Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Comprehensive Guide to CNC Milling | PCBasic
In today's manufacturing industry, product updates are accelerating, and the requirements for components are continuously increasing. Dimensional accuracy, batch consistency and lead time have become the basic requirements of the project. With the development of manufacturing towards digitalization and automation, traditional manual machining methods have become difficult to meet the current demands for precision and stability.
Meanwhile, downstream applications are constantly upgrading. Aerospace components have complex structures and strict requirements for strength and dimensional consistency; medical devices and medical electronics are highly sensitive to dimensional deviations, while in industrial equipment and electronic enclosure production, manufacturers pay more attention to stable batch manufacturing capabilities. These changes have put forward higher requirements for machining processes.
Against this backdrop, CNC milling has become one of the most widely used and technologically mature machining methods. By controlling machining movement through programmed instructions, CNC milling manufacturing can stably convert design drawings into high-precision parts and is widely used in the fields of aerospace, industry and electronics.
This comprehensive guide will systematically analyze the CNC milling definition, machine components, machining workflow, suitable materials, core advantages and its typical application scenarios. It will also further illustrate that in the current highly competitive and fast-paced manufacturing environment, choosing a partner with engineering capabilities and manufacturing experience is as important as selecting the appropriate machining process.
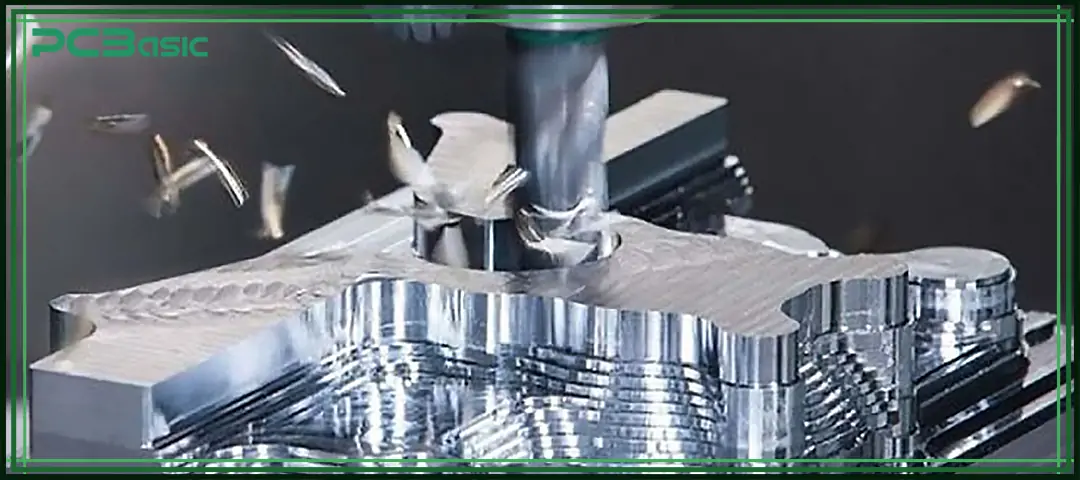

To understand what CNC milling is, we can start with the process itself.
CNC milling is a common subtractive manufacturing process. During machining, the machine controls the rotating cutting tool through a computer program, gradually removing material from a solid workpiece and eventually forming the required part geometry. CNC is the abbreviation of Computer Numerical Control, indicating that the movement of the machine is not operated manually but precisely controlled by digital instructions.
a machining method that uses a computer numerical control milling machine to precisely cut and shape parts in accordance with design documents.
Milling is a machining method that removes material by a rotating cutting tool. Unlike turning--in which the workpiece rotates while the tool remains mostly stationary--milling, on the other hand, usually involves keeping the workpiece fixed while the cutting tool rotates and moves in multiple axes to complete the processing.
Compared with traditional manual milling machines, modern CNC milling machines have obvious advantages in processing accuracy, tolerance control and batch consistency, and are more suitable for the current industrial production demands.
CNC milling is widely used mainly because it performs reliably in terms of accuracy, consistency, and production efficiency that can meet the actual needs of the current manufacturing industry.
CNC milling manufacturing can stably control tight tolerances consistently. When the equipment is in good condition, the CNC milling machine can repeatedly produce parts with near micron-level accuracy.
When the machining program is proven, CNC milling machines can continuously produce a large number of parts with consistent size and minimal variation, making it suitable for both prototyping and mass production.
Multi-axis milling machines can handle complex shapes, deep cavities, and 3D surfaces, which are difficult to achieve reliably with manual machining.
Since the computer numerical control milling machine operates automatically according to the programmed instructions with less manual intervention, it helps to reduce operator errors, while improving processing efficiency and controlling labor costs.
CNC milling can machine a variety of metals and engineering plastics, thus being suitable for different industries and multiple application scenarios.
