Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCB History – A Brief Introduction to the Development of PCBs
The PCB is the core of electronic devices. Before the emergence of circuit boards, engineers commonly used point-to-point wiring to build circuits. This method was cumbersome, inefficient, extremely unstable and difficult to expand. The produced devices were often large in size and prone to damage. It was not until the advent of printed circuit boards (PCBs) that everything changed.
The appearance of circuit boards completely transformed the face of the electronics industry. Over the past few decades, PCBs have evolved from the initial single-sided PCBs to more complex forms such as multilayer PCBs and flexible PCBs. Each technological upgrade not only brought advancements in design and materials, but also promoted the rapid development of industries such as communication, computers, automobiles, and aerospace.
Understanding the history of PCBs is not merely a nostalgic look back. It enables us to see more clearly how circuit boards have gradually become the cornerstone of modern technological innovation. Perhaps, many people do not know that every electronic device, such as a mobile phone, has a circuit board. Next, let's first understand what a circuit board is. (At the end of the article, we will provide a link to the article on the basics of circuit boards, and we welcome you to keep learning at any time.)
PCB is a flat circuit board that achieves mechanical support and electrical connection for electronic components through thin copper foil traces. We can consider PCB as the "skeleton" and "nerve network" of electronic devices. On the one hand, it supports chips, resistors, capacitors and other components, keeping them in the right positions; on the other hand, it connects these components through copper foil traces to ensure smooth transmission of power and signals. It can be said that without PCBs, electronic components cannot form a complete circuit system.
If we explain the definition of a circuit board in simple terms, it is the green (sometimes blue or black) board that we see inside computers, mobile phones or televisions. Various components such as chips, resistors, capacitors and connectors are fixed on it. These components can function only when they are interconnected through copper traces. A standard electronic circuit board usually consists of a substrate, copper layers, solder mask layers and silkscreen layer... These layers are essential parts of the PCB and their combination makes the printed circuit board both durable and reliable.
The development history of PCB reveals how electronic technology has evolved from fragile, handcrafted prototype wiring to reliable, mass-producible systems. In the history of PCB, each milestone has directly driven the emergence of new applications. For example, early military radio equipment; in the 1950s, consumer electronics and early computers. Subsequently, the emergence of multilayer circuit boards made high-density computing systems possible, while modern HDI and flexible PCBs have driven the development of smartphones, medical implant devices, and aerospace technology.
Understanding the history of PCB is crucial for the entire electronic industry chain. For manufacturers, understanding the history of PCB helps them grasp the direction of process upgrading and quality control. For procurement and supply chain personnel, being familiar with the development history of PCBs can help them explain the huge differences in price, delivery time, and reliability of different types and processes of circuit boards. This can support more reasonable decisions. For customers, understanding the development of PCB helps them weigh performance, volume, and cost in product design and selection. PCB history is an important reference for industry decisions, educational research, and product innovation. Now, let's learn about the development history of PCB!
It has been over a century since the early prototype of the circuit board first appeared.
The period from 1850 to 1900 was when the early prototypes of circuit boards emerged. Engineers soldered components one by one using wires, creating the first electronic boards. This method was not only bulky and prone to errors, but also difficult to maintain and replicate. During this stage, there was an urgent need for a more efficient and reliable circuitry platform.
From 1900 to 1950, the concept of circuit boards gradually took shape. The earliest concept of circuit boards was proposed in 1903. In 1927, Charles Ducas applied for a patent for printed wiring, which was an important milestone in the history of PCB development. The real breakthrough occurred in 1936 when Paul Eisler manufactured the first functional PCB while designing a radio. This gave the world its first intuitive understanding of what a PCB is. In 1948, PCB technology was made available to the civilian sector. During World War II, it was widely used in military radios and radar equipment. Many years later, Eisler was officially recognized as the inventor of printed circuit boards. During this period, the basic prototype of circuit boards emerged: a combination of insulating substrate, conductive copper layer, and protective coating.
