Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCB Encapsulation: A Complete Guide
PCBs that are exposed to moisture, dust, chemical media and other conditions for a long time are prone to solder joint aging, corrosion and electrical failure. In such complex and harsh environments, it is very important to protect the circuit boards in electronic equipment.
PCB encapsulation is a reliable protection solution in modern electronic manufacturing. This is also the theme of our article. Next, this article will introduce PCB encapsulation, including its definition, common encapsulation methods, material types, process flows, and so on.
PCB encapsulation refers to covering or filling the surface of electronic components and conductive circuits on a PCB with a protective material (i.e., PCB encapsulant). After curing, this material forms a solid or slightly flexible protective layer that isolates electronic components from the external environment and mechanical stress. This protective layer can effectively resist the following common risk factors:
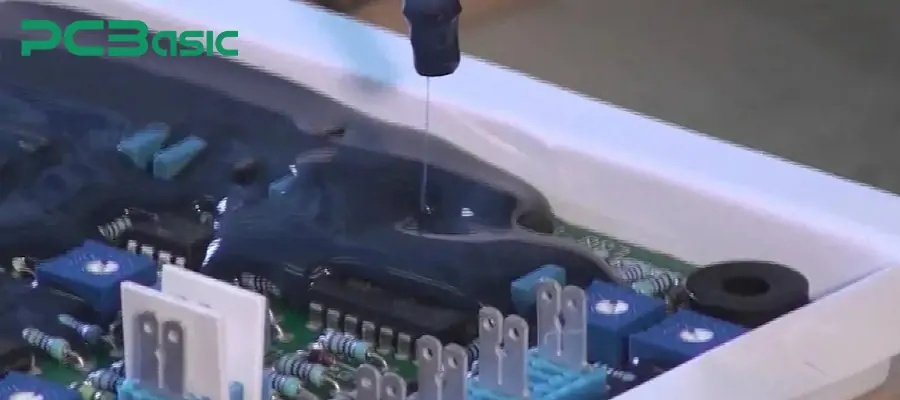

Moisture and water
Dust and air pollutants
Corrosive chemicals
Mechanical shock and vibration
Leakage and short circuits
PCB encapsulation technology is widely applied in the field of electronic manufacturing and high-reliablity applications. It can extend the service life of the entire machine and the circuit board, ensuring that electronic products can operate stably even under complex conditions. Among the common methods of PCB encapsulation, PCB potting is one of the most widely used methods. This process involves placing the entire circuit board or electronic module into an enclosure, followed by injecting liquid encapsulation material. After the material solidifies, the electronic components are completely encapsulated within the encapsulation layer.
From the perspective of purpose, both encapsulation and potting are essentially aimed at protecting electronic components. The main difference between them lies in the covering method. PCB encapsulation can either partially cover the critical areas or achieve complete enclosure, while PCB potting usually refers to completely filling the interior of the entire housing. For applications that are exposed to high humidity, strong vibration, or have a risk of disassembly for a long time, potting is regarded as one of the most reliable PCB encapsulation methods.
