Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > The Ultimate Guide to Circuit Boards: Types, Manufacturing, and Applications
In the modern electronics industry, the circuit board is the most core and fundamental structure of all electronic devices. With the rapid growth of the global electronics industry, circuit board technology is also continuously advancing. According to industry data, the global PCB market size exceeded USD 70 billion in 2024 and is expected to maintain a stable growth in the coming years, driving the development of various electronic industries. In particular, the development of new energy vehicles and autonomous driving has fueled demand for high-layer, multi-material, and ultra-reliable circuit boards. Consumer electronics, on the other hand, drive the continuous evolution of thinner, lighter and higher-density PCB boards.
In the past, circuit boards were mainly single-layer or double-layer, but nowadays, technologies such as multilayer structures, HDI high-density interconnect, rigid-flexible architectures, and embedded-component circuit boards are becoming increasingly popular. The motherboards of many devices have reached 8 layers, 12 layers or even more than 20 layers to accommodate increasingly complex chip routing and high-speed signal transmission. The PCB design of high-speed digital devices (such as servers, base stations, and GPU acceleration cards) requires extremely precise impedance control, signal integrity, and material stability.
Against such an industry backdrop, this article will start from the basics and clearly explain what a PCB is, the structure of the circuit board, the most common circuit board components, different types of PCB boards, the fundamentals of PCB design, manufacturing steps, typical applications in the data industry, and effective methods for extending the lifespan of printed circuit boards.
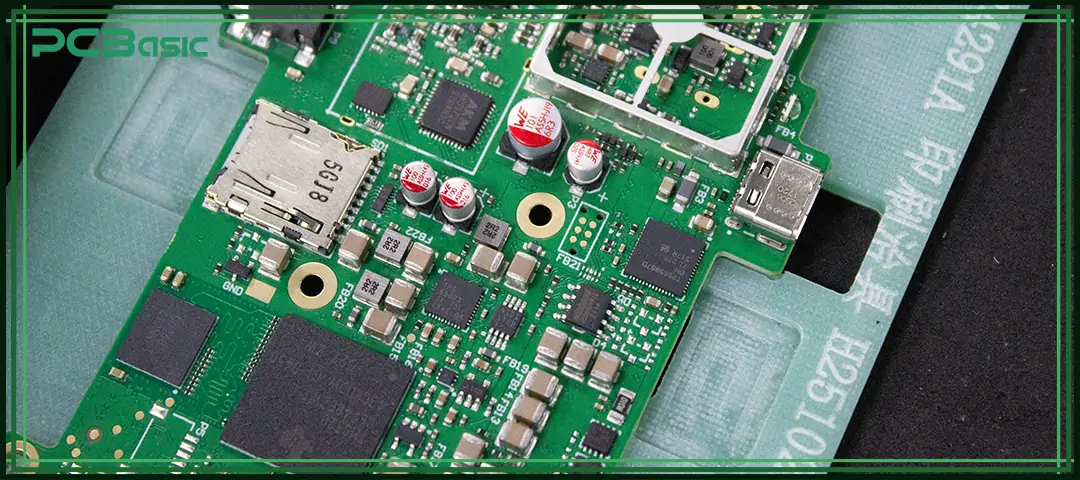
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a precisely engineered flat board used to support, secure and connect various electronic components. When people ask, "What is a PCB?" In fact, we can summarize it in one sentence:
The circuit board uses conductive copper traces on its surface to provide solid physical support and a clear, reliable electrical connection for all electronic components.
In early electronic products, circuit boards were often referred to as wiring boards. People often manually wired circuits point-to-point, which was not only messy but also very prone to poor contacts and short circuits. Modern PCB boards, through professional design, plan all signal, power and data paths in an orderly manner, making the entire system more stable and efficient.
Copper traces are like highways in a device, ensuring that information and current can be smoothly transmitted between various circuit board components such as resistors, capacitors, IC chips and connectors, allowing devices to work normally as designed.
Modern circuit board design not only pursues stability and reliability, but also emphasizes miniaturization, high-density routing, material durability and compatibility with automated manufacturing. This makes PCB an indispensable core foundation in almost all modern electronic devices, including embedded systems, consumer electronics, automotive electronics, industrial equipment, communication equipment and aerospace electronics.
A circuit board is composed of multiple layers of materials stacked together like a "sandwich". Each layer in the PCB has a specific function, such as signal transmission, mechanical support, electrical insulation or surface protection. These different layers are combined together, enabling the printed circuit board to stably complete electrical connections and structural strength.
FR4 is the basic material of a circuit board. It is a kind of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The FR4 substrate endows the entire printed circuit board with sufficient mechanical strength, good heat resistance and stable electrical insulation performance.