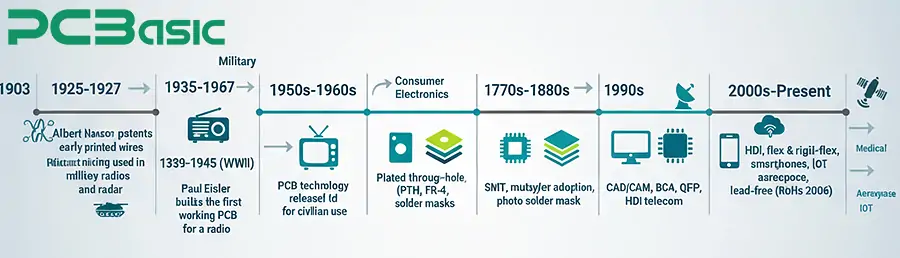
From 1950 to 2000, the second half of the 20th century, PCB entered a period of rapid development. In the 1950s and 1960s, single-sided PCB was commercialized. Additionally, the birth of integrated circuits (ICs) enabled the miniaturization and mass production of electronic products. Circuit boards began to be widely used in televisions, radios, and early computers. From the 1970s to the 1980s, multilayer circuit boards became popular and a solder mask layer was introduced. This change significantly enhanced the reliability of circuit boards. In the 1990s, with automated production and strict quality standards, electronic boards achieved low costs and high consistency, promoting the popularity of personal computers, mobile phones, and consumer electronics.
From 2000 to the present, HDI technology has met the demands of smartphones and wearable devices for miniaturization and high performance. Flexible circuit boards and rigid-flex combined boards have made complex three-dimensional installations possible, playing a significant role in medical implants, automotive electronics, and aerospace. At the same time, environmental regulations (such as RoHS, lead-free HASL) have prompted manufacturers to adopt greener processes.
|
Era / Year |
Key Breakthrough |
Applications / Notes |
|
1903 |
Albert Hanson patents early “printed wires” on insulating substrate |
Experimental circuit prototypes |
|
1925–1927 |
Charles Ducas patents printed wiring methods (precursor to printed circuits) |
Early printed circuit concepts |
|
1936 |
Paul Eisler builds the first working PCB while designing a radio in the UK |
First functional PCB |
|
1939–1945 (WWII) |
Printed wiring used in military radios and radar, improving reliability and size |
Military communication, radar |
|
1948 |
PCB technology released for commercial civilian use |
Consumer electronics, communication |
|
1950s–1960s |
Plated through-hole (PTH) enables double-sided & multilayer PCBs; FR-4 and early solder masks appear |
Radios, TVs, early computers |
|
1970s–1980s |
Surface-mount technology (SMT) emerges; multilayer adoption expands; photo-imageable solder mask becomes common |
Industrial control, telecom, personal computers |
|
1990s |
CAD/CAM tools mature; BGA & QFP packaging; automated reflow; early HDI adoption in telecom |
PCs, household appliances, portable electronics |
|
2000s–Present |
Mass adoption of HDI; flexible & rigid-flex surge with smartphones/wearables; RoHS (2006) drives lead-free processes |
Smartphones, IoT, medical devices, aerospace |
Every advancement in PCB technology brings about new design and manufacturing methods. Each type plays a significant role in the modern electronics industry.
According to their structure and application requirements, PCBs can be classified into the following categories:
Single-Sided PCB: A single-sided PCB is the earliest commercially available PCB. It has only one layer of copper foil and all components are installed on the same surface. Although it has simple wiring and limited functionality and complexity, it is still widely used in low-cost electronic products, toys, and simple household appliances to this day.
Double-Sided PCB: As electronic devices became more complex, double-sided circuit boards were developed. These circuit boards have copper layers on both sides of the substrate, allowing components to be placed on both sides and connected through vias between the upper and lower layers of circuits. Compared to single-sided PCBs, they can carry more components and have more complex circuits, making them an important choice for computer peripherals, power amplifiers, and industrial control equipment.
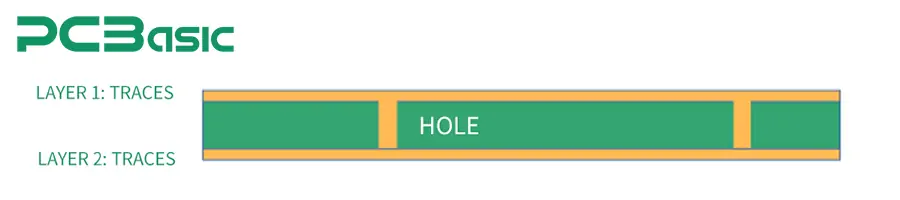
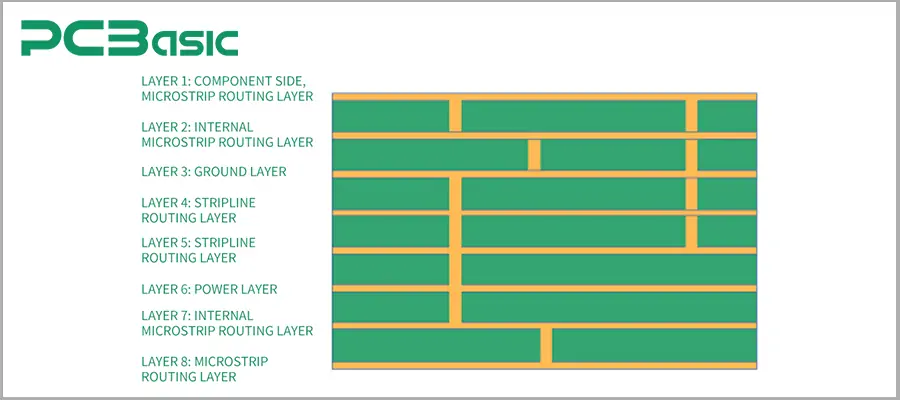
Multilayer PCB: Multilayer circuit boards represent a significant breakthrough in the history of PCB development. By stacking multiple layers of copper foil and insulating layers within the substrate, multilayer boards can achieve high-density wiring, ensuring signal integrity and electromagnetic compatibility. Today's smartphones, laptops, and high-performance servers almost all rely on multilayer PCBs to carry complex circuits.
