Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Solder Joint – Guide to Quality, Defects, and Best Practices
In electronic manufacturing, a solder joint is a crucial part that connects components to circuit boards and is also the foundation for ensuring the reliable operation of equipment. Whether it is the daily repair of simple wire joints, the soldering of circuit boards for student projects, or the precise assembly in high-end medical, automotive, and aerospace systems, the quality of solder joints will directly affect the performance, stability and lifespan of the products. A good solder joint not only provides a firm mechanical support, but also ensures the stable conduction of current. By contrast, the occurrence of solder joint defects may lead to poor contact, short circuit, rework, and even cause serious system failure.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to solder joints, systematically explain the types of solder joints, the characteristics that a good solder joint should possess, common solder joint defects and their causes, as well as detection and testing methods. And in practice, what we can do to continuously obtain reliable and aesthetically pleasing solder joints through good habits and process control.
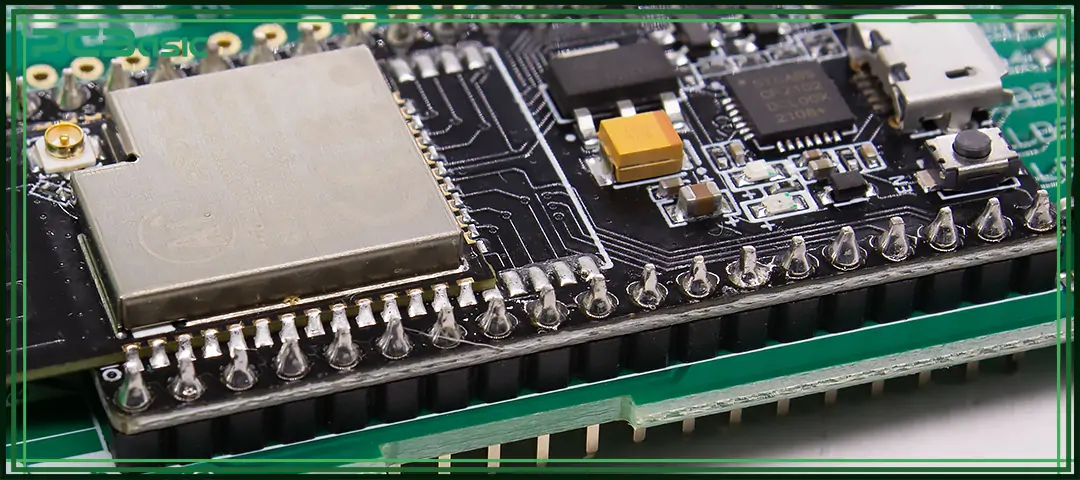
A solder joint is the place where melted solder is used to firmly connect the leads of components, wires or pads to the printed circuit board (PCB) or other conductors. It has two main functions:
Mechanical connection: Fix the components firmly and prevent them from moving.
Electrical pathway: Let current flow smoothly.
Without high-quality solder joints, even the most advanced circuits cannot function properly. For this reason, soldering has always been one of the most important processes in electronic assembly. Whether it is wire joints in cables or solder joints on PCBs, the basic requirements are the same: firm bonding, good solder wetting, and consistent quality.
The types of solder joints vary depending on the assembly method and the type of component.
