Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > FPC Electronics: A Complete Guide to Flexible Circuits and Manufacturing
As electronic devices become smaller and lighter, the demand for flexible electronics is growing rapidly. Under this trend, flexible circuit boards have become a key technology. It is a flexible and lightweight circuit solution suitable for wearable devices, medical electronics, and aerospace systems.
This guide will provide a comprehensive introduction to FPC electronic technology. You will learn what FPC is, the main advantages of flexible circuits, the structure and materials of flexible printed circuit boards, how to design FPC, the production process, cost influencing factors, and why choosing PCBasic as a flexible electronics manufacturing partner is a wise decision.
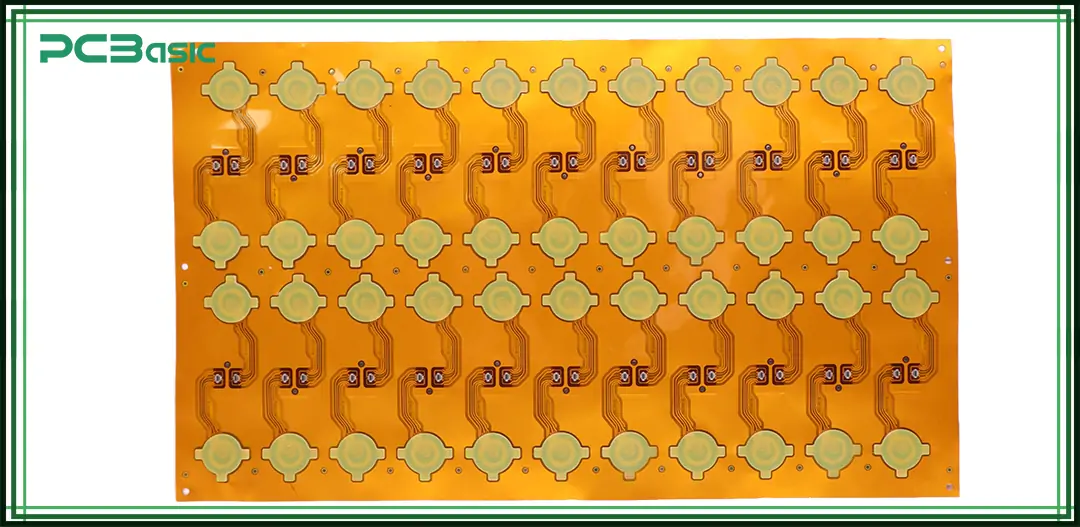

The FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a kind of flexible circuit board that can be bent. It is applicable to scenarios where space is limited or dynamic movement is required. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs that use FR4 material, FPCs are manufactured using flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester (PET).
FPC electronic products are very common in modern devices. It can reduce size, simplify the wiring, and support foldable or movable structures. For instance, flexible printed circuit boards are commonly used in the hinges of smartphones, medical sensors, and satellite modules. Although flexible printed circuit boards are often hidden, their function is crucial.
Common terms related to this technology include:
• Flex circuit
• Flexible circuits
• Flexible printed circuits
• FPC board
• Printed flexible electronics
The use of flexible circuits in electronic products has multiple practical and design advantages:
Space Saving and Lightweight
Flexible printed circuit boards can replace traditional bulky cables and connectors. This helps to reduce the size of the device and lower the overall weight, making the product thinner, lighter, and more compact, particularly suitable for portable devices.
Bendable and Supports Dynamic Movement
Flexible circuits can be bent, twisted and folded without breaking, making them highly suitable for products that require frequent movement or frequent flexing. For example, foldable mobile phones, wearable medical devices and cameras with rotating structures.
High Reliability
FPC electronics require fewer solder joints and connectors. Thus, the number of failure points also decreases. Even under repeated bending, it can still maintain excellent electrical performance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for long-term use and environments with high-reliability requirements.
3D Integration
FPC design can achieve a 3D layout. Circuits can be wrapped around the corners of equipment, installed on curved surfaces or in compact spaces, which helps optimize space utilization in complex assemblies.
For these reasons, flex electronics have been widely applied in consumer electronics, automotive electronics and medical devices, achieving greater design flexibility without sacrificing performance.
