Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Comprehensive Guide to FR-4 Material in PCB Manufacturing
In the field of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, FR-4 material occupies an important position. As the most commonly used PCB substrate material, FR-4 is widely applied in the production of various circuit boards, especially playing a crucial role in ensuring the performance and durability of circuit boards. Whether in consumer electronics, communication equipment, or high-demand fields such as aerospace, FR-4 material remains the preferred material in many applications due to its outstanding mechanical strength, electrical insulation performance, and good thermal stability.
This guide will provide a detailed explanation of the definition, types, main characteristics and limitations of FR-4 material. We will compare FR-4 with other common materials to help you better understand how to select the appropriate material for different applications. We will also focus on the key factors to consider when choosing FR-4 substrate during PCB design, and analyze the important role of FR-4 material in modern PCB manufacturing.
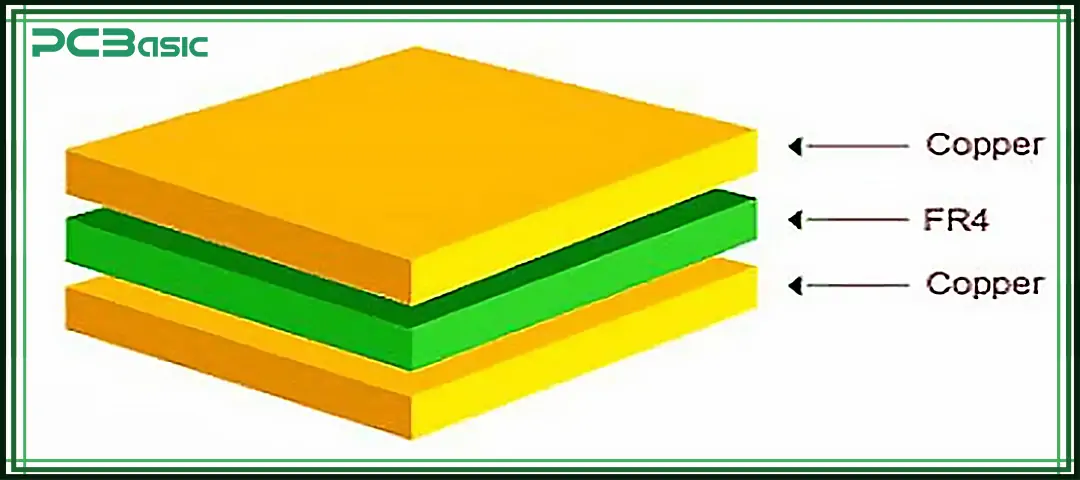
FR-4 is a type of epoxy resin composite material reinforced with fiberglass. It is a common PCB material. FR-4 material is widely used in the manufacturing of circuit boards for various electronic products. "FR" is the abbreviation of "Flame Retardant", indicating that FR-4 material has excellent flame retardant properties. That is to say, FR-4 material is less likely to burn at high temperatures, which helps enhance the safety and reliability of the circuit board.
Structurally, FR-4 materials are usually laminated with multiple layers of FR-4 fiberglass, bonded and cured with epoxy resin. The material formed in this way has excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability and insulation performance. It can not only withstand electrical stress, but also resist a certain level of thermal stress, making it suitable for PCB substrates in most electronic applications.
There are many types of FR-4 materials on the market, each with different properties and suitable for different electronic applications. Understanding these types will help you choose the right FR-4 substrate when designing FR-4 PCBs to ensure stable and durable circuit board performance.
|
Type |
Structural Characteristics |
Performance Features |
Typical Applications |
|
Standard FR-4 |
Glass fiber cloth with standard epoxy resin |
Good mechanical strength, electrical insulation, moisture and chemical resistance |
Home appliances, consumer electronics, general industrial devices |
|
High-Tg FR-4 |
High Tg epoxy system (Tg > 170°C) |
High thermal stability, anti-delamination, dimensional reliability |
Automotive electronics, power tools, industrial control |
|
Flame-Retardant FR-4 |
Enhanced resin system with high flame resistance |
Excellent flame retardancy, stable in high-heat or high-voltage conditions |
Military PCBs, elevators, safety-critical systems |
|
Lead-Free FR-4 |
Modified epoxy for lead-free solder compatibility |
Withstands high soldering temperature, RoHS compliant |
Medical devices, green electronics, wearables |
According to different working environments and performance requirements, choosing the right type of FR-4 material is crucial to ensure the functional stability, safety and service life of the FR-4 PCB.
