Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > How to Discharge a Capacitor?
In electronic engineering, capacitor discharge is a necessary step because it is not only related to the safety of operation but also to the efficiency and accuracy of subsequent work. Similarly, in PCB manufacturing and maintenance, capacitor discharge is also a crucial step; before assembly, testing and maintenance, capacitors need to be safely discharged so that the safety and efficiency of the entire manufacturing process can be ensured. So how to safely and efficiently discharge a capacitor? The following article will introduce in detail the necessity, safety measures, common methods and tools of capacitor discharge, hoping to help you complete capacitor discharge.
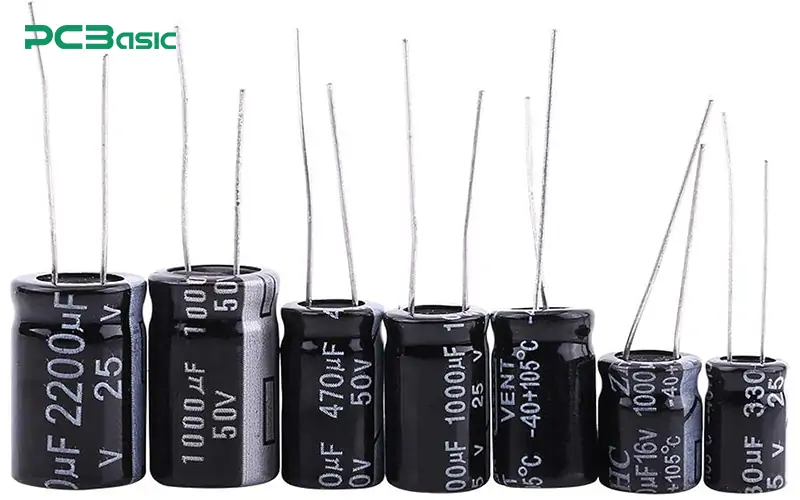

Capacitors are found in a wide range of electronic devices, such as televisions, computers, air conditioners and other household appliances. It stores charge in the energized state, and even after the device is powered off, there is still a high voltage charge inside the capacitor, which can lead to electric shock accidents. Therefore, the capacitor should be discharged before repair, replacement or operation.
Discharging capacitors can also prevent electrical components from being damaged by accidental short circuits because when disassembling or reassembling circuits, if the capacitor is not discharged, the stored electrical energy can cause unexpected current flow and damage sensitive components on the circuit board.
Undischarged capacitors can not only damage circuit boards and other components but may also endanger the safety of operators. So, high-voltage capacitors on PCB boards must be discharged; otherwise, the risk of short circuits will increase, affecting the performance and reliability of the circuit board.
Before learning how to safely discharge capacitors, we need to understand the basics of capacitors.
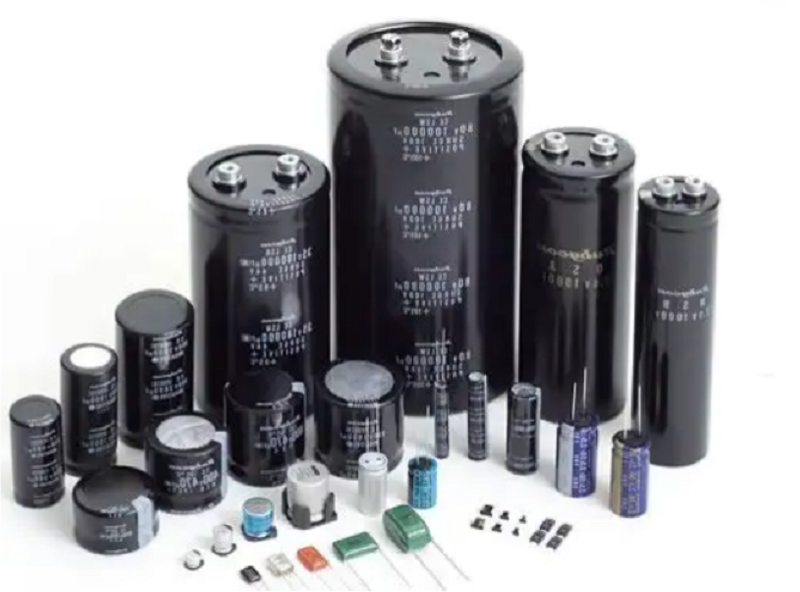

Different types of capacitors have different discharge characteristics (know more about capacitor types and capacitor symbol). For example, the commonly used capacitors on PCBs are ceramic capacitors and electrolytic capacitors. They have different discharge speeds and discharge characteristics: electrolytic capacitors discharge slowly, while ceramic capacitors discharge quickly; the self-discharge rate of electrolytic capacitors is relatively high, while the self-discharge rate of ceramic capacitors is low. Understanding the types of capacitors and discharge characteristics will help us choose the appropriate discharge method and improve the safety of operation.
