Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Wire Harness Assembly Explained: Process, Design, and Applications
As modern electronic systems continue to evolve towards miniaturization, complexity and high performance, the efficiency of internal wiring has become particularly important. Wire harness assembly is the core component in this structure. It is responsible for properly organizing and fixing numerous wires and cables to ensure that they can reliably transmit power and signals for automobiles, aircraft, industrial equipment and consumer electronics.
Wiring harness assembly is not merely about bundling cables together. Its function is to simplify the assembly process, reduce human errors, and enhance the safety and stability of electronic devices.
This article will introduce what wire harness assembly is, how it is designed and manufactured, and why it is indispensable in multiple high-demand industries. This article will provide a detailed explanation from wiring design, prototype development, to the complete wiring harness assembly process, electrical testing and material selection, to help you fully understand this key technology.
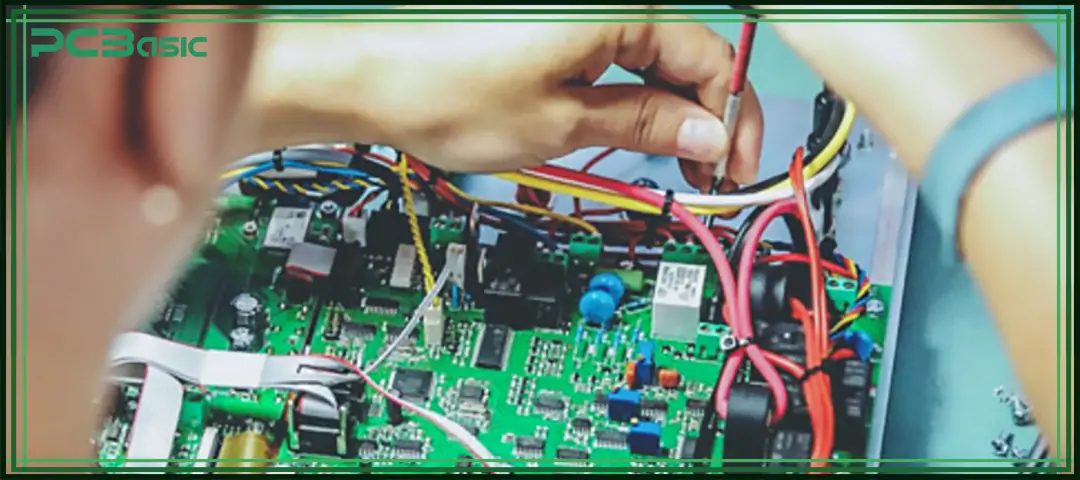
Wire harness assembly, also known as cable harness assembly, wiring assembly or electrical harness, is an assembly method that orderly combines multiple wires or cables together, with the aim of reliably transmitting electricity or signals in an electronic system. These wires are uniformly organized and fixed by materials such as cable ties, sleeves, corrugated tubing, heat shrink tubing or tapes to form a compact wire assembly, which is convenient for installation, saves space and reduces the risk of wiring errors.
In industrial applications, wire harness assembly is often used to integrate complex internal wiring into a single complete unit, enabling installers to install all wires at one time, thereby enhancing production efficiency. It also helps to enhance the reliability and safety of the equipment and provides convenience for future maintenance.
Carry current or signals. Usually made of copper or aluminum. Choose a size based on current and flexibility needs.
Link wires to devices or PCBs. Ensure stable connections and easy maintenance.
Attached to the wire ends to connect with the connectors. Common types: blade, ring, pin.
Heat-shrink tubing, tape, etc., protect wires from damage, moisture, and short circuits.
Use colors, tags, or barcodes to identify wires and reduce errors.
A guide board based on the design to help route wires neatly and correctly.
