Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Teflon PCB (PTFE PCB): The Complete Guide
As electronic products develop towards higher speeds and frequencies, choosing the right PCB materials is becoming increasingly important. Traditional FR4 circuit boards are no longer able to meet the requirements for electrical and thermal performance in RF, microwave, aerospace and advanced communication systems. This is also the main reason why Teflon PCBS are widely used.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain in a more intuitive way what a Teflon PCB is, the materials and laminates it uses, as well as its typical specifications, electrical and thermal properties, manufacturing process, and design considerations. At the same time, the differences between Teflon PCB and other PCB materials will be compared, and explanations will be provided in combination with actual application scenarios. Finally, we will explain why choosing a reliable manufacturer like PCBasic is very important for producing high-quality Teflon PCBs.
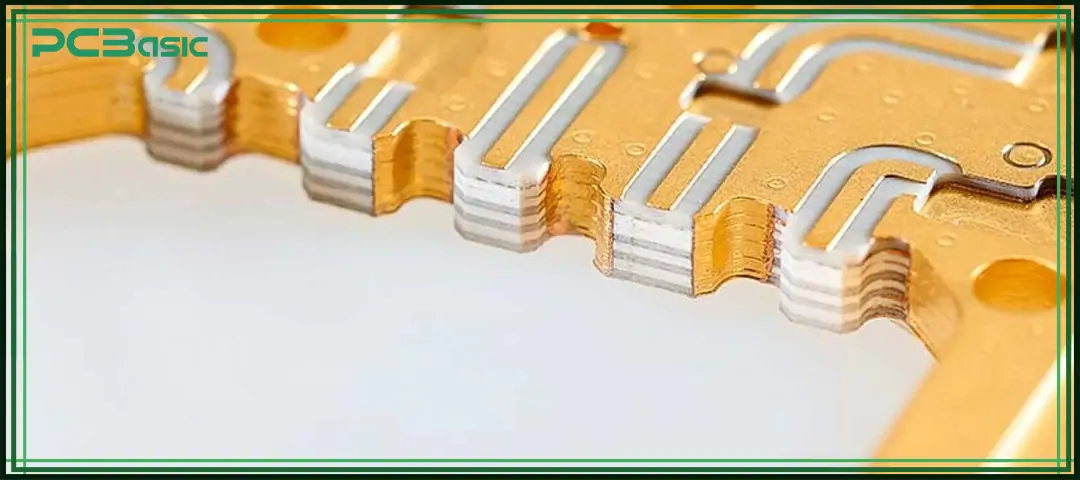
Teflon PCB, also known as Polytetrafluoroethylene PCB (PTFE PCB), is a type of circuit board made from PTFE material as the base material, which is different from the common FR4 epoxy glass laminate. "Teflon" was originally the trade name given by DuPont to PTFE materials. Therefore, in the electronics industry, people often refer to PTFE circuit boards as Teflon PCBs.
This type of circuit board is mainly used for high-frequency signal transmission above 5 GHz and is highly suitable for microwave and radio frequency (RF) circuits. Compared with FR4, the Teflon PCB has more advantages in signal performance, mainly in the following aspects:
• Lower dielectric constant, allowing faster signal transmission
• Very low dielectric loss, resulting in less signal attenuation
• Lower signal distortion and better stability
• Stable performance across a wide frequency range
It is precisely because of these characteristics that PTFE PCBs are widely used in fields with high requirements for signal quality, such as radar systems, satellite communications, 5G communication equipment, and medical testing equipment.
Pure PTFE material is relatively soft, with a smooth surface. Moreover, copper foil is not easy to bond firmly, making processing rather difficult. Therefore, in actual production, pure PTFE is rarely used directly. Instead, composite laminates with reinforcing materials, namely PTFE laminate, are adopted. Common reinforcing materials include:
• Glass fiber
• Woven fiberglass
• Ceramic fillers
• Microfiber materials
These reinforcements can enhance the mechanical strength, dimensional stability and heat resistance of circuit boards without affecting the electrical properties of PTFE, making them more suitable for the production of Teflon PCBs.