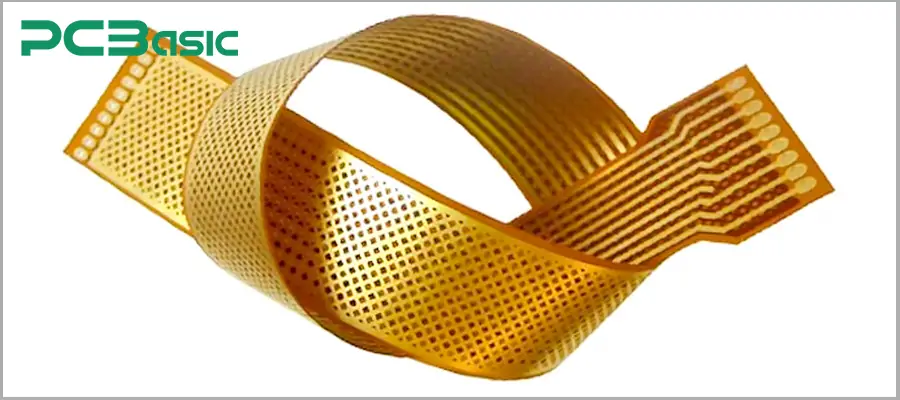
Flexible PCB and Rigid-Flex PCB: With the development of wearable devices, automotive electronics and aerospace, flexible PCBs and rigid-flex circuit boards have become increasingly popular. This type of PCB demonstrates the new directions that circuit boards have taken in the 21st century.

After a century of development, today's PCB has far exceeded the prototype invented by Paul Eisler back then. In terms of design, manufacturing, and assembly capabilities, modern circuit boards can demonstrate the maturity and efficiency of the electronics industry. Electronic circuit boards have become an indispensable core platform for various devices.
|
Category |
Technology |
Description |
|
PCB Manufacturing Capabilities |
Multilayer PCBs |
Can reach 4–32 layers or more; stacked design enables high-speed signal transmission and complex circuit layouts. |
|
HDI PCBs |
Uses laser microvias, blind vias, and buried vias to greatly increase routing density; essential for smartphones and high-performance computing devices. |
|
|
Flexible & Rigid-Flex PCBs |
Made from polyimide and other flexible materials; can bend and fold; widely used in wearables, automotive electronics, and medical implants. |
|
|
Special Materials & Surface Finishes |
No longer limited to FR-4; also includes PTFE, Rogers high-frequency materials, and metal substrates (e.g., aluminum). Surface finishes such as ENIG, ENEPIG, OSP, and lead-free HASL ensure solderability and long-term reliability. |
|
|
PCBA Capabilities |
SMT |
High-speed pick-and-place machines install tens of thousands of components in a short time; supports ultra-small packages like 01005. |
|
THT |
Suitable for components requiring high mechanical strength, such as connectors, inductors, and high-power devices. |
|
|
Automated Inspection |
Includes SPI (Solder Paste Inspection), AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), X-Ray inspection, and functional testing to ensure every electronic board meets design requirements. |
|
|
|
Full Process Automation |
From placement, soldering, to testing and packaging, modern factories use MES systems and smart manufacturing to achieve efficient and traceable production. |
Compared with the early PCB history, today's manufacturing capabilities have not only enhanced the reliability and performance of circuit boards, but also provided a platform for future innovation. PCB and PCBA are the pillars of the electronics industry and are the core driving forces behind the continuous development of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and sustainable technologies.
From the early bulky point-to-point wiring to the current advanced HDI and flexible PCBs, the development of PCBs is also the progress history of the electronics industry. Modern PCBs and PCBA not only ensure the high reliability and performance of equipment, but are also constantly driving innovation in fields such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and aerospace.
Learn more:
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