The rated voltage and capacitance of the capacitor can be seen on the shell of the capacitor or its data manual, and its voltage and capacitance will affect the amount of charge it stores. Therefore, when discharging a capacitor, it is necessary to check its rating, choose the appropriate discharge mode, and not exceed its safety threshold to prevent damage to the capacitor or create safety hazards.
When handling charged capacitors, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (such as insulating gloves and goggles) to prevent electric shock. And check the surroundings to ensure that there are no flammable materials or other dangerous factors around.
Low voltage capacitors:
Do not need special discharge tools.
Medium-voltage capacitors:
Need discharge tools like discharge rods and safety glasses.
High voltage capacitors:
Need professional discharge tools like high-voltage discharge rods, insulated protective gear and voltage detectors.
Before learning how to safely discharge a capacitor, make sure that the capacitor still has charge. If capacitors, especially high-voltage ones, are operated without confirmation, it may pose serious risks to personal safety or equipment. We can use the following methods to identify whether the capacitor is still charged:
1. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage
The most reliable method is to use a capacitor multimeter or an ordinary digital multimeter for measurement. Note: A power outage of the device does not mean that the capacitor has discharged, so it is best to test it. Set the multimeter to the DC voltage range and touch the two pins of the capacitor respectively. If the reading is higher than 0V, it indicates that the capacitor is still charging and there is a risk of electric shock.
2. Identify electrolytic capacitors
In the process of mastering "how to discharge a capacitor", it is very important to understand the types of capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors are often used in power circuits and tend to retain high voltage most easily. Its shape is usually cylindrical and marked with polarity.
3. Observe the voltage or high power warning on the circuit board
Many PCBs are marked with warning words such as "HIGH VOLTAGE", or insulation gaps, heat sinks, etc. are set beside large capacitors. When seeing these structures or signs, they must be handled with care. This type of capacitor discharge must be carried out in accordance with strict safety regulations.
1. Metal tools (such as screwdriver) :
A metal tool is used to short-wire the poles of the capacitor so that the capacitor can discharge quickly. Before using this method, the operator should ensure that the handle of the tool has good insulation protection, and then ensure that the insulation gloves and safety glasses are worn to prevent the debris when the capacitor is damaged. When operating, you must also be careful because discharging a capacitor through metal tools can easily cause an accidental short circuit.
2. Light bulbs:
To discharge a capacitor with a light bulb, you only need to connect an ordinary light bulb to both ends of the capacitor, and then the resistance of the light bulb will gradually discharge the capacitor. At the time of discharge, the bulb will light up; although the speed of discharge is slower, it helps to observe the process of discharge and also reduces the thermal damage to the capacitor.
3. Bleed resistor:
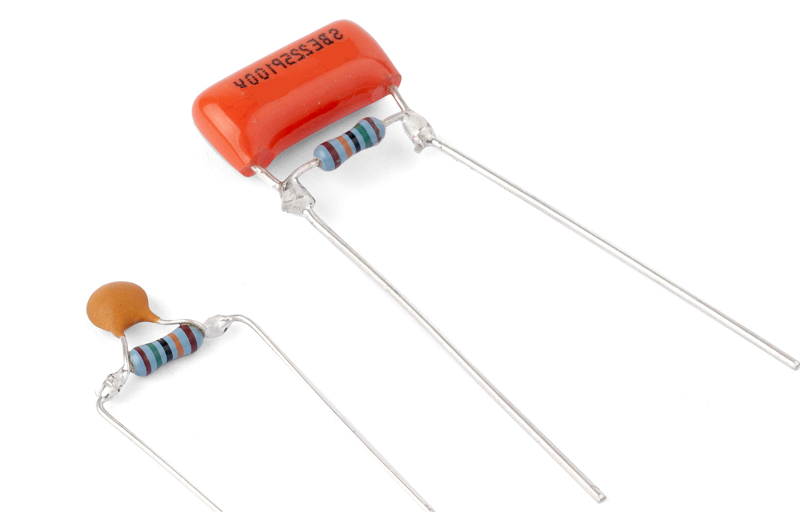
This method is to select a suitable resistance value of the resistor connected to both ends of the capacitor, and then safely discharge; this method can effectively reduce the spark and instantaneous current generated during discharge and improve the safety of the discharge process. What needs attention is the choice of resistance. Choose a resistance that is large enough to ensure that the discharge current is within a safe range and that the power of the resistance can withstand the energy generated during the discharge process.