Currently, common PTFE laminate suppliers include Rogers, Taconic, Arlon, Nelco and Isola. Their products are generally divided into two categories:
• Military-grade materials: such as the Rogers RT/duroid series
• Commercial-grade materials: such as the Rogers RO3000 series
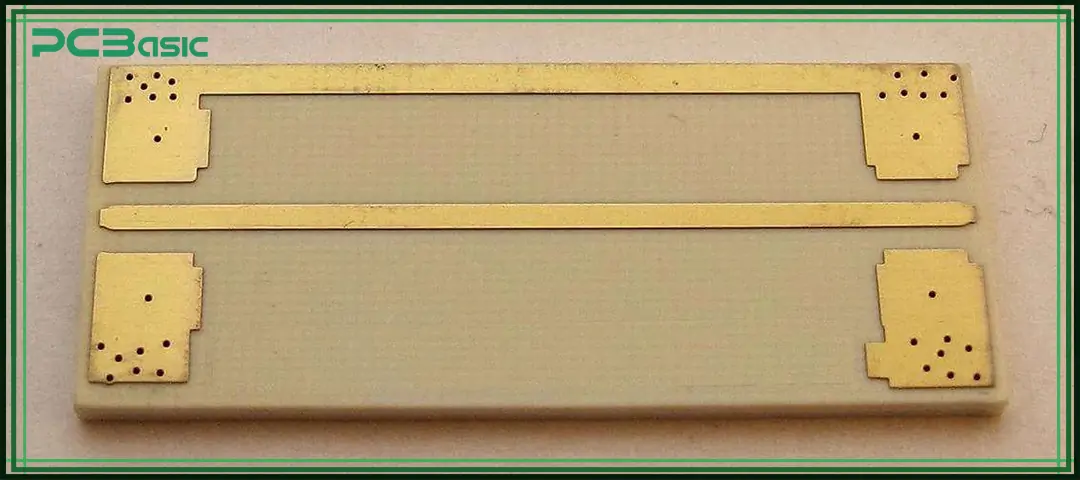
When choosing a PTFE PCB, engineers usually focus on several key parameters in the material data sheet, including:
• Dielectric constant
• Dissipation factor
• Thermal conductivity
• Coefficient of thermal expansion
• Moisture absorption
• Peel strength
• Maximum operating temperature
Common materials include:
• Rogers RO3003 (dielectric constant about 3.0, low loss)
• RT/duroid 5880 (dielectric constant about 2.2, ultra-low loss)
• Taconic TLY series
• Arlon CuClad series
These parameters directly affect the performance of Teflon PCB in RF and microwave environments and can also assist designers in selecting the appropriate PTFE laminate based on specific applications.
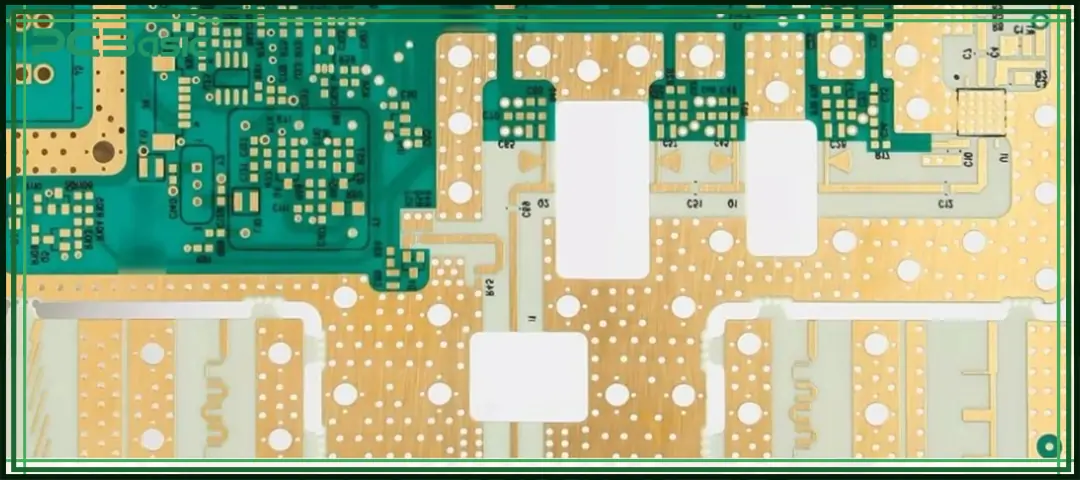
The greatest advantage of the Teflon PCB lies in its electrical performance:
• Low dielectric constant (Dk), which allows signals to travel faster
• Low dissipation factor (Df), resulting in less signal loss during transmission
• Stable dielectric performance, with little change across different temperatures and frequencies
It is precisely because of these features that Teflon PCBs can maintain good signal integrity and are thus often used in high-frequency circuits such as RF amplifiers, filters and antennas.
