Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Passive Components in Electronics – A Complete Guide
In the modern electronic world, circuits are mainly composed of two types of components: passive components and active components. These two types of electronic components are the foundation of all circuits. Among them, passive components account for more than 80% and are the core to ensure the stable operation of electronic systems. Whether it is a simple power supply circuit or a complex communication device and computer system, they all cannot do without these key passive electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors and transformers.
Understanding passive electrical components is the first step in learning basic electronic components and is also essential knowledge in circuit design, manufacturing and testing. Mastering the characteristics and applications of these components is helpful for quickly identifying electronic components and making the right choice when facing different types of electronic components.
In this guide, we will introduce:
• The definition of passive components
• The core characteristics of passive components
• Several common types of passive devices (resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers and the special case of diodes)
• The differences and connections between passive components and active components
• The application of passive technology in power management, signal processing and energy storage

Passive components are the most fundamental electronic components. They cannot amplify signals or provide energy like active components do. Instead, they operate by utilizing the existing energy in the circuit. In simple terms, a passive device can only store, dissipate or release energy, but does not generate energy on its own.
Passive electronic components do not have gain functions. When signals pass through, they will only be attenuated and not amplified. Meanwhile, they cannot generate signals by themselves like oscillators. Passive components can affect voltage, current and frequency, but they do not add energy to the circuit.
The most common passive electrical components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers and diodes, etc.
The working mode and characteristics of passive components determine whether the circuit can remain stable. Now, let's take a look at the core properties of passive electronic components from several aspects.
Passive electrical components do not generate energy but only process the existing energy. Dissipative components, such as resistors, control current by consuming electrical energy and converting it into heat. Lossless components, such as capacitors, inductors and transformers, do not consume energy immediately; instead, they temporarily store energy and release it when needed.
Unlike active components that require a power supply to operate, passive components do not need additional power sources. They function entirely by relying on the electrical energy already present within the circuit. This is also one of the most obvious signs when distinguishing types of electrical components.
Most passive devices are bi-directional and are installed in both forward and reverse directions, such as resistors and inductors. Only a few components have polarity, such as electrolytic capacitors, which need to be connected in accordance with the circuit requirements.
The parameter values of passive electronic components are always positive. These values will not be negative, which makes circuit analysis more intuitive and also facilitates testing and calculation.
To better understand the role of passive components in electronic circuits, it is necessary for us to first take a look at their main categories. Each type of passive device has its unique characteristics, working mode and application scenarios, but their common point is that they can all operate without an external power supply. The following table presents several common types of passive components and briefly explains their characteristics and main applications in the field of electronics.
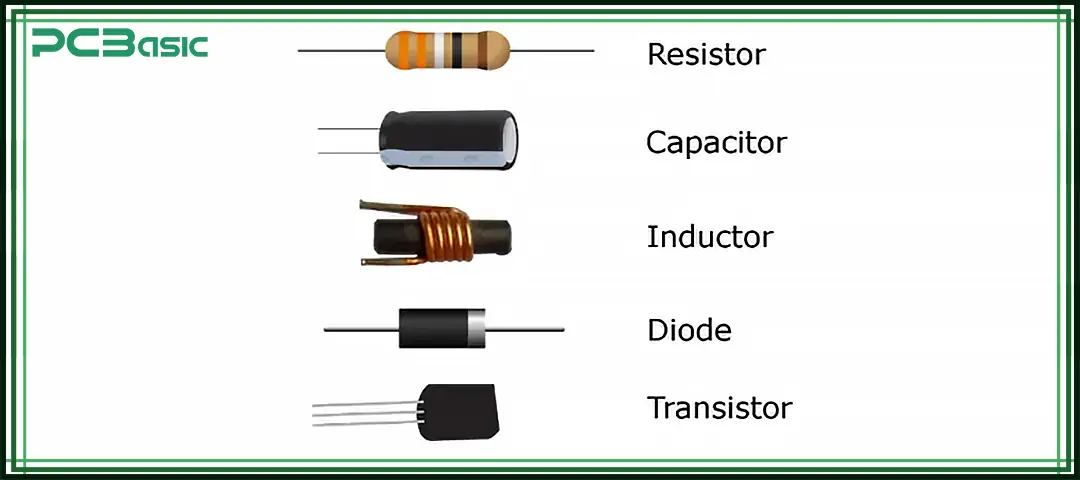
Major Types of Passive Components Table
|
Type |
Description |
Common Applications |
|
Resistors |
The most common passive component, resistors, oppose the flow of current and regulate voltage and current in a circuit. Measured in ohms (Ω). |
Voltage division, current limiting, transistor biasing, signal attenuation |
|
Capacitors |
Store energy electrostatically between two conductive plates separated by a dielectric. Block DC while allowing AC signals to pass. |
Noise filtering, power supply smoothing, coupling/decoupling, tuning and impedance matching |
|
Inductors |
Passive electrical components that store energy in magnetic fields. They resist changes in current, making them critical in filtering and power circuits. |
DC-DC converters, low-pass/high-pass filters, energy storage in switching circuits |
|
Transformers |
Classified as passive devices, transformers transfer energy between circuits via electromagnetic induction. They step the voltage up or down but do not generate new energy. |
Voltage regulation, circuit isolation, impedance matching |
|
Diodes (special case) |
Usually considered active electronic components, but in some contexts, they are treated as passive components since they operate without an external power source. |
Rectification (AC to DC), reverse polarity protection, signal demodulation |

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Passive components are very important in all kinds of electronic products and are used in almost all circuits. Their typical applications include:
|
Application Area |
Passive Components |
Function/Role |
|
Power Management |
Resistors |
Limit current |
|
Capacitors |
Smooth voltage |
|
|
Inductors |
Filter noise in power lines |
|
|
Transformers |
Adjust voltage levels |
|
|
Signal Filtering & Conditioning |
RC Filters |
Shape frequency response |
|
LC Filters |
Modify frequency characteristics |
|
|
Resistors & Capacitors in audio circuits |
Tone control |
|
|
Inductors in speaker crossovers |
Separate frequencies |
|
|
Energy Storage |
Capacitors |
Temporarily store and release energy |
|
Inductors |
Store energy in a magnetic field |
|
|
Consumer Electronics |
Capacitors |
Stabilize power in smartphones |
|
Inductors |
Used in crossovers of audio equipment |
|
|
Transformers |
Power distribution in EVs |
Active components are electronic components that require an external power supply to operate. They can amplify signals, control current, and even generate new signals. Common active components include transistors, diodes, integrated circuits and operational amplifiers.
