Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > > What Is a Control Board?
In almost all modern electronic devices today, the core intelligence that drives all functions is the control board. With the rapid growth of the global electronics manufacturing industry, the global shipment of smart devices has exceeded several billion units in 2024, and almost every device relies on one or more control boards inside to complete logic processing, execute control actions, and coordinate system operation. Precisely because of this, more and more people have begun to pay attention to: what is a control board? What exactly does it do? Why is it so crucial?
A well-designed electronic control board determines whether a device can operate stably. More importantly, the control board undertakes a series of invisible but crucial tasks within the device: power management, motor or relay driving, communication interfaces, protection circuits, fault detection, and overall system coordination. This means that the control board is not only the "command center", but also the "guardian" ensuring the stable and safe operation of the entire equipment.
This article will systematically explain what a control board is, analyze which core components it consists of, how it works, the major steps included in its manufacturing process, and its specific applications in various industries. At the same time, it will also combine the practical experience of PCBasic in the manufacturing of high-reliability PCBA to enable readers to have a clearer understanding of the engineering logic and manufacturing requirements behind a high-quality control board.

The control board, also known as the electronic control board, is the "brain" of the entire electronic system. No matter how complex the equipment is, it relies on the control board to determine when to start, how to operate, and how to respond when an abnormal condition occurs. A control board typically integrates a microcontroller, various sensor interfaces, communication modules, power-management circuits, and an actuator-driver circuit, enabling the device to make real-time decisions and automatically complete control actions.
Simply speaking, when someone asks "What is a control board?", we can describe it as:
The control board is a printed circuit board (PCB) that is responsible for collecting external and internal data, processing logical instructions, and controlling the normal operation of electronic devices or systems.
The responsibility of the control board is far more than just switching a machine on or off. It will constantly read sensor data, such as temperature, current, pressure and position. It will evaluate whether the device is in a safe state. It will issue instructions according to the programmed logic to drive motors, relays, LEDs, valves or various functional modules. Meanwhile, the electronic control board will also interact with other systems through communication methods such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, CAN, and RS-485 to ensure the coordinated operation of the entire device.
A modern electronic control board is a highly integrated system. The following are the common key components in the control board.
This is the main processor responsible for executing software instructions. It determines the operation mode of the control board, processes sensor data, executes algorithms, communicates with peripherals, and drives various outputs.
Common MCUS include ARM Cortex-M series, ESP32, STM32, PIC, Renesas, etc.
• Temperature sensors
• Humidity sensors
• Hall sensors
• Pressure sensors
• Current/voltage sensors
• I²C
• SPI
• UART
• ADC/DAC
Every control board relies on stable power:
• DC-DC converters
• LDO regulators
• Battery management ICs
• Over-current / over-voltage protection
Power management ensures the control board operates safely across all load conditions.
A modern electronic control board often supports communication:
• Wi-Fi for IoT
• Bluetooth / BLE for wireless control
• CANbus for automotive applications
• RS-485 / Modbus for industrial control
• Zigbee / Thread for smart home
Communication is crucial for remote control, telemetry, and firmware updates.
These output circuits enable the control board to control various devices, such as motors, valves, heaters, pumps, lights, fans, and more.
• Relays for AC appliances
• MOSFETs for PWM control
• Motor drivers (H-bridge, BLDC drivers)
• Terminals, pin headers, sensor connectors
• Fuses, TVS diodes, ESD protection
• Reverse-polarity protection
Protection ensures the control board survives harsh environments.
|
Type of Control Board |
Application Scenarios |
Key Features and Requirements |
|
Consumer Electronics Control Boards |
- Washing machines - Refrigerators - Coffee makers - Smart TVs - Air purifiers |
- Focus on cost efficiency - Basic reliability requirements - Designed for everyday household environments |
|
Industrial Control Boards |
- PLC systems - Motor drives - Industrial robots - Packaging machinery - Factory automation equipment |
- High durability - Long-lifecycle components - Strong EMC performance - Suitable for 24/7 industrial operation |
|
IoT & Smart Home Control Boards |
- Smart switches - Smart locks - Smart home gateways - Various home automation devices |
- Wireless connectivity: Wi-Fi / BLE / Zigbee - Remote monitoring - Low-power consumption - Cloud integration capability |
|
Automotive & Medical Control Boards |
- Automotive ECUs - BMS battery management systems - Medical control boards (ISO 13485) - Sensor control units - In-vehicle infotainment modules |
- Extremely high reliability - Must meet IPC Class 3 standards - Compliance with automotive/medical industry certifications - High safety and operational stability |
Custom control boards:
• Perfect match for your product
• Better performance and reliability
• Optimized BOM cost
• Stronger protection and safety
• Full control of firmware and hardware
Off-the-shelf controllers:
• Faster development
• Lower initial cost
• Limited customization
• Lower performance flexibility
Most companies eventually switch to custom electronic control boards as production scales.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
When explaining what a control board is, it is very important to understand its basic workflow. A control board usually manages and operates a device through the following steps:
The control board first acquires information about the operating status of the equipment or the external environment through various sensors. Examples include temperature, humidity, current, voltage, pressure, position, and speed. These data are the basis for the electronic control board to make a decision.