4. Discharge tool with resistance probe:
Most automatic discharge tools have user-friendly interfaces, usually contain built-in resistors and control circuits, and are specifically designed to discharge capacitors with high voltage and large capacity. It can automatically control the discharge speed and current to prevent capacitor and circuit damage. It is suitable for industrial applications where frequent or specific conditions are required to power down, such as the maintenance of power systems, high-voltage test equipment, and environments where equipment safety needs to be ensured on production lines.
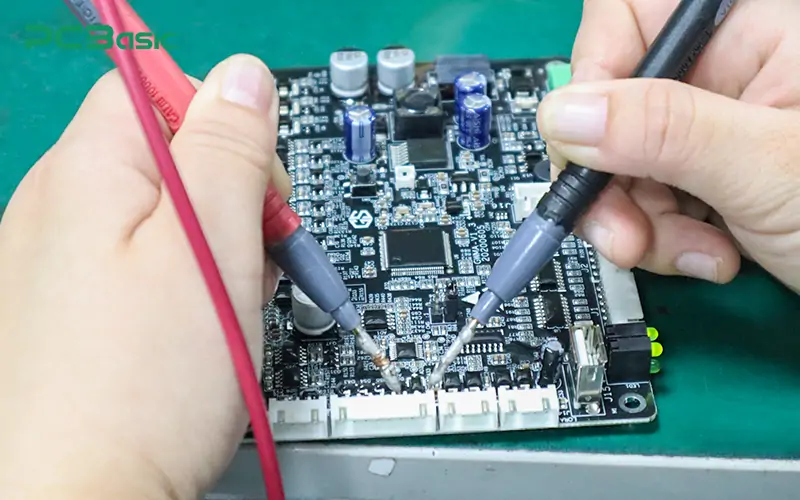
It is extremely important to safely discharge the capacitor before repairing electronic devices or performing circuit operations. The following is a safe method for capacitor discharge using a capacitor multimeter and a discharge resistor, which is applicable to most common electronic products.
Step 1: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage of the capacitor
Before starting capacitor discharge, use a multimeter to measure whether there is still residual voltage across the capacitor terminals. First, check the rated voltage on the capacitor label and select the appropriate DC voltage range (DCV) for measurement. Then, connect the black test lead to the negative terminal of the capacitor and the red test lead to the positive terminal, and read the current voltage.
Safety reminder: Be sure to use the correct voltage range to avoid incorrect readings or damage to the equipment.
Step 2: Prepare the discharge resistor and connecting wires
According to the voltage and capacitance of the capacitor, select an appropriate discharge resistor (for example, 1kΩ - 10kΩ, with a power of at least twice the energy stored by the capacitor). Prepare wires with insulating clips for convenient connection.
The selection of resistors directly affects the safety of discharge and whether it causes sparks or breakdown, so it should be carefully considered.
Step 3: Connect the resistor and start discharging the capacitor
Put on the insulating gloves and start discharging the capacitor. Clamp one end of the wire to the two ends of the resistor to form a complete resistance path. Then connect the two ends of the resistor to the positive and negative terminals of the capacitor respectively. Keep the connection for a few seconds and wait for the energy in the capacitor to be slowly released through the resistor. Discharging with resistors is much safer than direct short-circuiting, and it can also prevent damage to the circuit board pads.
Step 4: Monitor the discharge process and the resistance status
In the process of discharging capacitor, wear goggles just in case and watch if the resistor overheats. During the normal discharge process, the resistor may heat up, but it should not overheat or smoke.
Step 5: Use the multimeter again to confirm that the capacitor has discharged
After a few seconds, disconnect the discharge circuit and use a multimeter again to measure the voltage across the capacitor. If the voltage is close to 0V, the capacitor has been safely discharged. If there is still residual voltage, the discharge step needs to be repeated.
Note: The multimeter is not used to discharge, but to determine whether a capacitor can be safely discharged (a capacitor can be safely discharged).
Step 6: Disconnect and complete the operation
After confirming that the voltage is safe, disconnect all wire fixtures and tidy up the capacitor discharge tools used. Be sure to wear insulating gloves when cleaning to prevent accidental residual pressure.
This method of how to discharge a capacitor with a multimeter and resistor is applicable to most medium and low voltage scenarios. If it is a high-voltage capacitor (such as in televisions, microwave ovens or industrial equipment), professional discharge probes and additional insulation measures should be used.
Always remember: As long as the voltage is not confirmed to be zero, any capacitor has potential risks. The key to safely discharging a capacitor lies in: check → discharge → recheck. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