Copper foil is the most important conductive layer on a PCB. It forms the traces, pads and copper planes, creating the electrical pathways of the PCB. For multilayer PCBs, multiple copper layers are laminated together to achieve higher density and more complex circuits.
The soldermask covers the copper on the PCB. It is the colored coating on the PCB. Common colors include green, red, blue and black. The solder mask is greatly important. It protects the PCB copper surface from oxidation and environmental erosion, and prevents solder bridging during soldering.
The silkscreen layer is the outermost layer of text and identification. It is printed on the soldermask layer and is used to mark component reference designators, pin orientations, polarity symbols, company information, and assembly notes. Silkscreen printing makes the layout of PCBs clearer, making it easier for assembly engineers, maintenance personnel or testers to identify the information on the circuit board, and improving the readability and efficiency of PCBs during production, debugging and maintenance.

Not all circuit boards are the same. The structure, flexibility and application scenarios of a PCB will determine which type it is suitable for. The following are the most common types of printed circuit boards:
|
PCB Type |
Typical Features |
Typical Applications |
|
Single-sided PCB |
Copper on one side; simple and low-cost |
Calculators, toys, and LED lighting |
|
Double-sided PCB |
Copper on both sides; supports more routing |
Power supplies, consumer electronics, automation devices |
|
Multilayer PCB |
Three or more copper layers; HDI capable |
Smartphones, servers, medical devices, automotive ECUs |
|
Rigid PCB |
Built on FR4; strong and dimensionally stable |
TVs, computers, routers, cameras, power tools |
|
Flexible PCB |
Polyimide-based; bendable, lightweight |
Wearables, medical sensors, camera modules |
|
Rigid-Flex PCB |
Combines rigid + flex layers; high reliability |
Aerospace, defence electronics, and medical implants |

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
A printed circuit board integrates many types of circuit board components, including:
• Resistors
• Capacitors
• Inductors
These handle filtering, charging, shaping, and stabilizing electrical signals.
• Microcontrollers
• Processors
• Memory chips
• Transistors
• Diodes
These enable computation, switching, control, and data processing.
• USB
• HDMI
• Pin headers
• FPC connectors
Connect external devices or additional PCB boards.
• Voltage regulators
• MOSFETs
• DC-DC converters
Manage stable power delivery across the circuit board.
• Temperature sensors
• Accelerometers
• Motors
• Relays
These allow the device to interact with the physical world.
Together, these circuit board components form the functional ecosystem of any device.

Every sector relies on circuit boards:
Smartphones, tablets, wearables, and gaming systems
PLC controllers, robotics, factory sensors
ADAS, EV power management, and infotainment systems
MRI machines, monitors, and diagnostic equipment
Avionics, radar, and communication modules
Solar inverters, smart meters, power distribution
The versatility of PCBs makes them indispensable.
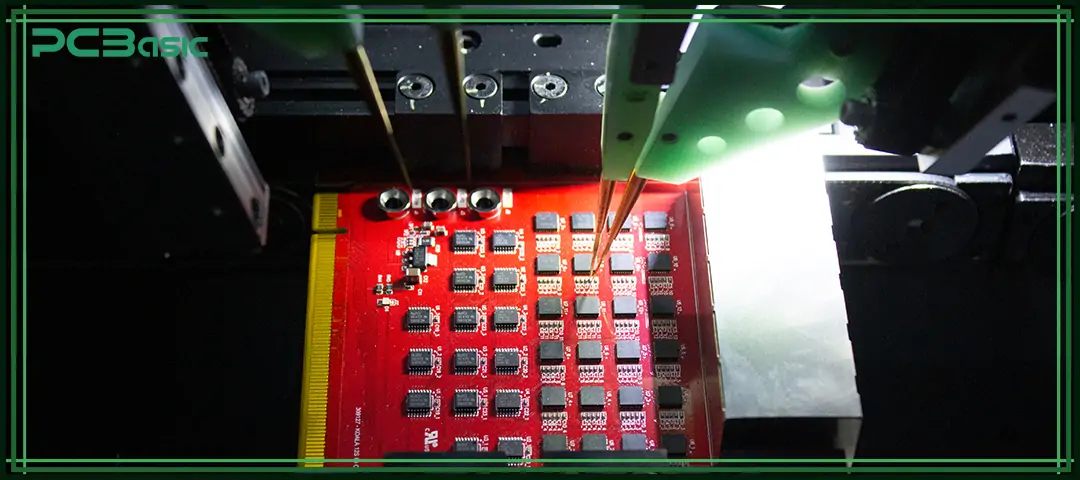
Effective circuit board design ensures electrical reliability, signal integrity, and efficient manufacturability.
Foundation elements include:
• Schematic creation
• Netlist generation
• Component placement
• Routing copper traces
• Ground plane design
• Thermal management
• DFM (Design for Manufacturing) considerations
Good PCB design is both an engineering discipline and an art that balances performance with cost.