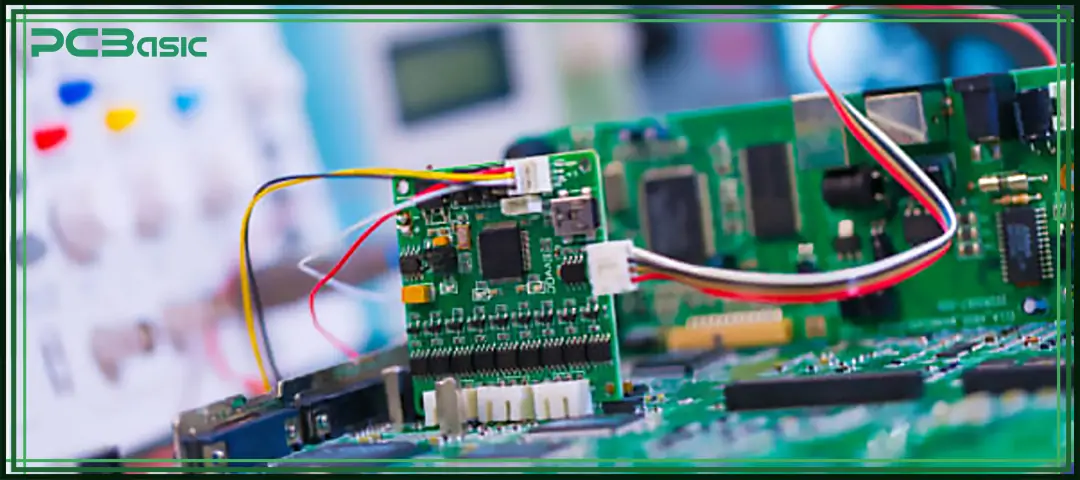
Wire harness assembly can be classified into various types depending on the usage environment and equipment requirements. Each type has its specific structural design and performance standards to meet the functional and reliability requirements of the corresponding industry. The common types are as follows.
Automotive wire harnesses are mainly used in vehicle internal systems, such as dashboards, lighting systems, sensors, and engine control units. This type of wiring harness needs to have good heat resistance, vibration resistance and reliable electrical connection to ensure the normal operation of the vehicle under various working conditions.
Aerospace wire harnesses are applied in aircraft, drones, and spacecraft. Such wiring harnesses must be capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, intense vibrations and electromagnetic interference. They must comply with aviation-grade standards to ensure flight safety and system reliability.
Medical equipment harnesses are used in medical imaging equipment, vital sign monitors, surgical equipment and more. The wiring harness is required to have high precision, low noise, strong anti-interference ability, and comply with the relevant hygiene and safety standards for medical equipment.
Widely used in automation systems, CNC machines, robotics, conveyor systems, and other industrial applications, this type of wiring harness usually needs to withstand harsh working environments such as mechanical stress, bending, oil exposure, and high temperatures.
Commonly found in household appliances such as televisions, laptops, air conditioners, and washing machines, they are mainly used for the electrical connections of various functional modules inside. They require clean wiring layout, flexibility, and compact size, and are often designed as custom wiring assemblies.
Each custom wire harness assembly must be precisely designed based on the current requirements, temperature and humidity environment, durability requirements and installation space in the application scenario to ensure the stable operation of the electrical system and a reasonable structural layout.