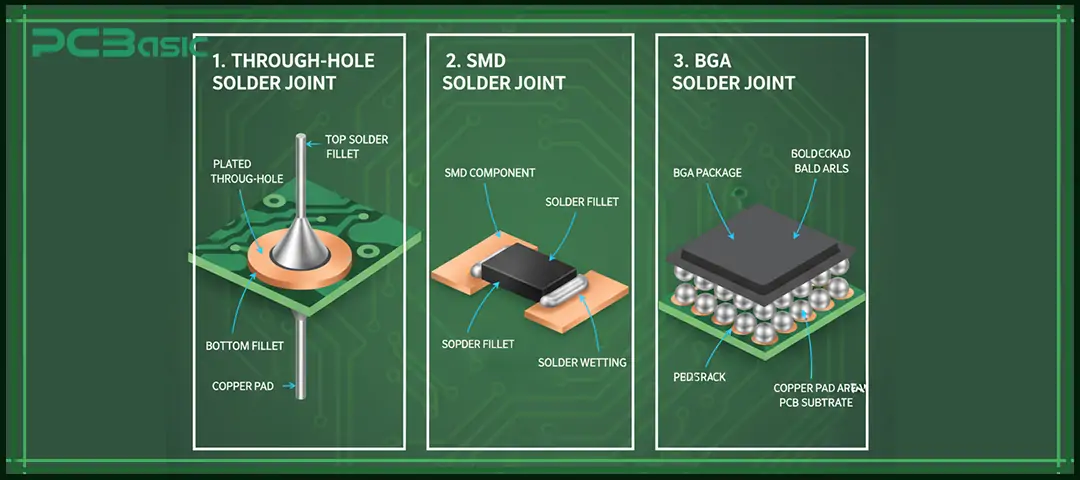
Through-hole solder joints refer to the solder joints formed when the leads of components pass through the holes on the PCB and are soldered on the other side. This type of solder joint has high mechanical strength and is very solid and reliable, so it is often used in connectors, large capacitors, transformers and other applications that need to withstand significant stress. However, such solder joints often have the problem of excess solder, which can easily lead to solder buildup or uneven fillets.
Surface mount solder joints are created in surface mount technology (SMT), where the terminals of components are directly soldered onto the PCB pads, usually accomplished through reflow soldering processes. This type of solder joint is small in size and can achieve high-density circuit design, making it highly suitable for modern electronic products. However, it is also prone to some defects, such as tombstoning, bridging and cold solder joints.
In certain applications, there are several particular solder joints that need attention. For instance, ball grid array (BGA) solder joints, which are hidden at the bottom of the package, must rely on X-rays to inspect their quality. The joint spacing between QFN and LGA is extremely small, and the precision requirements for the soldering process are very high. Although wire joints have a simple structure, they are very crucial in power connections and wire harness assembly.
High-quality solder joints can be identified by their appearance and structure.
Features of a Good Solder Joint
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Shiny appearance |
Indicates proper wetting and even cooling, showing stable quality. |
|
Smooth and continuous surface |
Flat and uniform, free from cracks, voids, or other irregularities. |
|
Proper fillet shape |
Concave shape around the component lead or pad, natural and well-formed. |
|
Adequate solder |
Enough solder to ensure a strong bond, but not excessive or piled up. |
|
Strong mechanical bond |
Withstands stress and vibration during use without loosening. |
|
No solder bridges |
Prevents short circuits between adjacent pins and ensures electrical safety. |
|
Consistency across solder joints |
All joints look uniform, reflecting professional soldering work. |

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
|
Defect Type |
Visual Feature |
Common Cause |
Risk |
|
Cold Solder Joint |
Dull, grainy surface, weak bond |
Inadequate heating, poor wetting |
Electrical failure, open circuits |
|
Solder Bridges |
Excess solder connecting adjacent pads |
Too much solder, poor stencil design, uncontrolled reflow |
Short circuits, component damage |
|
Insufficient Solder |
Pad not fully covered, small joint |
Too little solder, insufficient flux, contaminated pad |
Weak bond, intermittent connection |
|
Excess Solder / Solder Blob |
Bulky, ball-like joint |
Excess solder deposition, manual error |
Mechanical stress, possible bridging |
|
Head-in-Pillow (BGA) |
Ball and pad not fused, looks like a “pillow” |
Warpage, contamination, misalignment |
Open joint, BGA failure |
|
Voids and Cracks |
Holes or cracks inside or on the surface of the joint |
Entrapped gas, poor reflow profile, thermal stress |
Long-term reliability issues, risk of failure |

To obtain a high-quality solder joint, we need to pay attention to some key details during the soldering process. First of all, choose the appropriate soldering iron tip and make sure the temperature control is correct. If the temperature is too low, the solder cannot melt fully. If it is too high, it may damage components or pads.
Secondly, it is necessary to use sufficient flux, which can enable the solder to better wet the metal surface and form a strong joint.
Before heating, components and wires should be placed in position to prevent shifting during the soldering process. When heating, let the solder flow smoothly and naturally and be evenly distributed instead of pushing it hard. During the cooling period of the solder, it must be kept stable. Do not shake or touch the solder joints; otherwise, it is easy to cause a cold or weak solder joint. After soldering, carefully inspect and remove any excess solder to avoid solder buildup or solder bridges.