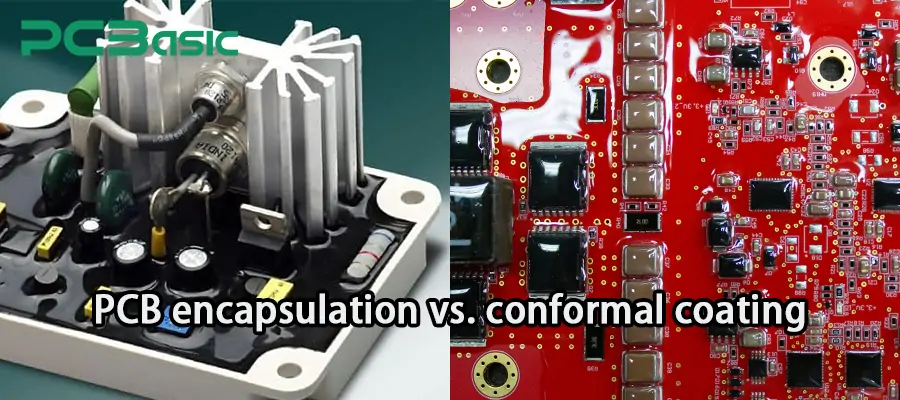
PCB encapsulation and conformal coating are both common protective processes for circuit boards, but they have significant differences. The following table conducts a systematic comparison of PCB encapsulation and conformal coating from multiple key dimensions to help you understand better:
|
Aspect |
PCB Encapsulation |
Conformal Coating |
|
Purpose |
Provide full environmental and mechanical protection for electronic assemblies |
Provide basic surface protection for PCB components |
|
Protection Method |
Components are covered or filled with PCB encapsulant |
Thin polymer coating applied on PCB surface |
|
Coverage Style |
Partial or full enclosure (potting = full cavity filling) |
Surface coating only |
|
Coating Thickness |
Thick (millimeter level) |
Thin (micron level) |
|
Repairability |
Difficult, usually permanent protection |
Easier to inspect and rework |
|
Typical Applications |
Automotive electronics, industrial control, outdoor devices, power modules |
Consumer electronics, indoor equipment |
|
Protection Level |
High-reliability, long-term protection solution |
Basic-level protection solution |
Modern electronic systems are often designed to operate for long periods in environments with significant temperature variations, high humidity, frequent vibrations, or the presence of chemical media. To meet the reliability requirements under these conditions, PCBs need higher levels of safety assurance. And PCB encapsulation provides this level of protection.. The main advantages of PCB encapsulation include:
1. Environmental protection capability
The PCB encapsulation can effectively prevent moisture from entering and reduce the accumulation of dust and chemical erosion. This advantage can prevent the corrosion of circuit board solder joints and the deterioration of component performance.
2. Mechanical strength enhancement
The PCB that has undergone encapsulation treatment has a stronger resistance to impacts, vibrations and external stress. Therefore, PCB encapsulation is very common in automotive electronics, industrial equipment and outdoor electronic products.
3. Electrical insulation performance
The PCB encapsulation material can reduce the risk of short circuits, suppress the generation of arcs, and enhance the dielectric strength between different conductors.
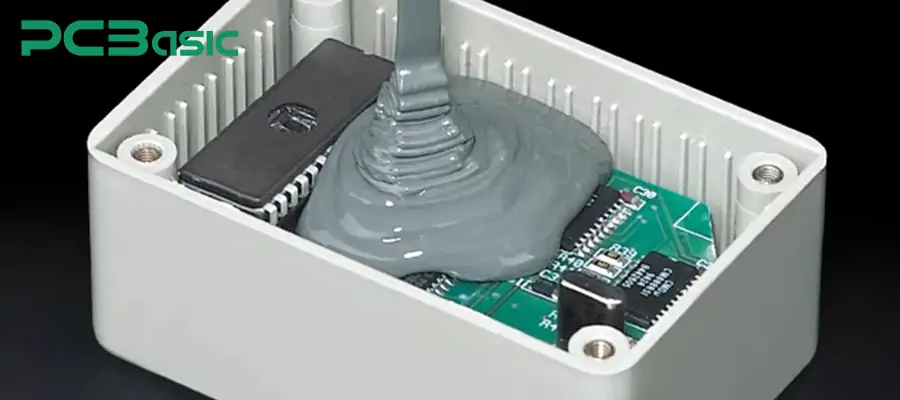

4. Thermal Stability
Some PCB encapsulation materials possess excellent thermal management capabilities, which can mitigate the damage to electronic components caused by extreme temperature changes or thermal cycling.
5. Intellectual Property and Security Protection
After the electronic modules are fully encapsulated or filled, it will increase the difficulty of disassembly and reverse analysis. To a certain extent, this can protect the product design from being easily copied or tampered with.