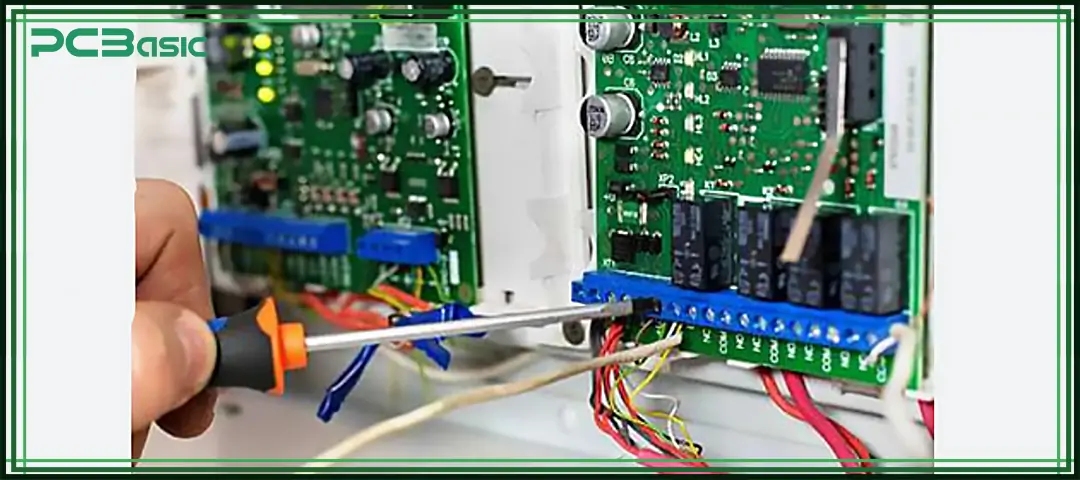

Building a wire harness assembly is a standardized and detailed process that usually includes several steps. Each step requires high precision and strict procedures to ensure the final product has good electrical performance, mechanical strength, and environmental durability. Below is a typical wire harness assembly process explained in plain terms:
Design is the first step. Engineers create electrical schematics and wiring diagrams based on how the equipment will be used. The design includes current levels, wire lengths, wire gauge, insulation materials, connector positions, and routing paths. All this information is laid out on a wire harness assembly board, which is used as a reference during production. The design also considers factors like heat dissipation, safety, ease of manufacturing, and available space.
Before mass production, a prototype is made. Engineers test its electrical performance and structural layout to check if the design works well. If any issues are found, the design can be improved. Prototyping helps avoid errors in later stages and increases the overall reliability of the cable and harness assembly.
Using automated cutting machines, wires are cut to the required lengths according to the diagram. Each wire is labeled or marked for easy identification. Then, the insulation at both ends of the wire is stripped to expose the metal core, making it ready for terminal crimping. Accurate length and clean preparation are important for the quality and performance of the wire harness assembly.
Stripped wires are crimped with terminals using either manual tools or automated equipment. After crimping, wires are inserted into the right connector or module according to the wiring diagram. Good terminal crimping is essential for stable electrical connections, especially in high-vibration environments like cars.
Once wires are ready, workers place them on the wire harness assembly board as per the design. The wires are routed, branched, and fixed in place. After wiring, protective materials like heat shrink tubing, tape, and sleeves are applied to form a neat and compact wire assembly. This step improves installation efficiency and makes future maintenance easier.
After the harness is assembled, electrical testing is done. This includes continuity tests, insulation resistance checks, and short-circuit detection. These tests make sure there are no loose connections, miswires, or open circuits. In industries with strict requirements like automotive or medical, additional high-voltage or interference tests are also performed to ensure the harness works reliably in harsh conditions.
Once the harness passes electrical tests, a final quality inspection is carried out. This includes checking appearance, measuring dimensions, and confirming structural integrity. In critical fields like aerospace and automotive electronics, extra tests like thermal cycling, vibration simulation, and aging tests may be added to ensure every electrical harness meets industry standards and works reliably over time.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Although cable assembly manufacturing has made significant progress, most wire harness assemblies still rely heavily on manual work.
In traditional assembly, workers manually route wires through sleeves and arrange them according to the wiring diagram. When the harness has branches or junctions, workers use tape to secure them by hand. If a terminal needs to connect multiple wires, it must be crimped manually. Once the wires are prepared, they are inserted into the connectors one by one. These tasks are simple but require skilled workers to ensure consistent quality.
Some repetitive steps have already been semi-automated. For example, wire cutting and stripping are done using machines, which are fast and precise. Terminal crimping can also be done with automated tools to improve efficiency and consistency. In harnesses with repetitive layouts, wire insertion can be partially automated. Soldering and wire twisting are often performed using handheld tools.