PTFE (Teflon) PCB offers strong resistance to high temperatures:
• Can operate in environments up to about 260°C
• Less likely to be damaged by heat during soldering and reflow processes
• Reinforced laminates have lower thermal expansion and better stability
These characteristics make PTFE PCBs suitable for applications with large temperature variations, such as aerospace equipment and automotive radar systems.
Teflon PCBs also perform reliably in complex and harsh environments:
• Very low moisture absorption, so it is not easily affected by humidity
• Strong resistance to chemicals
• Good resistance to corrosion and weather conditions
• High-dimensional stability with minimal size change over long-term use
Therefore, even in humid, highly corrosive or outdoor environments, Teflon PCBs can maintain stable operation.
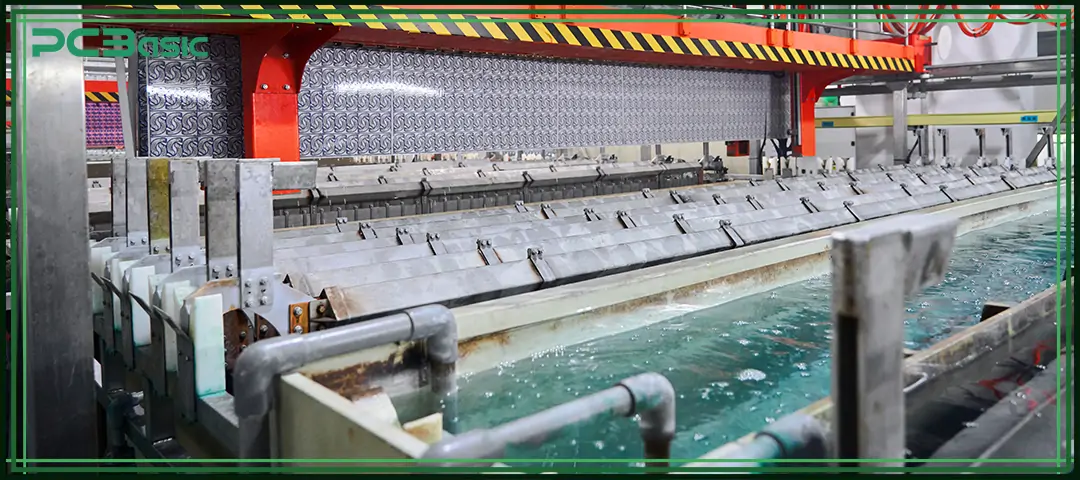

Due to the significant differences in material properties between PTFE and FR4, the Teflon PCB production has higher requirements for equipment and process experience.
Before processing, the PTFE laminate must be cleaned and treated to ensure that the copper foil can bond firmly to the surface. The commonly used methods are sodium etching or plasma treatment, which enhance adhesion by modifying the surface condition.
Copper foil is bonded to the PTFE substrate through a vacuum lamination process, with strictly controlled temperature and pressure parameters. This step is directly related to whether the Teflon PCB will have delamination problems, and thus is extremely crucial.
After copper cladding, the board will first be coated with a layer of photoresist, and then undergo ultraviolet exposure and chemical etching to form the required circuit pattern. Since PTFE PCBs are mainly used in RF circuits, they have very high requirements for circuit size and precision. This step must be extremely precise.
PTFE material is relatively soft and prone to deformation during drilling. Therefore, a ceramic-filled PTFE laminate is usually selected to enhance machining stability. After the drilling is completed, copper plating will be applied to the hole wall to enable electrical connection of each layer of circuits.
After etching, the solder mask needs to be applied within the specified time. Each Teflon PCB undergoes electrical testing, visual inspection and reliability testing to ensure that the product meets the requirements in terms of performance and quality.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
When designing with PTFE PCB material, it is necessary to be more meticulous and cautious than common FR4 circuit boards, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
• Controlled impedance routing
• Accurate stack-up design
• Simulation of signal integrity
• Selection of compatible surface finishes (ENIG, immersion silver, immersion tin)
• Tight manufacturing tolerances
Due to the fact that the surface of PTFE material is non-stick and relatively soft in itself, even minor dimensional changes can affect its RF performance. Therefore, when engineers design Teflon PCBs, they must maintain close communication with the manufacturer to ensure the stable final performance of the product and smooth production.