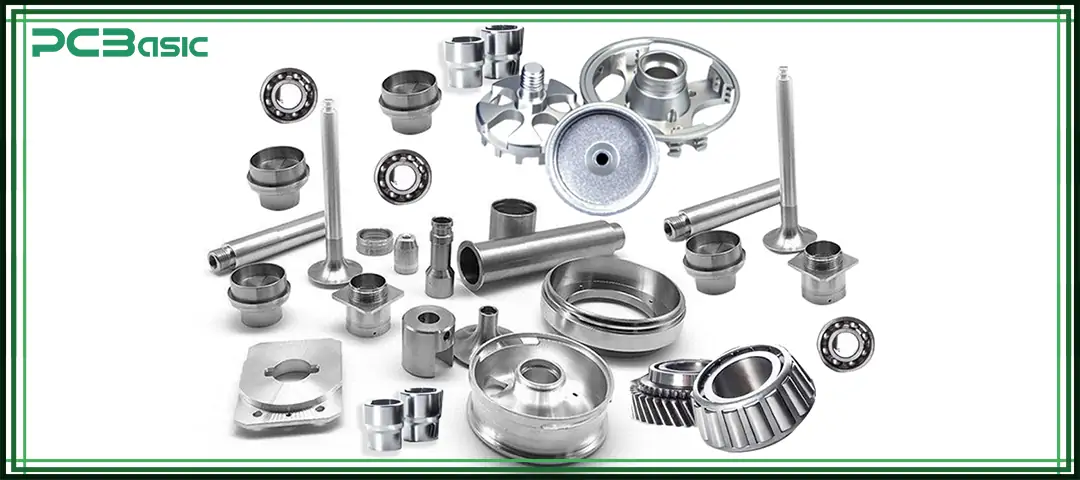

With its excellent flexibility and processing accuracy, CNC milling manufacturing is widely used in multiple industries.
• Aerospace: Structural components, brackets, housings, and precision fittings
• Automotive: Engine parts, transmission components, jigs, and fixtures
• Medical: Surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment components
• Electronics: Heat sinks, enclosures, frames, and mounting parts
• Industrial Equipment: Machine parts, tooling plates, and custom assemblies
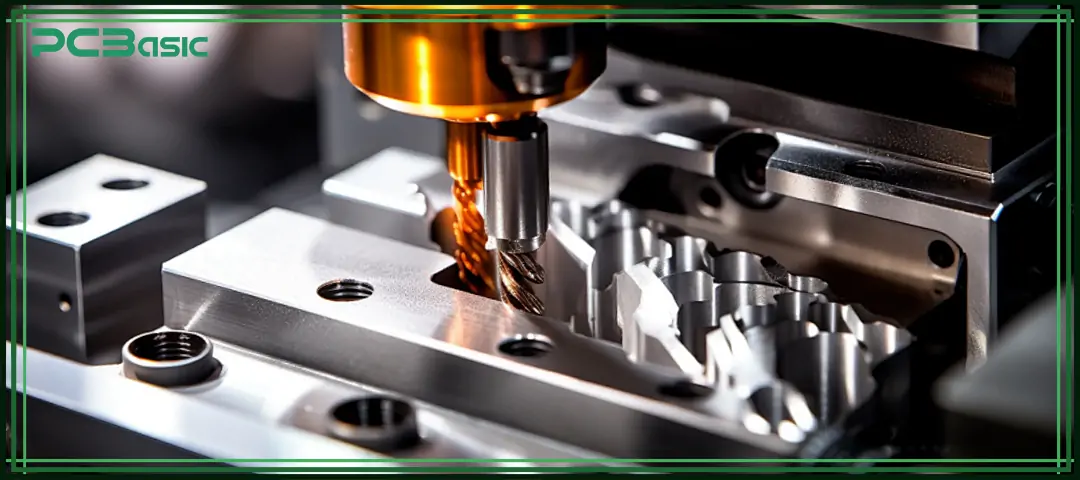

To truly understand what CNC milling is, it is necessary to first understand its entire machining workflow from design to finished product.
The process begins with 2D or 3D models created in CAD software. The design file clearly defines the dimensions, tolerances and various structural features of the parts, which serve as the foundation for subsequent machining steps.
Import the CAD file into the CAM software to set the toolpaths, machining strategies, cutting speeds and feed rates. The CAM software then generates G-code, which serves as the operating instructions for the CNC milling machine.
The operator secures the workpiece, installs the appropriate cutting tool, and sets the machining reference points. Although CNC milling machines have a high level of automation in operation, the accuracy of machine setup directly affects the machining precision.
A computer numerical control milling machine operates according to the programmed instructions. While the cutting tool rotates, it moves along multiple axes to remove material from the workpiece.
After processing is completed, parts usually need to undergo deburring, surface finishing or quality inspection to ensure that the final product meets the design and application requirements.