PCB encapsulation can be achieved through various techniques, and the level of protection provided by different methods varies. Common methods include potting/encapsulation in a housing, dam and potting encapsulation, drip coating, and the use of various electronics encapsulants. The following table provides a comparison of these PCB encapsulation methods:
|
Method |
Description |
Advantages |
Typical Applications |
|
Potting/Casing Encapsulation |
The PCB is placed inside a case and completely filled with liquid PCB encapsulant. Once cured, the electronics are fully sealed. |
- Maximum moisture and vibration protection - High electrical insulation - Strong tamper resistance - Excellent durability |
Power supplies, automotive modules, outdoor electronics |
|
Dam and Fill Encapsulation |
Selective encapsulation where a dam material is applied around components, then the PCB encapsulant is poured inside. |
- Protects critical components - Keeps connectors or heat - sensitive parts exposed - Flexible design |
Industrial electronics, modules requiring partial protection |
|
Glop Top Encapsulation |
Small drops of epoxy or silicone are applied over bare semiconductor dies and wire bonds. |
- Space-efficient - Protects COB assemblies - Prevents contamination and mechanical damage |
LEDs, sensors, compact consumer electronics |
The selection of PCB encapsulation materials is very important, as it directly affects the protection effect and service life of electronic components. Commonly used encapsulation materials include epoxy, silicone, and polyurethane.
Epoxy is one of the most commonly used PCB encapsulation materials, and its advantages lie in:
High mechanical strength
Excellent chemical resistance
Strong adhesion to electronic components
Good electrical insulation performance
Epoxy is suitable for encapsulated PCBs that require long-term and permanent protection, such as high-reliability power modules and outdoor electronic devices. However, after curing, it has strong adhesion, making repair and maintenance difficult, and is not suitable for products that need to be disassembled frequently.

Silicone encapsulation materials feature high flexibility and wide temperature range adaptability. They can maintain stable performance in both high-temperature and low-temperature environments, and exert minimal mechanical stress on components. Their characteristics include:
High flexibility
Outstanding moisture resistance
Low mechanical stress on sensitive components
Silicone is widely used in encapsulation electronics for automotive electronics, LED lighting, medical equipment, and other applications that require high temperature resistance or flexibility of components.
Polyurethane encapsulation materials strike a balance between flexibility and strength, and also possess certain abrasion resistance and chemical resistance. Their main features include:
Good wear resistance
Moderate chemical resistance
Easier to repair or maintain compared to epoxy
Polyurethane is typically used for industrial electronics, outdoor equipment or encapsulated PCBs that require moderate protection and may need to be repaired.
A standard PCB encapsulation process typically includes the following key steps:
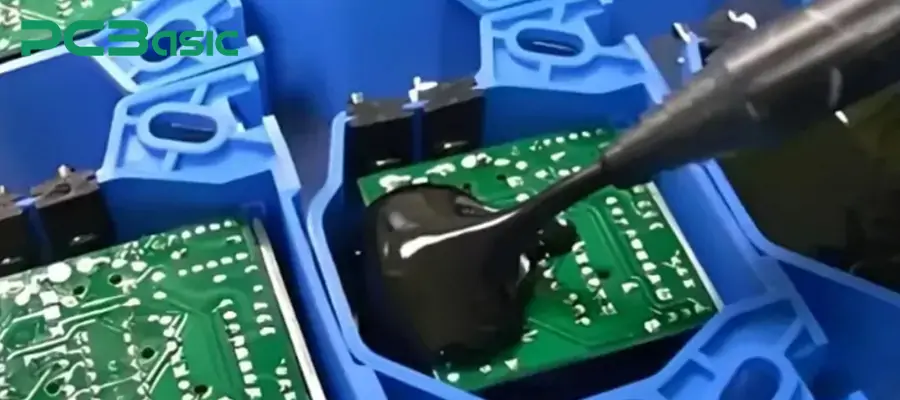

1. PCB Cleaning and Surface Treatment
Before encapsulation, it is essential to thoroughly remove dust, oil, flux residue and moisture from the surface of the PCB. This process is to ensure that the encapsulation material (such as PCB encapsulation epoxy) can fully bond with the surface of the circuit board.