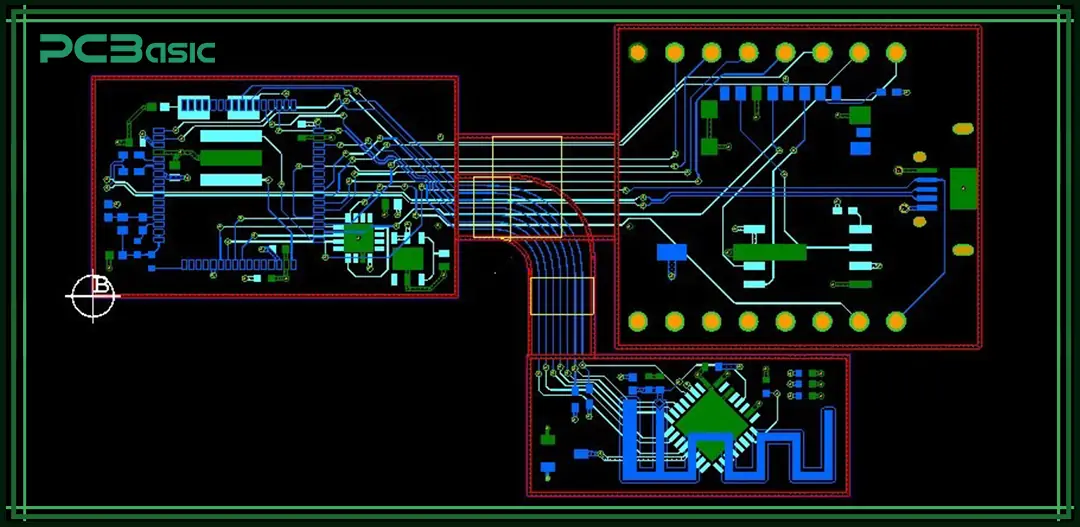
The performance of flexible circuit boards largely depends on the FPC material used. These materials have been specially designed to ensure that the circuit has good flexibility, heat resistance and electrical performance. The following are the main structure components of an FPC:
The base material is the main carrier of FPC and determines the flexibility and environmental resistance of the circuit. Common FPC materials include polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET). Among them, polyimide is more commonly used because it can withstand higher temperatures and has better mechanical strength, making it suitable for complex or highly reliable applications.
The conductive layer is usually made of copper foil because it has excellent electrical conductivity. It can be attached to the substrate by lamination or electroplating to form circuit traces.
Adhesives are used to bond the copper layer and the substrate together to ensure structural integrity. The coverlay (such as polyimide film) is laminated over the surface of the circuit, providing protection to prevent the circuit from being exposed to moisture, dust and mechanical damage while also offering electrical insulation.
According to application requirements, FPC boards can be designed with different layers. Common ones include:
Single-sided FPC: With only one layer of copper. It has a simple structure and low cost.
Double-sided FPC: Having two layers of copper connected by a through hole. It is suitable for circuits with more complex routing.
Multilayer FPC: Containing three or more copper layers, which can achieve more complex signal transmission and higher wiring density.
Selecting the correct FPC material and layer structure is of great significance for meeting product performance requirements, controlling costs, and enhancing the reliability and durability of flexible electronics.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Compared with traditional rigid PCBs, FPC design has many different requirements. As flexible circuit boards must withstand bending and deformation, special attention must be paid to mechanical structure, electrical performance and manufacturing feasibility during the design stage. The following are several key design elements:
1. Bending Radius
In FPC design, the layout of the bending area is very crucial. The specification of the minimum bending radius must be followed to prevent copper traces from cracking or breaking during flexing. Generally speaking, the thicker the copper foil, the larger the minimum bending radius required. When designing, the bending area should be set as far as possible in a position without components or through holes to ensure reliability.
2. Routing Strategy
The layout of conductors greatly affects the lifespan and performance of flexible circuit boards. To reduce stress concentration, traces should follow smooth curves and avoid sharp angles. When routing through bending zones, traces should be oriented perpendicular to the bend direction to avoid breakage. Avoid placing vias or pads in the bend area as well.
3. EMI Shielding
In high-speed or high-frequency applications, flexible printed circuits are prone to electromagnetic interference (EMI). To address this issue, shielding layers can be added to the design, such as metal layers or ground mesh structures. This effectively reduces signal interference and improves circuit stability and reliability.
4. Impedance Control
For RF or high-speed digital signal transmission, maintaining stable impedance is crucial. The trace width, dielectric thickness, and material type in flexible printed circuit boards all influence impedance. During design, the impedance must be precisely calculated using simulation tools, and manufacturing tolerances must be strictly controlled to ensure signal integrity.