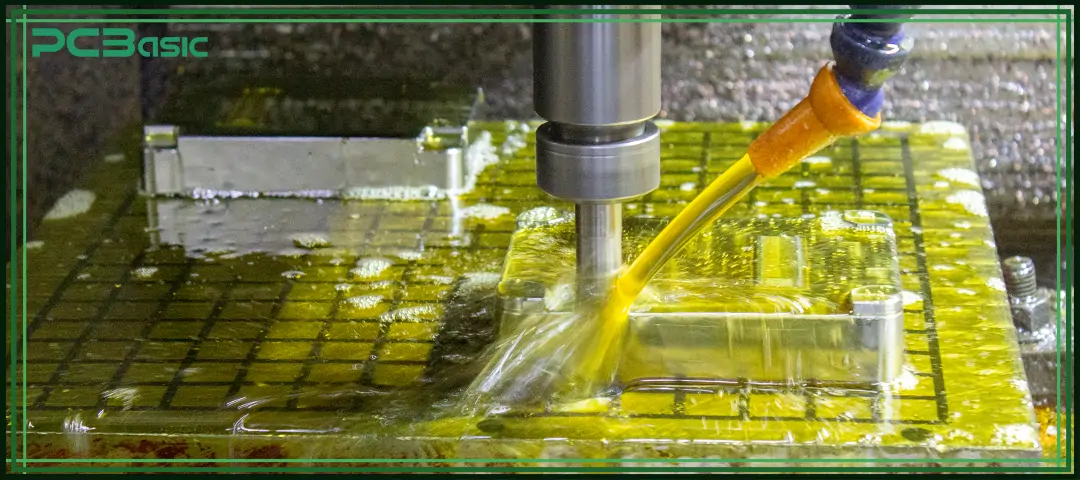

A modern CNC milling machine is composed of multiple key components, each of which plays a significant role in processing performance and precision control.
• Spindle: Holds and rotates the cutting tool
• Cutting Tools: End mills, face mills, drills, and specialty tools
• Worktable: Secures the workpiece in place
• Axes System: Controls movement in X, Y, Z (and sometimes rotational axes)
• Controller: The brain of the computer numerical control milling machine, interpreting G-code instructions
These components cooperate with each other, enabling the CNC milling machine to stably complete high-precision and repeatable processing operations.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Different machining tasks require different types of CNC milling machines. Not all milling machines are suitable for the same processing scenarios.
The spindle is oriented vertically, with a simple structure and convenient operation. It is commonly used for face machining, slotting, and general part processing.
The spindle is oriented horizontally, which is more conducive to chip evacuation and is suitable for processing tasks with high material removal rates and is often used in heavy-duty cutting operations.
It is mainly used for large or heavy workpieces. This type of milling machine has better rigidity and stability when machining large surface areas.
In actual production, appropriate equipment is selected based on part size, structural complexity and machining requirements. Different machine types play different roles in CNC milling manufacturing.
The number of axes of a machine determines the structural complexity that a CNC milling machine can handle.
Moves along X, Y, and Z axes. Suitable for simple geometries and flat features.
Adds a rotational axis, allowing machining on multiple sides without repositioning the part.
Offers simultaneous movement along five axes, enabling highly complex shapes, undercuts, and superior surface finishes.
The number of axes of a machine tool determines the degree of structural complexity that a CNC milling machine can process.
CNC milling includes a wide variety of machining operations, such as:
• Face milling
• Plain (surface) milling
• Slot milling
• Pocket milling
• Contour milling
• Climb milling and conventional milling
Each operation uses specific tools and strategies to optimize accuracy, surface quality, and efficiency.
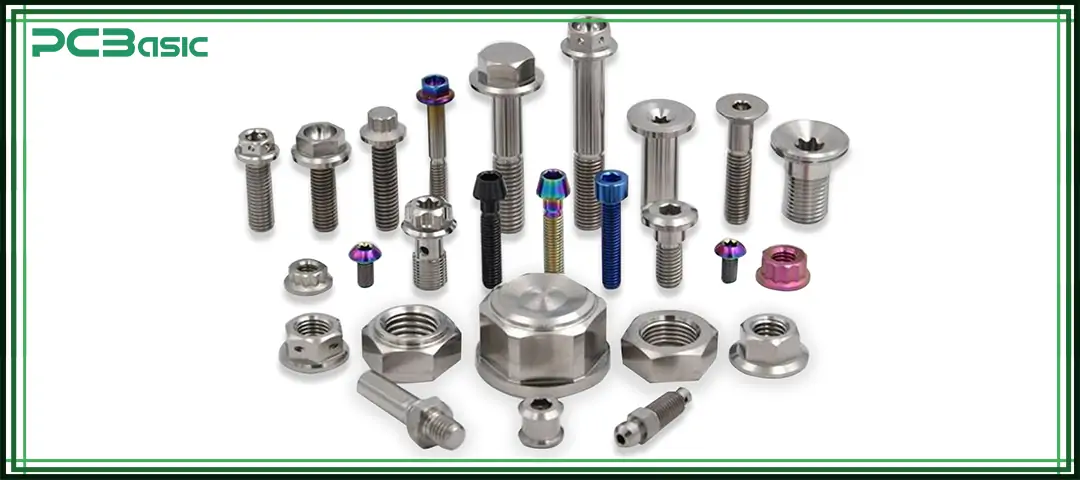

One reason CNC milling manufacturing is so popular is its compatibility with many materials.