For wire joints, the insulation layer should be removed before soldering, and the wires should be neatly twisted and then tinned. Only in this way can the solder joints be firm and reliable.
The final step is cleaning. Use isopropyl alcohol to remove the residual flux on the surface of the solder joints to prevent corrosion and extend the service life of the solder joints.
As long as the correct tools are used, the basic skills are mastered, and sufficient patience is maintained, even beginners can learn to make professional-grade solder joints that are bright in appearance and solid in structure.
To ensure the long-term stability of the product, high-quality assembly must conduct comprehensive testing and inspection of all solder joints.
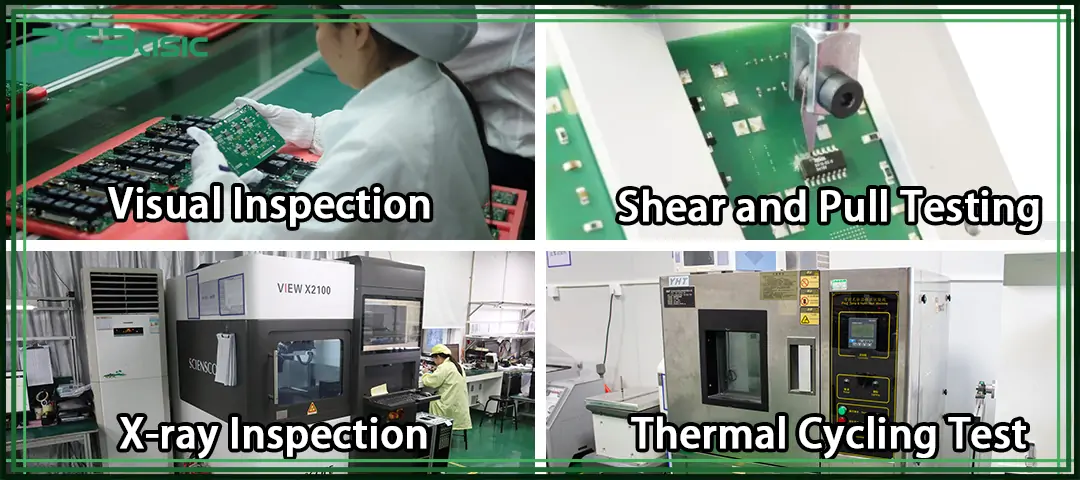
This is the most fundamental step in checking solder joints. By observing through a magnifying glass or microscope, we can directly see whether the solder joints are bright, whether the surface is smooth, and whether there are defects such as cracks, voids or solder bridges. Although this method is simple, it can effectively identify the most common issues.
For hidden solder joints that are invisible to the naked eye, such as those in BGA, QFN and other packages, X-rays are needed for detection. X-rays can penetrate the package and reveal whether there are voids, incomplete fusion or misalignment inside the solder joints, which is crucial for high-density assembly.
This is a method for detecting the mechanical strength of solder joints. Tensile or shear force is applied to the solder joint through dedicated equipment to measure whether it can withstand stress. If the solder joint is too fragile, it may detach under vibration or impact.
Circuit boards will experience temperature changes during use. Thermal cycling test simulates this environment, constantly switching the PCB between high and low temperatures to check whether the solder joints have cracked or failed due to thermal expansion and contraction. This can evaluate the long-term durability of solder joints.
IPC Standards (IPC-A-610):
This is an internationally recognized quality standard for electronic assembly, which provides detailed regulations on the appearance, size, and defect range of solder joints. By comparing with the IPC standard, we can determine whether a solder joint meets the industry requirements.
Through these inspection methods, whether it is a wire joint or a PCB solder joint, it can be ensured that it meets industrial-grade reliability standards, thereby ensuring the stable operation of the entire electronic product.
Although solder joints may seem small, they are the pillars of every electronic product. By understanding the types of solder joints, learning to identify high-quality solder joints, and avoiding common solder joint defects, both manufacturers and enthusiasts can ensure long-term reliability.
High-quality soldering requires the right materials, equipment and process control. From the wire solder joints in simple cables to the hidden BGA solder joints in advanced electronic products, the principle remains the same: clean, bright, firm and consistent.
In short, mastering the technology of solder joints means grasping the core of electronic technology.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