The microcontroller (MCU) is the core processing unit of the control board. It will calculate, filter, compare and analyze the raw data sent back by the sensor, and determine the next action of the device based on the preset logic.
The firmware algorithms determine the operation mode of the device. For example: reducing power when the temperature is too high, entering a protection mode when an error is detected, or starting/stopping a function when a threshold is reached.
Based on the logical results, the control board will drive the corresponding output devices: switching circuits through relays, starting or adjusting motor speed, turning LEDs on or off, or triggering a buzzer or alarm. These outputs enable the device to perform actual actions.
The communication modules in the control board (such as Wi-Fi, BLE, CAN, RS485, etc.) will interact with other devices or the upper computer for data exchange. For instance, they can upload the operating status to the cloud platform, receive instructions from the mobile app, and work in coordination with other control board devices.
Electronic devices usually require different levels of voltage. The power management circuit on the control board converts the input power into a stable voltage required by the MCU, sensors and drivers, avoiding system failure caused by voltage fluctuations.
To prevent equipment damage or safety issues, the control board also includes multiple protection circuits, over-current protection, over-voltage protection, reverse-polarity protection, temperature protection, and ESD protection. These protection measures ensure the long-term stable operation of the control board in various working environments.
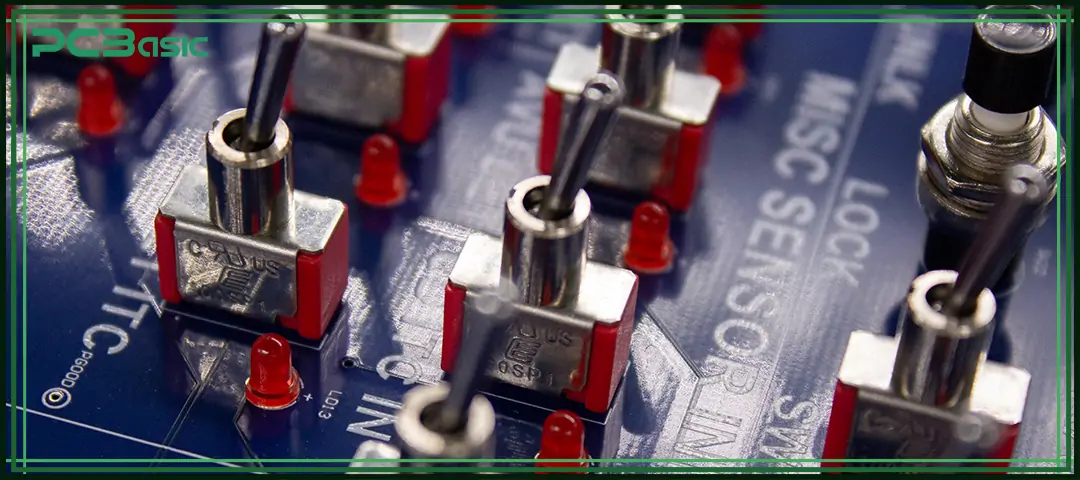

Designing a professional electronic control board requires engineering depth:
• Ground separation
• Filtering circuits
• Shielding
• Copper thickness
• Heat spreaders
• Component placement
• Short and clean signal paths
• Proper power/signal isolation
• Controlled impedance for high-speed signals
• Surge protection
• Over-temperature protection
• Short-circuit design
• Watchdog timers
• Safe bootloader
• OTA updates (for IoT control boards)
Good design ensures the control board remains stable for 5–10+ years.
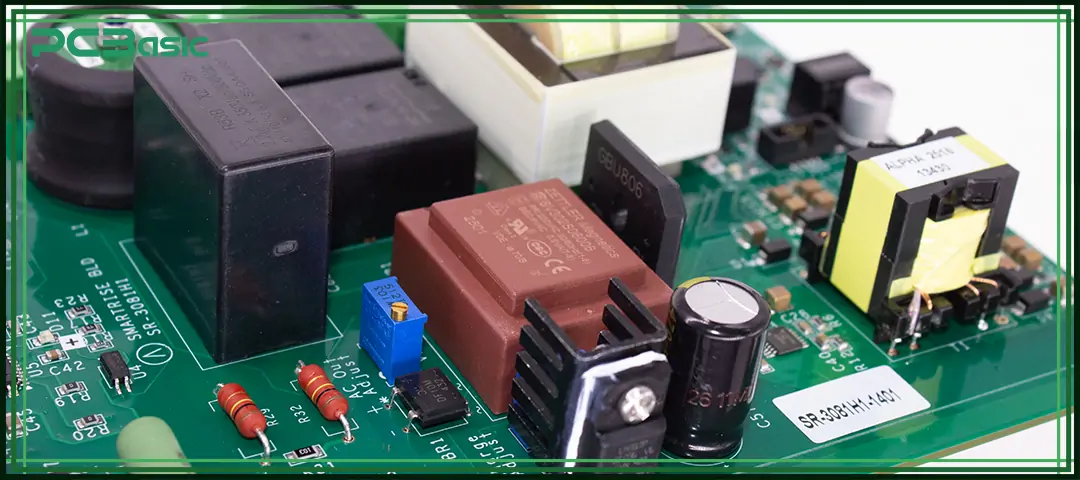

The manufacture of a control board requires going through multiple precise and strict process steps.