The PCB manufacturing is a very meticulous process, which requires strict process control, a clean production environment and a stable quality system. For a circuit board to work reliably, every step must be accurate, clean and traceable. The following is the general process of a PCB board from raw materials to finished products.
Print the designed circuit pattern onto the copper-clad laminate. This step determines the positions of all traces on the printed circuit board. This is the basis of the entire PCB manufacturing process.
The excess copper is removed through chemical etching, leaving only the designed copper traces. Etching ensures that the electrical paths on the PCB are clean and accurate, preventing short circuits or leftover copper that could affect performance.
If it is a multilayer PCB board, several layers of copper foil and insulating materials need to be laminated together. Lamination enables the printed circuit board to achieve high-density routing and is an indispensable step for smart devices and high-speed electronic products.
Use high-speed drilling machines or laser drilling to drill vias, through-holes, and alignment holes on PCBs. These holes connect circuits between different layers and are also used to install circuit board components.
Deposit a layer of copper on the drilled hole wall to turn the hole into a conductive metal channel. Plating enables electrical intercommunication among the layers of a multilayer circuit board. It is a key step in the printed circuit board.
Apply a layer of green, red or black soldermask on the surface of the PCB. The solder mask layer protects the copper from oxidation and prevents solder bridges during soldering. It is the most obvious color layer on almost all PCB boards.
Print the reference designators, polarity marks, and company information on the surface of the PCB. Silkscreen makes circuit boards easier to install, test and maintain, and it is an important layer in PCB design.
ENIG, HASL, OSP and other surface finishes are applied to the surface of the solder pads to enhance the reliability of soldering. Different applications of the printed circuit board will select different surface processes.
Circuit board components such as resistors, capacitors, ICs and connectors are mounted onto the PCB board through SMT, reflow soldering or through-hole soldering. This stage transforms the printed circuit board from an empty board into a truly functional electronic module.
The quality of circuit boards is inspected by methods such as AOI, X-ray, flying probe testing, ICT, and functional testing. Testing ensures that each PCB board can operate stably, making it the most crucial step before the final shipment.
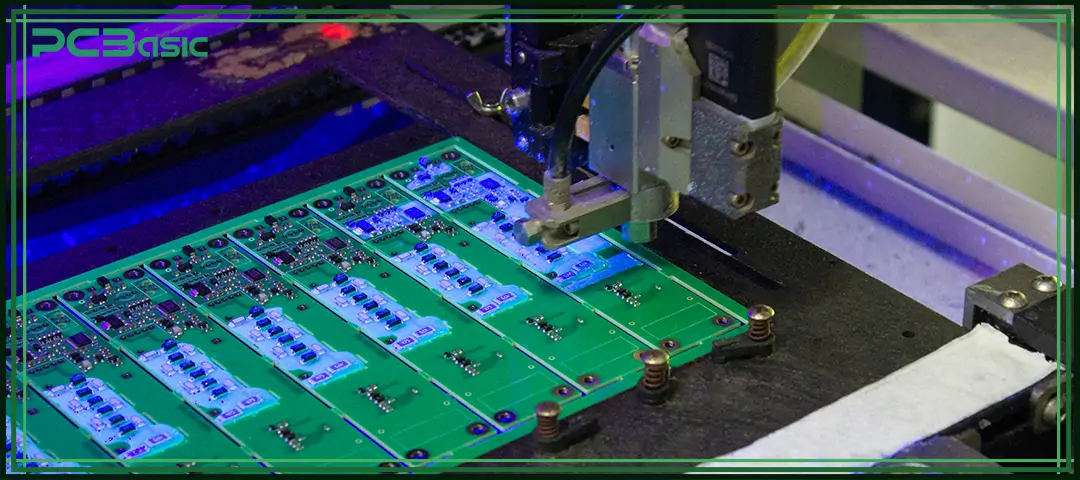
To maximize longevity:
Dust, oils, and contaminants can cause shorts or corrosion.
Moisture is a major enemy of printed circuit boards.
Look for burnt spots, lifted pads, cracked components, or broken solder joints.
Static discharge can destroy sensitive circuit board components.
Use anti-static bags, dry cabinets, and controlled environments.
Well-maintained circuit boards last significantly longer and perform more reliably.
The circuit board is the foundation of modern electronic products - from the simplest devices to the most advanced aerospace systems, none can do without it. Understand what a PCB is, its structure, materials such as FR4 and copper, various circuit board components, and the basic principles of circuit board design. It can help engineers and manufacturers create more efficient, durable and innovative electronic devices.
With the continuous development of technology, the role of printed circuit boards will only become increasingly important. In the future, electronic products will continue to drive higher integration, smaller structures, higher-density PCB design, as well as smarter and more automated manufacturing methods.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
