consistency.
Automatic soldering machines such as selective wave soldering machines can precisely control the supply of solder only where it is needed, effectively reducing solder waste and preventing defects such as solder sticking. These systems can achieve solder delivery through wave peak nozzles, selective nozzles or customized paths.
Whether it is an industrial soldering machine or a manual soldering system, precise flux coating is emphasized to enhance wettability and solder joint quality. Most automated equipment uses spray or foam coating, while many soldering tool kits are equipped with flux pens or paste fluxes.
Although the pick-and-place soldering machine itself is not a soldering device, it works with reflow soldering machines and wave soldering machines to ensure that components are properly placed, laying the foundation for ideal solder joints.
The automatic soldering machine is equipped with a programmable path to achieve precise soldering of high-density or complex PCBs, ensuring consistent soldering for each board. This is particularly important for selective soldering machines that require local soldering.
High-end industrial soldering machines usually integrate conveyor belts and fixture systems to stably transfer PCBs during the soldering process. This is particularly crucial in wave soldering machines and reflow soldering machines to ensure the accurate position and angle of the board cards.
High-quality soldering equipment and professional soldering stations are all equipped with safety features such as electrostatic protection, compatible smoke and dust removal systems, and automatic standby, to safeguard the safety of operators and electronic components.
Understanding these core functions will help you choose the right soldering combination - whether it's the best soldering iron on your workbench or an automatic soldering machine that will help you achieve the desired soldering results.

The application of soldering machines is very extensive and plays an indispensable role in many industries. For example,
1. Consumer electronics
Devices such as smartphones, laptops and smart home appliances have extremely high requirements for precise soldering. An automatic soldering machine like a reflow soldering machine can complete such high-density surface mount assembly.
2. Automotive electronics
The reliability of solder joints is of vital importance to automotive PCBs. This requires industrial soldering machines such as selective soldering machines and selective wave soldering machines to ensure consistent and reliable joints. The automatic soldering machine can ensure the consistency of the weld points of thousands of products.
3. Industrial control system
PCBs in industrial automation equipment are usually assembled using hybrid technology. For example, selective soldering machines can precisely complete local soldering without damaging the surrounding sensitive components.
4. Medical equipment
Medical electronics have extremely high requirements for soldering accuracy and quality standards. The reflow soldering machine combined with the pick and place soldering machine process can meet the precision requirements for the complex assembly of medical PCBs.
Whether it is a high-speed industrial soldering machine or a precise , choosing the right equipment is the key to ensuring high reliability and high performance in all fields of electronic manufacturing. So, how do you choose the right soldering machine?
In addition to the several soldering machines mentioned above, there are other types of soldering machines. Here are some common soldering machine options we have summarized.
|
Selection Factor |
Considerations |
Recommended Soldering Machine / Tool |
|
Assembly Type |
SMT (surface-mount), THT (through-hole), or hybrid board |
Reflow soldering machine (SMT), wave soldering machine (THT), selective soldering machine (hybrid) |
|
Production Volume |
High-volume mass production |
Automatic soldering machine, industrial soldering machine, wave soldering machine |
|
Small-batch, prototyping, repair |
Soldering iron, soldering kit, professional soldering station |
|
|
PCB Design Complexity |
Fine-pitch, high-density components |
Reflow soldering machine, selective soldering machine |
|
Large connectors, power components |
Wave soldering machine, selective wave soldering machine |
|
|
Required Precision |
Localized soldering without damaging nearby components |
Selective soldering machine, selective wave soldering machine |
|
Automation Level |
Fully automated |
Automatic soldering machine, pick and place + reflow soldering machine |
|
Manual flexibility |
Soldering iron, best soldering iron for electronics, soldering stations |
|
|
Budget & ROI |
Lower initial investment, hands-on control |
Soldering iron, soldering tool, soldering kit |
|
Higher initial investment, long-term efficiency for mass production |
Industrial soldering machine, automatic soldering machine, wave soldering machine, reflow soldering machine |
Tip: No matter the choice, selecting the right soldering equipment—whether the best soldering iron for your lab or a high-speed industrial soldering machine for your factory—is key to ensuring quality and efficiency.
In the manufacturing of PCBs and PCBA, soldering machines and manual soldering tools play an indispensable role. How to choose the right soldering equipment? This depends on the production scale, assembly complexity, precision requirements and budget. As electronic products continue to develop toward miniaturization and high performance, soldering technology is also constantly advancing toward higher levels of automation, precision and reliability. A thorough understanding of the characteristics and applications of various soldering equipment is the key for us to achieve high-quality and low-cost production.
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