The following is a comparison table of Teflon PCB with other common PCB materials, providing an intuitive comparison in terms of electrical performance, thermal behavior, moisture absorption, and cost:
|
Comparison Item |
Teflon PCB (PTFE PCB) |
FR4 PCB |
Metal Core PCB |
Polyimide PCB |
|
Electrical performance |
Excellent, low dielectric constant and low loss, ideal for high-frequency and RF applications |
Moderate, suitable for low-frequency and general circuits |
Weak, not suitable for high-frequency signals |
Good, but less stable than PTFE PCB |
|
Signal integrity |
Very high, ideal for RF and microwave circuits |
Medium |
Poor |
Good |
|
Thermal stability |
High, can withstand about 260°C |
Medium |
Very high, strong heat dissipation |
High |
|
Heat dissipation |
Moderate (focuses more on electrical performance) |
Moderate |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Moisture absorption |
Very low |
Higher |
Low |
Higher |
|
Dimensional stability |
Very good |
Moderate |
Very good |
Good |
|
Mechanical strength |
Medium (requires reinforced PTFE laminate) |
Good |
Very good |
Good |
|
Cost |
High |
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
Typical applications |
RF, microwave, radar, 5G, satellite communication |
Consumer electronics, industrial control |
LED, power electronics |
Flexible circuits, high-temperature environments |
|
Best use case |
High-frequency, high-speed, high-reliability systems |
Low-frequency, cost-sensitive products |
Applications requiring strong thermal management |
Applications requiring flexibility or high temperature resistance |
We can see from the above table that:
• FR4 PCB is best for low-frequency and cost-sensitive products.
• Metal Core PCB is ideal for applications with high heat dissipation requirements, but not for RF signals.
• Polyimide PCB works well in flexible and high-temperature environments but has higher moisture absorption.
• Teflon PCB (PTFE PCB) is the best choice for high-frequency, RF, and microwave applications where signal integrity is critical.
Due to its unique performance advantages, Teflon PCB is widely used in the following fields:
• Aerospace and defense systems (radar, satellites, antennas)
• Telecommunications (5G base stations, RF front-end modules)
• Automotive electronics (ADAS radar systems)
• Medical devices (diagnostic imaging equipment)
• Industrial RF equipment
In these applications, Teflon can ensure the stability and reliability of signal transmission.

Choosing the right manufacturer is a crucial step in making a good Teflon PCB. PCBasic can provide one-stop Teflon PCB services from prototyping to mass production, helping customers complete projects more quickly.
The main advantages of PCBasic include:
• Advanced PTFE processing technology
• In-stock PTFE laminate materials for fast delivery
• Engineering support for RF design optimization
• Strict quality control and testing
• Cost-effective solutions compared to Western suppliers
With years of experience in high-frequency PCB production, PCBasic can ensure that each Teflon PCB meets high standards in terms of electrical performance and reliability.
Teflon PCB has become a very important circuit board material in high-frequency electronic products. Due to its low dielectric constant, low signal loss, strong high-temperature resistance and good environmental adaptability, Teflon PCB performs exceptionally well in RF and microwave applications.
Although the cost of Teflon PCBs is higher than that of FR4 and the manufacturing process is more complex, in fields such as aerospace, communication equipment, automotive radar and medical systems, its performance advantages are difficult to be replaced by other materials. As long as the material properties, technical parameters, design requirements and production processes are fully understood, the value of Teflon PCB can be better brought into play.
To ensure product quality and stability, it is very important to choose an experienced manufacturer like PCBasic, which helps to strike a balance among quality, reliability and cost. With the increasing demand for high-speed and high-frequency electronic products, PTFE laminate and Teflon PCB will remain indispensable key technologies in the future electronics industry.
Q1: What is the main difference between Teflon PCB and FR4 PCB?
A: Teflon PCB uses PTFE PCB material with a much lower dielectric constant and signal loss than FR4, making it suitable for RF and microwave applications, while FR4 is mainly for low-frequency electronics.
Q2: Why is PTFE laminate not used alone without reinforcement?
A: Pure PTFE is soft and has poor copper adhesion. Reinforced PTFE laminate (with glass fiber or ceramic fillers) improves mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
Q3: Is Teflon PCB suitable for all electronic products?
A: No. Teflon PCB is designed for high-frequency and high-speed circuits. For low-cost, low-frequency products, FR4 is usually sufficient.
Q4: What frequency range typically requires a PTFE PCB?
A: Applications above about 5 GHz, such as RF, microwave, radar, and 5G systems, usually require a PTFE PCB for stable signal performance.
Q5: Why is Teflon PCB more expensive than FR4?
A: PTFE laminate materials cost more and require specialized processing equipment and tighter manufacturing control, which increases overall production cost.
Q6: What surface finishes are commonly used for Teflon PCBs?
A: Common finishes include ENIG, immersion silver, and immersion tin, which are compatible with PTFE PCB materials.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