In the PCB manufacturing stage, the copper-clad laminate is produced first, including:
• Copper-clad laminate manufacturing
• Inner layer imaging
• Etching and plating
• Via drilling and deposition
• Solder mask and silkscreen
• Surface finishes (ENIG, HASL, OSP)
The SMT process includes solder paste printing, component mounting, reflow soldering and AOI inspection. This stage completes the main logic circuits and signal circuits of the control board, which is the most crucial step in the assembly.
Relays, connectors, transformers and other through-hole components usually require wave soldering, selective soldering or manual soldering.
Industrial control boards and home appliance control boards often adopt a hybrid structure of SMT and through-hole components to enhance reliability.
PCBasic will conduct AOI, SPI, X-Ray, ICT and flying probe testing on the control board to confirm whether the solder joint quality, circuit conduction and component positions comply with the design. These tests ensure that each control board meets a stable and consistent quality standard.
Functional testing verifies button inputs, sensor calibration, Wi-Fi/BLE connectivity, relay and MOSFET outputs, and all protection functions. Only a control board that passes these tests can operate as intended in the final device.
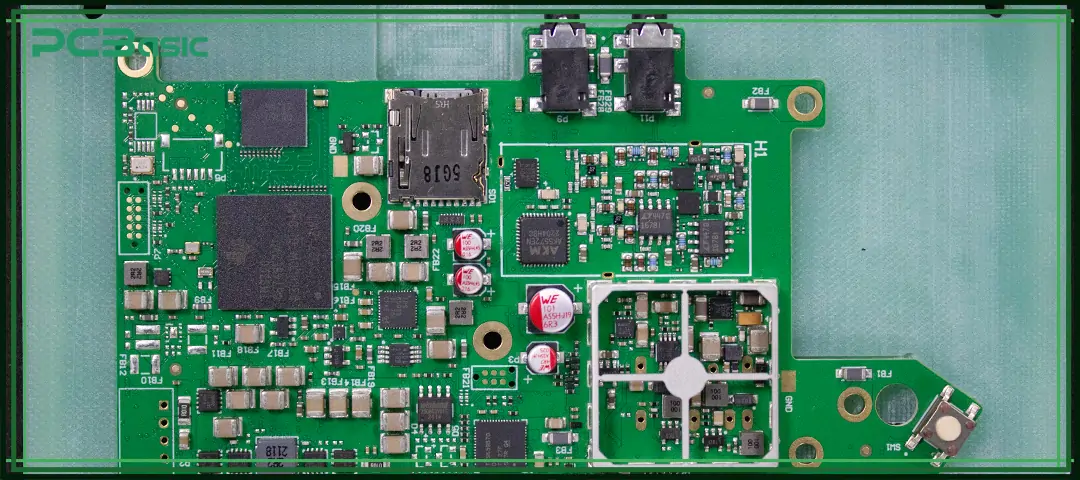
PCBasic is a Shenzhen-based turnkey PCBA manufacturer trusted for high-reliability control board production.
Why engineers choose PCBasic for electronic control boards:
• 9 high-speed SMT lines
• Supports IPC Class 3 manufacturing
• MES traceability for every board
• AOI, SPI, X-Ray, ICT, FCT testing
• Strong engineering support (DFM/DFT)
• Reliable global component sourcing
• Small to medium batch specialists
• Fast global shipping to 170+ countries
Whether you need consumer electronics, industrial automation, IoT, automotive, or medical control board production, PCBasic delivers dependable, repeatable results.
Understanding the control board is significant to all those engaged in the development and manufacturing of electronic products. A well-designed electronic control board integrates sensors, microcontrollers, communication modules, power circuits and safety protection functions to manage the entire operation process of equipment - from household appliances to industrial equipment and even high-end medical devices.
By choosing the right design approach and collaborating with reliable PCBA manufacturers such as PCBasic, enterprises can create stable, high-performance control boards that can operate for a long time in harsh environments.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