FR-4 material is widely used in various PCB manufacturing due to its excellent comprehensive performance. Understanding the main performance of FR-4 material will help you make more reasonable decisions in the design and material selection process. The following will introduce the key FR-4 material properties from three aspects:
FR-4 material has high mechanical strength and can withstand significant external impact and bending deformation. Compared with other PCB substrates, it is not easy to crack or deform in long-term use, making it suitable for applications that require structural stability. This strength also makes FR-4 board not easy to be damaged during transportation, assembly and use, improving the reliability and service life of the entire board.
FR-4 substrate is an excellent electrical insulation material that can effectively prevent short circuits or electrical interference in circuits. The dielectric constant of FR-4 material is stable, supporting high-speed signal transmission, making it suitable for RF, high-frequency or high-speed data transmission circuits. At the same time, FR-4 material has low signal loss and can still maintain good signal integrity in multilayer boards or complex circuits.
FR-4 material has moderate thermal conductivity. Although the FR-4 thermal conductivity is not as good as ceramic or metal substrates, it is sufficient for most electronic devices. It can operate stably within the normal operating temperature range, helping the circuit board release heat and avoiding local overheating that causes performance degradation or component damage. For devices that are more sensitive to temperature rise, heat dissipation copper foil or thermal vias can be used in the design to improve thermal management.
In summary, the comprehensive performance of FR-4 material in strength, electrical insulation and thermal stability makes it one of the most commonly used FR-4 PCB materials, suitable for various circuit board designs from ordinary electronic products to complex industrial equipment.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Although the FR-4 material has a wide range of applications, it also has some limitations. Understanding these issues in PCB design can help in making more appropriate material selections and optimizing the design.
Thermal Conductivity: The thermal conductivity of FR-4 material is relatively low, which cannot dissipate heat as quickly as metal core circuit boards (MCPCBs). Therefore, in applications with high power or high heat density, FR-4 may not be able to remove heat in time, which may affect performance or cause overheating.
Flexibility: Although FR-4 fiberglass has a certain degree of flexibility, it is still a rigid material overall and is not suitable for making flexible circuit boards. For designs that require bending and flexing, flexible materials such as polyimide are better.
Moisture Absorption: The FR-4 material can absorb moisture from the air, especially in high-humidity environments. The absorption of moisture can lead to a decline in insulation performance or deformation of the board. Although it has some chemical resistance, prolonged exposure to humidity may shorten the service life of the FR-4 PCB.
During the PCB manufacturing process, FR-4 material is used as the base substrate for the circuit board. The circuit patterns are directly etched or printed onto this layer of material. The general process flow typically consists of the following main steps:
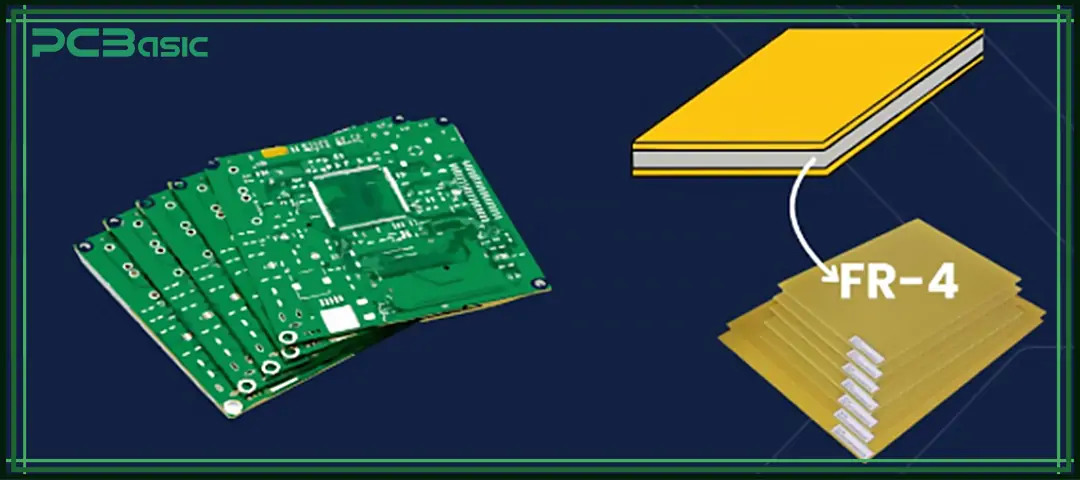
Multiple layers of FR-4 fiberglass are stacked together and bonded with epoxy resin to form a solid FR-4 PCB material. This process determines the thickness and structural strength of the PCB and is the foundation for manufacturing multilayer boards.
Apply copper foil onto the cured FR-4 board and remove the unwanted copper through chemical methods (such as acid etching), leaving only the required circuit patterns. This step will complete the initial construction of the circuit paths.
Cover the surface of the etched FR-4 PCB with a green solder mask to protect the circuit, prevent accidental soldering, and enhance the durability and reliability of the board. This layer also helps improve soldering quality.
