Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Rapid Prototyping: 3D and PCB Prototyping
In the fast-paced hardware industry, the time from concept to market launch of a product is getting shorter and shorter. In the past, developing an electronic product might have taken 12 to 18 months, but nowadays many start-ups and large enterprises hope to complete the iteration within 3 to 6 months. Meanwhile, consumers have put forward higher requirements for product experience, appearance quality and reliability. Global supply-chain competition also forces enterprises to verify designs more quickly, improve yield rates, and reduce rework. These pressures have driven rapid prototyping to become an indispensable key strategy in the development of electronic and mechanical products.
Industry research also shows that teams using rapid prototyping processes can, on average, shorten the overall development cycle by 30%-50% and reduce early design errors by more than 60%. In other words, teams that can obtain physical prototypes within a few days rather than months naturally have an advantage in market competition.
This article will take you on a deep dive into what rapid prototyping is and explore how developers rely on 3D prototyping and rapid electronic prototyping during different stages of hardware development. The article will also introduce how PCBasic, as a modern rapid prototyping company renowned for its speed and reliability, helps teams transform CAD files into precise, stable and repeatedly verifiable physical prototypes, accelerating every step from concept to mass production.
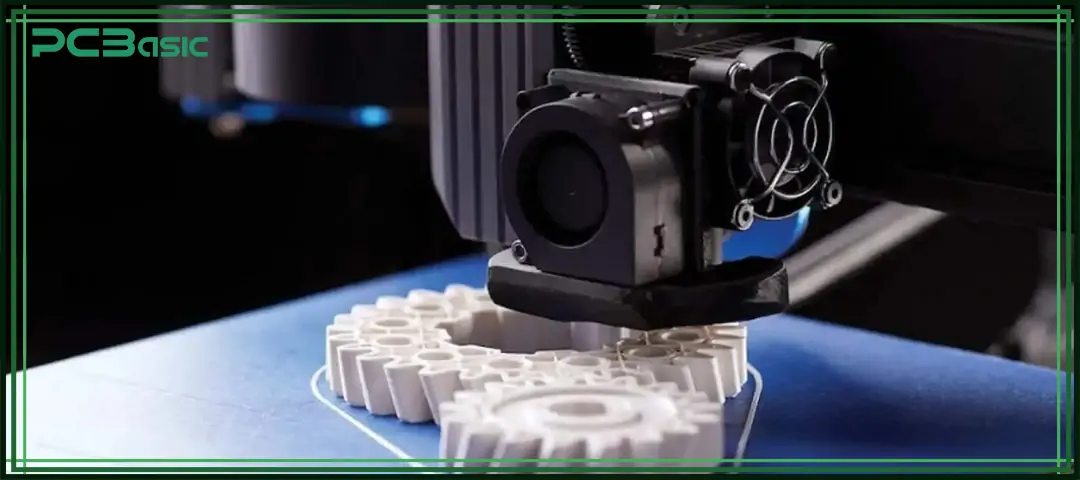

Rapid prototyping mainly covers two parts in product development: structural component prototypes and electronic hardware prototypes, enabling teams to verify appearance, assembly and electrical functionality.
3D prototyping is based on digital 3D models and uses rapid manufacturing tools, such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting, to build structural parts, enclosures, assemblies, or complete models within an extremely short period of time. It is the most commonly used verification method in the development stage of mechanical structures. 3D prototyping enables teams to identify structural design issues before mass production, making the design more mature and assembly smoother, thereby significantly shortening the development cycle and reducing risks.
Complementing structural component verification, electronic development relies on the rapid prototyping of PCBs and PCBA. PCB rapid prototyping can quickly produce small batches of circuit boards through files such as Gerber/BOM/CPL, which are used to check layout routing, electrical performance, impedance control and manufacturability. On this basis, PCBA rapid electronic prototyping incorporates SMT/THT assembly, soldering, debugging and functional testing to verify the complete circuit system and the behavior of the entire machine. The rapid electronic prototype iterations enable the development team to accurately identify problems and optimize designs before entering EVT/DVT/PVT and mass production, significantly reducing rework costs.
Modern R&D teams are increasingly relying on rapid prototyping services because this approach can not only significantly accelerate the speed of product development, but also reduce the cost of trial-and-error and lower the overall project risk.
Through 3D prototyping or rapid electronic prototyping, engineers can transform an idea into a physical prototype in an extremely short time.
In the early stage of product development, through rapid manufacturing, the team can quickly identify structural, functional or electrical problems before mass production, preventing large-scale rework in the later stage and significantly saving time and budget.
Teams can continuously optimize structural strength, appearance proportions, ergonomics, and even internal heat dissipation or electronic layout. Each iteration brings the product closer to the polished, high-quality final product.