Common methods include:
Solvent or water-based cleaning
Removal of ionic contaminants
Drying and dehumidification treatment
2. Shielding and Area Protection
Then, we need to shield the connectors, test points, heat sinks and the functional areas that need to be exposed to prevent the encapsulation material from covering these parts. Only in this way can we ensure the normal operation of the circuit and facilitate subsequent assembly and maintenance.
3. Encapsulation Material Mixing and Deaeration
According to the process requirements, the selected PCB encapsulation materials (epoxy resin, silicone or polyurethane) are mixed in proportion. Subsequently, vacuum degassing is carried out to remove the air in the materials, avoiding the formation of bubbles or voids after curing. This step affects the following properties:
Electrical insulation performance
Mechanical strength
Long-term stability after encapsulation
4. Dispensing or Potting
According to the structural design, select the appropriate coating method:
Overall potting / casing encapsulation: Completely fill the encapsulation material into the casing.
Dam and fill encapsulation: Form an encapsulation layer in a local area.
Glop top encapsulation: Commonly used in the area of direct chip attachment encapsulation.
This step is a crucial link in forming the protective layer.
5. Curing and Solidification
After the dispensing or encapsulation process is completed, it is necessary to allow the material to fully cure and form a stable protective layer. Common curing methods include:
Room temperature curing
Heating curing (in an oven)
Some special materials use UV curing
At this step, we need to properly control the curing conditions to ensure the bonding strength and structural stability of the PCB encapsulation epoxy.
6. Inspection and Quality Testing
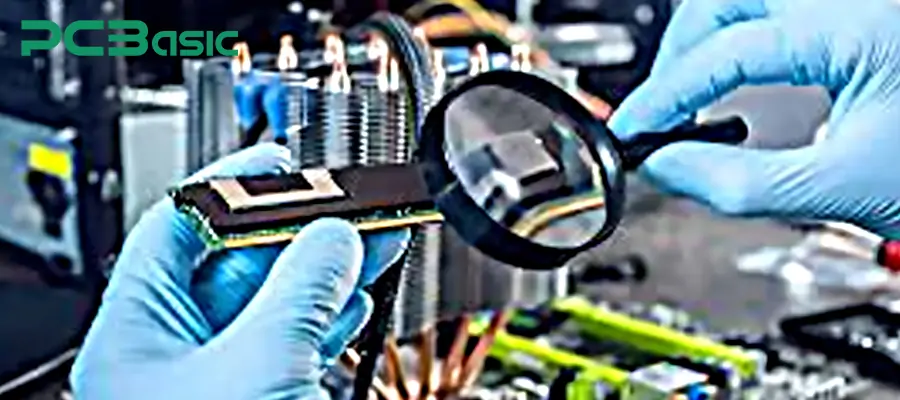

Conduct quality verification on the encapsulated PCB after the encapsulation process to ensure it meets the design and reliability requirements. Common inspection items include:
Visual inspection (for bubbles, cracks, and glue leakage)
Electrical testing (insulation resistance, conductivity)
Environmental and reliability testing (high/low temperature, vibration, etc.)
This step is used to verify the actual protective effect of the encapsulated electronics.
The standardized PCB encapsulation process can effectively prevent:
Water vapor intrusion
Corrosion and chemical medium damage
Structural failure caused by vibration
Electrical short-circuit risk
PCB encapsulation is widely used and is a common protective process in multiple industries. This process is often applied to electronic products that have high requirements for reliability and environmental adaptability.
1. Automotive Electronics
Automotive electronics are constantly exposed to high temperatures, vibrations and humidity. The PCB encapsulation epoxy is mainly used for protecting:
Engine Control Unit (ECU)
Various sensors and control modules
Car lighting system circuit board
Through encapsulation, the electrical insulation performance and structural stability of automotive electronics can be enhanced, and the service life of the entire machine can be extended.