After the circuit layout and soldering process are completed, electronic components are installed. Common methods include Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through Hole Technology (THT). The components are firmly soldered onto the FR-4 board to form a complete electronic functional system.
Through the above steps, FR-4 material not only serves as the supporting structure for the circuit, but also directly affects the electrical performance, structural strength and reliability of the PCB. Therefore, the FR-4 material plays a crucial role in the entire PCB manufacturing process.
In PCB manufacturing, there are various types of FR materials that are commonly used to meet different performance, cost, and design requirements. Among them, FR-4 material is widely used in various circuit boards due to its high strength, good insulation performance, and strong heat resistance. It is currently the most common substrate.
However, in some products with lower cost requirements and simpler structures, such as low-end electronic devices, materials like FR-1, FR-2, and FR-3 are also often used. These materials are cheaper, but there are certain performance differences.
To select the appropriate PCB material, it is necessary to understand the specific differences between FR-4 and these other FR materials in terms of material composition, heat resistance, mechanical strength, electrical insulation ability, and application scope. Through clear comparisons, engineers can more accurately judge the advantages and disadvantages of various materials and make more appropriate design decisions.
|
Property |
FR-1 |
FR-2 |
FR-3 |
FR-4 |
|
Base Material |
Paper + phenolic resin |
Paper + phenolic resin |
Paper + epoxy resin |
Glass fiber (fiberglass) + epoxy resin |
|
Thermal Resistance |
Low (up to ~105°C) |
Low (up to ~130°C) |
Moderate (similar to FR-2 but better heat resistance) |
High (Tg from ~130°C to >170°C depending on type) |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Poor |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Excellent mechanical strength |
|
Electrical Insulation |
Basic insulation |
Moderate |
Moderate to good |
Excellent insulation properties |
|
Moisture Resistance |
Low |
Low to moderate |
Moderate |
High moisture resistance |
|
Flame Retardancy |
Not rated |
Limited (not always flame retardant) |
Slightly better than FR-2 |
UL94 V-0 flame retardant certified |
|
Cost |
Very low |
Low |
Low |
Moderate cost, higher performance |
|
Common Applications |
Low-end electronics, toys, LED indicators |
Simple electronics, radios, calculators |
Household devices, low-heat applications |
Consumer electronics, industrial, automotive, aerospace, and multilayer PCBs |
G-10 is a thermosetting composite material made by compressing fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin together. It has high mechanical strength, good electrical insulation, and dimensional stability. Therefore, it is often used in industrial insulating boards, structural parts, tool handles, and other scenarios. In the early days of PCB manufacturing, G-10 material was also widely used.
However, G-10 does not have flame-retardant properties and does not meet flame-retardant standards such as UL94 V-0. This made it no longer applicable in most electronic products, especially in circuit boards that require large-scale production.
To solve this problem, the industry developed FR-4 material. It is an improved version based on G-10, with flame retardants added to the formula to give it flame-retardant capabilities and meet UL94 V-0 standards. Therefore, FR-4 PCB material gradually replaced G-10 and became the standard board in the modern electronics industry.
|
Category |
G-10 |
FR-4 |
|
Base Material |
Fiberglass cloth + epoxy resin |
Fiberglass cloth + flame-retardant epoxy resin |
|
Flame Retardancy |
Non-flame retardant, does not meet UL94 V-0 or similar standards |
High flame retardancy, meets UL94 V-0, suitable for most electronics |
|
Mechanical Strength |
High, suitable for structural applications |
Also high strength, suitable for both electronic and structural use |
|
Electrical Insulation |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
Thermal Performance |
Moderate, slightly lower heat resistance |
Better thermal stability, suitable for reflow soldering and high-temp processes |
|
Typical Applications |
Industrial insulation parts, mechanical components, knife handles, some custom PCBs |
Consumer electronics, communication devices, automotive electronics, multilayer PCBs |
Overall, FR-4 material outperforms G-10 in all aspects of performance, especially in terms of flame resistance, making it more suitable for use in various electronic products. G-10 material is currently mostly used in industrial structural applications where flame resistance is not required. Understanding the differences between these two materials can help engineers make the right selection based on project requirements.
FR-4 material is currently the most commonly used PCB substrate. Although it has some limitations, due to its stable performance, wide range of applications, and moderate price, FR-4 PCB board remains the preferred choice for most manufacturers.
When designing FR-4 PCB, several key aspects need to be considered: the thickness of the board, the layer structure, and whether there is good thermal management. These factors will directly affect the reliability and lifespan of the circuit board.
Understanding the properties of FR-4 material and comparing them with those of other materials can help in selecting a solution that better meets the requirements of the project.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