• Aluminum
• Carbon steel
• Stainless steel
• Brass
• Copper
• Titanium
• ABS
• POM (Delrin)
• Nylon
• PTFE
Material selection affects cutting parameters, tool choice, and overall machining cost, making engineering expertise essential.
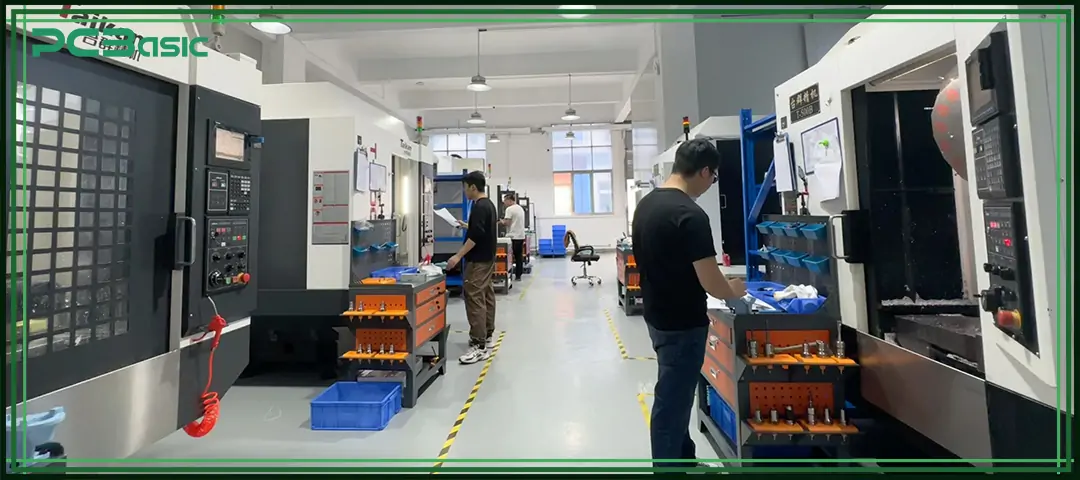

PCBasic offers stable and reliable CNC milling and CNC machining manufacturing services, supporting various projects ranging from prototyping to small and medium batch production.
1. Complete Machining Capability
Support for 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling, plus turning and post-processing.
2. Stable Precision Control
Modern CNC milling machines ensure tight tolerances and consistent quality.
3. Wide Material Options
Machining support for aluminum, steel, stainless steel, titanium, and engineering plastics.
4. Engineering & DFM Support
Early DFM feedback to reduce risk, cost, and machining difficulty.
5. Fast Turnaround, Flexible Quantities
Suitable for prototypes and low-volume production with reliable lead times.
6. Quality Inspection
In-process and final inspection to ensure parts meet drawing requirements.
From CAD files to finished product delivery, PCBasic combines computer numerical control milling machines with engineering experience to facilitate the smooth implementation of projects.
CNC milling remains one of the most widely used and versatile machining methods in today’s manufacturing industry. By understanding the CNC milling definition, types of machines, working principles and practical applications, engineers and project managers can more clearly determine whether it suits their production needs.
Whether you are just beginning to understand what CNC milling is or hope to enhance production efficiency through professional CNC milling manufacturing, choose a reliable partner like PCBasic. All of these contribute to ensuring processing accuracy, delivery time and overall stability.
If the project has clear requirements for precision, batch consistency and flexibility, PCBasic's CNC milling machines can provide stable and controllable processing support.
1. What is CNC milling used for?
CNC milling is used to produce precision parts by removing material from a solid block. It is widely used in aerospace, medical, electronics, and industrial applications.
2. What does milling mean?
Milling is a machining process where a rotating tool cuts material while the workpiece remains fixed.
3. What materials can be used for CNC milling?
CNC milling manufacturing supports metals such as aluminum, steel, stainless steel, titanium, and engineering plastics like ABS and POM.
4. What is the difference between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling?
A 3-axis CNC milling machine handles simple geometries, while a 5-axis machine supports complex shapes and fewer setups.
5. Is CNC milling suitable for small batches?
Yes. CNC milling is suitable for prototyping and small to medium batch production.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