2. Industrial Control Systems
In industrial environments, there are often dust, oil mist, chemical media and continuous vibrations. Under such conditions, it is necessary to perform PCB encapsulation. Electronics encapsulation is commonly used for:
PLC control board
Motor drive and servo controller
Automation equipment control module
The encapsulated PCB can effectively reduce the failure risks caused by corrosion and mechanical stress.
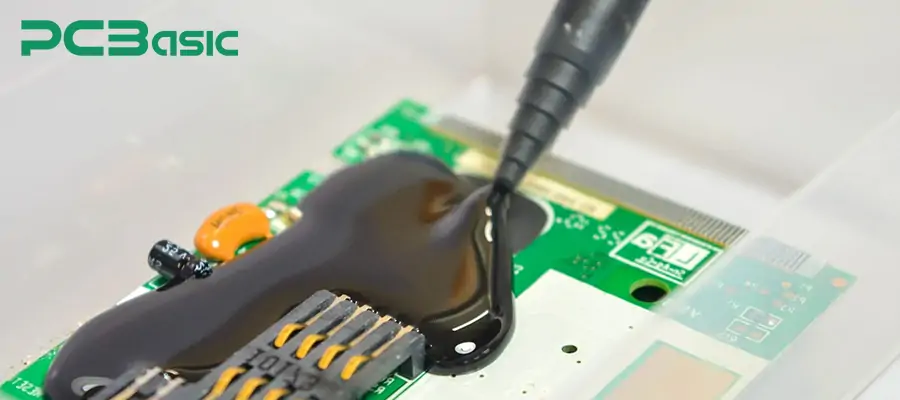

3. Power supplies and inverters
Power supply products are subjected to high voltages and thermal stresses. Potting and encapsulation are widely used in this field:
AC/DC power module
DC/DC converter
Photovoltaic inverter control board
PCB encapsulation can enhance its insulation performance, preventing water vapor and contaminants from affecting the high-voltage circuits.
4. Medical Devices
Medical electronic devices have extremely high requirements for safety and long-term stability. Encapsulated PCBs are commonly used in:
Vital sign monitoring equipment
Diagnostic instruments
Portable medical electronic product
PCB encapsulation helps to reduce the risk of leakage and meets strict reliability and regulatory requirements.
5. Outdoor communication equipment
Outdoor electronic products need to withstand long-term exposure to rain, dust and temperature changes. PCB encapsulation is commonly used in:
Communication base station equipment
Signal transmitting device
Antenna control module
Using PCB encapsulation can ensure that the equipment operates stably under complex climatic conditions.
In fields such as automotive electronics, industrial control, medical equipment and outdoor applications, PCB encapsulation solutions are an important protective measure for highly reliable electronic products.
The following table summarizes several practical tips for effectively conducting PCB encapsulation.
|
Key Aspect |
Best Practice |
Benefit |
|
1. PCB encapsulant selection |
Choose material based on temperature, chemical exposure, and flexibility requirements |
Ensures environmental compatibility and reliability |
|
2. Surface preparation |
Clean PCB thoroughly before encapsulation |
Improves adhesion and prevents delamination |
|
3. Bubble control |
Use controlled dispensing and vacuum degassing |
Prevents voids and insulation failure |
|
4. Thermal management |
Control encapsulation thickness and use thermally conductive materials |
Maintains heat dissipation performance |
|
5. PCB design for encapsulation |
Keep proper component spacing and protect connectors and test points |
Simplifies processing and improves consistency |
|
6. Pre-production testing |
Perform thermal, humidity, and electrical tests on samples |
Reduces risk in mass production |
PCB encapsulation is a mature and reliable solution for protecting circuit boards. It can effectively resist moisture, dust, chemical media, vibration, and electrical stress, thereby significantly enhancing the reliability and service life of the products. Therefore, in various fields, such as automotive electronics, industrial control, power equipment, medical equipment, and outdoor electronic products, PCB encapsulation plays an important role.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