In the rapid prototyping process, the costs of both trying and failing are very low. Engineers and designers can confidently test more ideas without worrying about wasting a lot of time or resources.
When users can directly interact with a prototype that is close to a real product, their feedback is usually more accurate and practical than that of comments on sketches or digital models. Physical prototypes can help teams truly understand the pain points in user experience, thereby making better design decisions.
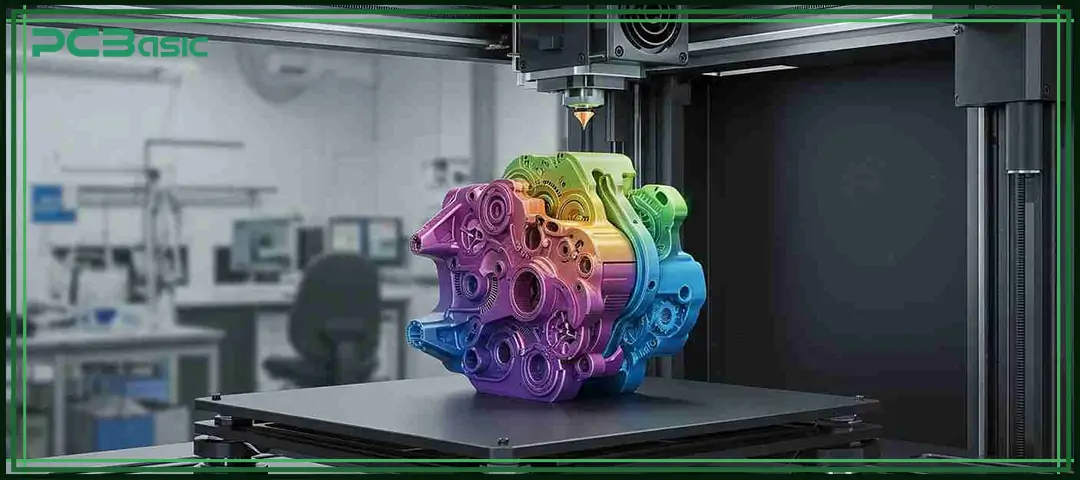
During different stages of product development, the team will select different types of prototypes based on requirements.
Proof-of-concept prototypes are mainly used to confirm the feasibility of the design. It does not emphasize appearance nor pursue structural integrity; it only needs to be able to prove whether the core functions can work.
The looks-like prototype is mainly used to demonstrate the industrial design of the product. It focuses on shape, size, color, MF (color-material-finish), as well as hand feel and ergonomics.
A work-like prototype focuses on whether the product can operate normally. It may have a rough appearance, but its internal functions are basically complete, such as the circuitry, sensors, and software logic.
The engineering prototype is already very close to the final mass-production version. It not only has complete functions but also needs to meet manufacturability requirements, such as assembly sequence, screw placement, structural support, thermal design, EMC behavior, and mass-production repeatability.
The validation prototype is used for more rigorous testing, such as reliability tests, certification tests, environmental tests (high temperature, high humidity, drop, vibration), regulatory compliance (such as CE, FCC), and small-batch trial production during EVT/DVT/PVT before mass production.
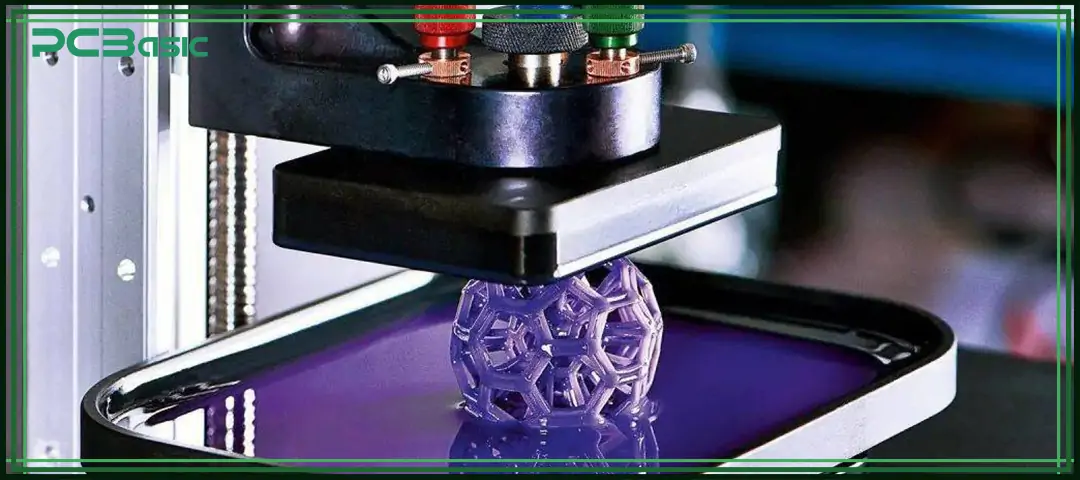

Engineers will first create the design of 3D models in CAD software such as SolidWorks or Fusion 360.