Relatively speaking, passive components do not require additional power supply and can only store, release or consume energy in the circuit, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors and transformers.
So, it can be simply understood that the active component is the power source of the circuit, while the passive component is the stabilizer of the circuit.
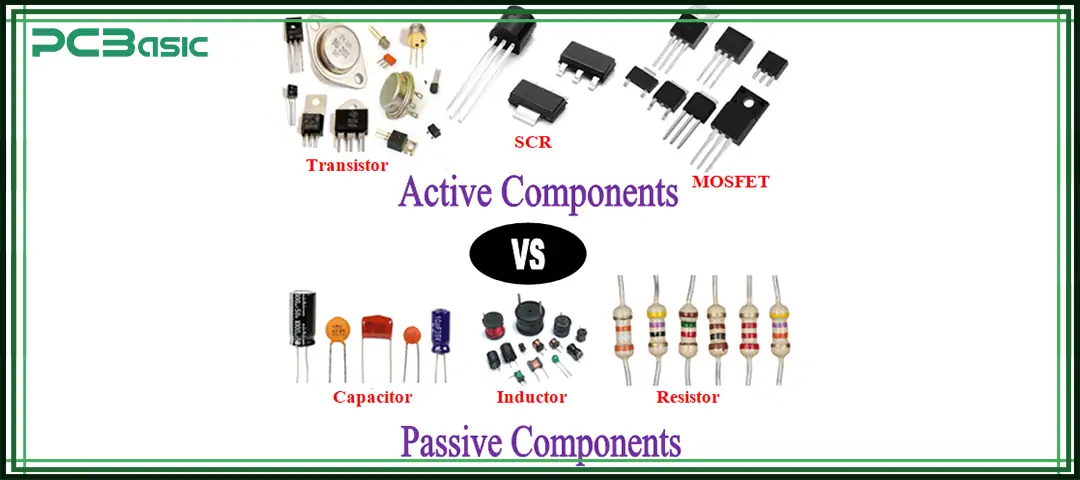
The distinction between passive components and active components is central to basic electronics components knowledge.
|
Characteristic |
Passive Components |
Active Components |
|
Power Usage |
Use power already in the circuit |
Deliver power to the circuit |
|
Energy Role |
Energy acceptor |
Energy donor |
|
Power Gain |
Cannot provide gain |
Provide gain/amplification |
|
External Source Requirement |
No external power needed |
Require external power |
|
Current Flow Control |
Cannot control the current |
Can control and switch the current |
|
Examples |
Resistor, Capacitor, Inductor, Transformer |
Transistor, Amplifier, IC, Op-Amp |
Understanding this table helps in identifying electronic components and differentiating between types of electronic components in practice.
Although passive components cannot generate or amplify energy by themselves, they are the indispensable basic framework of all electronic systems. From the simplest circuits to complex consumer electronic products, these basic electronic components play a significant role in circuit stability, signal filtering and power management.
When engineers compile the electronic components list, passive electronic components often account for the majority because they are used in almost all circuit designs. When used in conjunction with active components, they jointly ensure that modern electronic devices can operate efficiently and reliably.
As long as one masters the functions of passive components, whether they are engineers, students or electronics enthusiasts, they can more easily design circuits, analyze circuit problems and even independently complete maintenance.
Q1: What are the “big three” passive components?
A1: The three most important passive electrical components are resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Q2: Why are transformers considered passive?
A2: Transformers transfer energy but do not generate or amplify it, so they are classified as passive devices.
Q3: Are diodes passive or active?
A3: Diodes are often classified as active electronic components, but in some contexts, they are considered passive components since they don’t require external power.
Q4: Do passive components waste energy?
A4: Yes. Resistors dissipate energy as heat. Capacitors and inductors are closer to lossless but still experience some inefficiencies.
Q5: Can passive components ever replace active ones?
A5: No. Passive electronic components cannot provide gain or amplification. They complement, but do not replace, active components.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