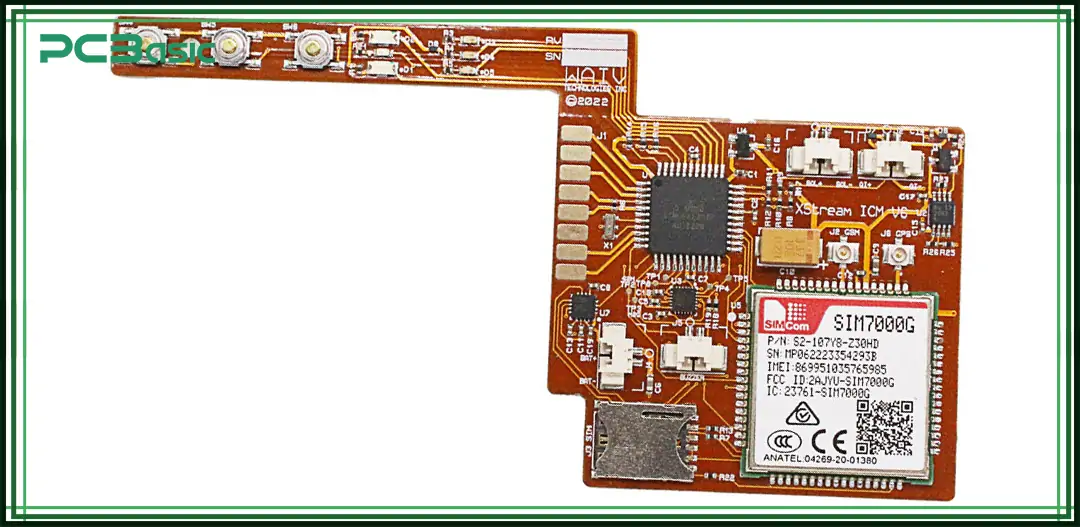
The flexible printed circuit board (FPC) manufacturing process is generally similar to that of rigid PCBs, but due to the soft and flexible nature of the materials, certain process steps must be specially adjusted. Below is a standard FPC manufacturing process, suitable for most application scenarios:
Before processing, flexible substrates such as polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) must be thoroughly cleaned and surface-treated. This removes dust, oil, and oxidation, improving copper adhesion and ensuring the long-term reliability and stability of the circuit.
Copper foil is laminated onto the substrate using a hot-press process. This can be done using adhesive-based (with glue) or adhesiveless (direct lamination) methods. The lamination method will affect the FPC’s thickness, flexibility, and heat resistance.
A photoresist (dry film or liquid) is applied to the copper layer. Then, UV exposure through a photomask is used to define the circuit pattern. After developing the image, the unprotected copper is chemically etched away, forming the required flexible circuit layout.
Mechanical drilling or laser drilling is used to create holes (vias) in the FPC. These holes are then plated with copper using chemical and electrolytic processes. This step creates electrical connections between layers, especially in double-sided or multilayer FPC boards.
A polyimide coverlay film is laminated over the finished circuit pattern using heat and pressure. This coverlay protects the circuit from dust, moisture, corrosion, and scratches while also providing electrical insulation.
The finished FPC is cut into its final shape using laser cutting or CNC routing based on the design outline. After shaping, the board goes through electrical testing to ensure proper connectivity. Visual inspection or AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) is performed to detect any open circuits, short circuits, or physical defects.
This complete flexible printed circuit manufacturing process enables the production of ultra-thin, lightweight, and high-density FPC boards. Thanks to their high reliability and flexible structure, FPCs are widely used in consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, and aerospace industries.
As a leading manufacturer in the FPC electronics industry, PCBasic provides one-stop flexible circuit board solutions, from design and development to mass production. With over 10 years of experience in technology and project management, we deliver efficient, professional services tailored to complex application needs.
1. Professional Engineering and Design Support
PCBasic has a skilled engineering team with more than 10 years of experience in FPC/PCB design. We offer complete design reviews and manufacturability optimization. In addition, we collaborate with PhD teams from top universities to promote continuous innovation in FPC design through industry-academia research.
2. Multi-site Manufacturing Capability
We operate multiple in-house factories in different regions. Our Shenzhen factory focuses on quick-turn small batches, while our Huizhou factory handles large-scale production. With advanced equipment, we ensure high precision and consistency in key processes such as trace width control via drilling and lamination.
3. High-Quality Material Assurance
We only use certified FPC materials, such as DuPont polyimide films and high-performance adhesives. These materials meet strict standards for reliability, flexibility, and heat resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications.
4. Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturing Capability
PCBasic specializes in producing rigid-flex PCBs, enabling seamless integration of rigid circuits and flexible printed circuits. This is especially suitable for compact, high-performance end products.
5. Certifications and Industry Recognition
We are recognized as a National High-Tech Enterprise and hold certifications including ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and UL. As a member of the IPC association, PCBasic also holds more than 20 patents related to quality inspection and production management systems. Our products are widely used in the automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.
6. Rapid Prototyping and Global Delivery
We support fast FPC prototyping and operate our own stencil and fixture factory, capable of delivering stencils within 1 hour. Our intelligent electronic components warehouse ensures a stable supply of original and genuine parts. With one-click BOM import and real-time quotation tools, we ensure efficient collaboration and on-time global delivery.
Whether you are developing next-generation wearable devices, medical sensors, or flexible printed circuit boards for industrial control, PCBasic is ready to provide reliable technical support and high-quality manufacturing—helping your project succeed with speed, precision, and confidence.
FPC electronics has completely transformed the way we design and integrate circuits in modern devices. By gaining a deep understanding of FPC, the advantages of flexible circuits, suitable FPC materials, and the manufacturing process of flexible printed circuits, engineers and product developers can achieve more innovative solutions.
When choosing a partner for your next flexible circuit project, please trust PCBasic's extensive experience in FPC design, flexible electronics manufacturing and assembly.
Learn about our services immediately and explore how to turn your flexible printed circuit board concept into a high-quality real-world product.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