After the design is completed, engineers will export the model as an STL or 3MF file and process it in the slicing software. The slicer will convert the 3D model into machine-readable toolpaths, ensuring that the prototype can be printed smoothly.
Select the appropriate equipment based on the requirements of the prototype, such as 3D printers, CNC machines or casting tools.
The equipment starts to operate, producing the physical part either through additive manufacturing (layer-by-layer printing) or subtractive manufacturing (cutting or milling).
After manufacturing is completed, the prototype usually needs to be cleaned and surface finishing, such as support removal, sanding, priming, painting, or assembly with additional components.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
• Affordable and accessible
• Good for form, fit, and early concept
• Lower precision, visible layer lines
SLA (Stereolithography)
• High precision
• Smooth surfaces
• Excellent for looks-like and functional parts
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
• Extremely strong nylon parts
• No support structures needed
• Suitable for engineering prototypes and complex geometries
These 3D printing methods form the foundation of modern rapid manufacturing workflows.
Examples of 3D prototyping include:
• Ergonomic hand-held enclosure models
• High-detail appearance models for marketing
• Mechanical assemblies (hinges, gears, snap-fits)
• Jigs and fixtures for PCB assembly or testing
• Shock-mounts, brackets, and mechanical frames
These prototypes accelerate product development before investment in mass tooling.
Electronics engineers first create the schematic and then use simulation tools to check whether the core circuits are working properly, such as power stability, signal integrity, and the timing of high-speed differential pairs.
Then, the layout stage begins. According to the design rules (such as constraints, impedance control, thermal considerations, and power distribution requirements), the component placement and signal routing are completed.
After the layout is completed, the manufacturing files-Gerber, BOM, and CPL (or Pick-and-Place files)-need to be exported. These files are the core data for PCB manufacturing and PCBA assembly.
In the rapid electronic prototyping workflow, PCB factories will produce small batches of circuit boards in a short delivery time.
After the PCB fabrication is completed, it enters the PCBA stage, which includes older paste printing, component placement, reflow soldering, and AOl inspection. Some builds may also require hand-soldering or DIP processes.
Engineers conducted power-on verification on the PCBA prototype, checking whether the power supply was normal, high-speed interfaces communicated correctly, sensors operated properly, and firmware ran as expected.
Optimize the design based on the test results, such as adjusting the layout, changing components, or optimizing power or high-speed circuitry. Then move on to the next round of rapid prototyping to achieve high-frequency iterations.
• PoC boards – breakout boards, basic functional samples
• EVT boards – validate electrical behavior
• DVT boards – near-final form factor
• PVT boards – pilot run for manufacturability and yield testing
As a highly reliable PCB and PCBA manufacturer, PCBasic provides a complete rapid prototyping service for electronic product R&D teams, covering the entire process from circuits, assembly, testing, and structural coordination.
• 24-hour PCB builds
• 2–14 layers FR-4
• Controlled impedance options
• ENIG, HASL, OSP surface finishes
• 01005 capability
• BGA/QFN fine pitch assembly
• SPI, AOI, X-Ray inspection
• DFM/DFT engineering review
• Firmware flashing
• Functional testing
• Debugging support
• Small-batch production from 5–50 boards
PCBasic assists with:
• PCB outline optimization
• Mounting hole alignment
• Connector positioning
• Enclosure–PCB fitting checks
Because prototypes are built inside a full factory environment, we provide:
• EVT → DVT → PVT pilot builds
• MES-driven traceability
• IPC Class 3 workmanship
• Consistent BOM sourcing
• Stable SMT reflow profiles
• Full production handover without changing suppliers
PCBasic is not only a rapid prototyping company but also a reliable long-term mass production partner, helping teams achieve the development rhythm of building prototypes today and scaling to thousands tomorrow.
From 3D printed enclosures to fully assembled PCBs, rapid prototyping has completely transformed the way hardware products are developed. Through multiple rounds of rapid, low-cost and high-precision iterations, it enables the R&D team to explore more ideas, reduce design errors and significantly shorten the overall R&D cycle.
Whether you are developing consumer electronics, industrial controllers, IoT devices, medical equipment or robotic systems, rapid prototyping services - from 3D prototyping to rapid electronic prototyping - are all fundamental capabilities for the successful mass production of hardware.
PCBasic offers a complete rapid R&D ecosystem, including rapid PCB manufacturing, high-quality SMT assembly, functional testing, prototype manufacturing, and seamless connection capabilities from prototype to mass production. By choosing the right rapid prototyping service, you can make the leap from concept to operational product at an unprecedented speed.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