However, because custom wire harness assemblies are complex and vary in design, many steps still require manual work. Especially in small- or medium-volume production, manual assembly remains the most effective and flexible method.
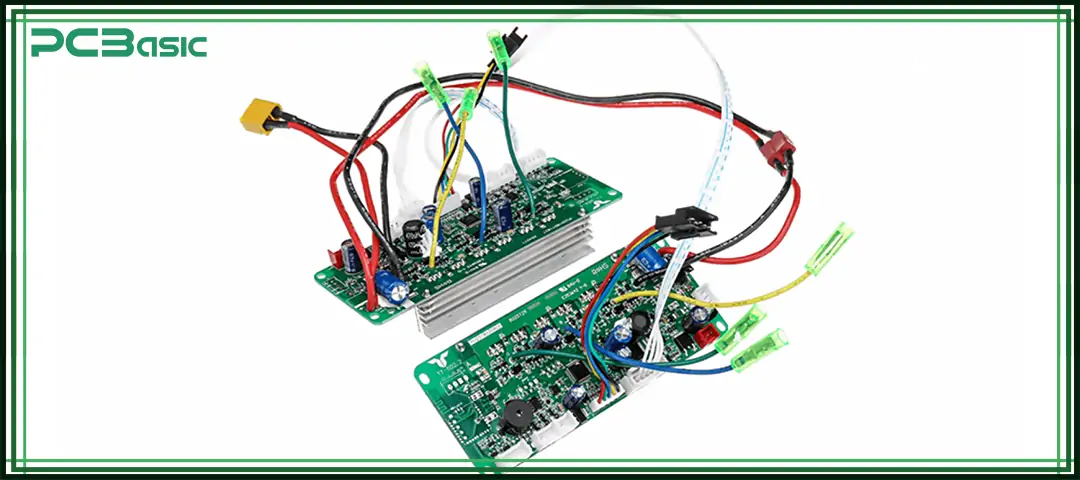
The reliability and service life of a wire harness depend on whether the materials used are suitable. The choice of conductors and insulation materials directly affects the wiring assembly’s electrical performance, mechanical strength, and ability to handle different environments.
Conductors are the core of the wire harness, responsible for carrying current or signals. Two common conductor materials are:
Copper: Copper offers excellent conductivity and is the most commonly used conductor. It’s flexible, easy to bend, and can carry larger currents. It’s ideal for most electronic devices.
Aluminum: Although it has lower conductivity than copper, aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective. It’s often used in products where weight reduction is important, such as automotive or aerospace wire harnesses.
Insulation materials cover the conductors and protect them from short circuits, leakage, and environmental damage. Different materials are used for different working conditions:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Commonly used for indoor or general-purpose wire harnesses. It’s inexpensive, flexible, and offers basic flame resistance.
Teflon (PTFE): Offers excellent heat and chemical resistance. It’s used in high-temperature or corrosive environments, ideal for industrial or special-purpose equipment.
Polyethylene (PE): Known for its strong moisture resistance. It's used in outdoor or humid environments, such as air conditioners or outdoor control panels.
Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Stronger and more heat-resistant than standard PE. It’s suitable for demanding environments that require durability and mechanical strength.
Santoprene: A thermoplastic elastomer that is soft, abrasion-resistant, and UV-stable. It’s commonly used in cable harness assemblies that are exposed to outdoor conditions or physical wear.
In summary, selecting the right conductors and insulation materials not only improves the wire harness’s safety and durability but also ensures stable performance across different environments. Proper material selection is the foundation of good wire harness design and manufacturing.
Wire harness assembly is not just about bundling a few wires together — it’s a key part of electronic and electrical systems. To produce a high-quality harness, every step — from design and prototyping to manufacturing and testing — requires professional engineering, the right materials, and stable processes.
As electronic devices demand more intelligence, smaller size, and higher reliability, wire harness assemblies become even more important. Whether it’s in automotive dashboards, aerospace systems, or industrial robots, a reliable cable and harness assembly is essential to ensure safe and stable performance.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
