Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > A Comprehensive Guide to Electronics Manufacturing Process
Electronics manufacturing refers to the complete process of transforming raw components into fully functional electronic devices. The entire process covers multiple links from product design, prototype development, component procurement, to electronic components assembly and final testing. In modern electronic manufacturing, manufacturers use automated systems and advanced technologies to achieve high-precision assembly of electronic parts. Whether it is consumer electronics manufacturing, industrial control systems, or medical equipment, the goal is to ensure high quality and high reliability in every link.
Overall, electronics manufacturing is not merely the process of manufacturing electronic products. It is a process that integrates innovation, automation and precision craftsmanship to build reliable technology for modern life. Now, let's take a deeper look at the electronic manufacturing process.
The electronic manufacturing process involves multiple key steps. The following is a detailed introduction we conclude to the entire electronic manufacturing process:
The electronic manufacturing process begins by defining the product’s functions, performance goals, and cost strategy. Subsequently, engineers select and evaluate the main control chip and key components, and used EDA software to complete the schematic diagram and PCB layout design.
After the design is completed, manufacturability analysis can be conducted. Then, the circuit board structure can be optimized to adapt to the mass production process. Before mass production, we need to first make a small batch of prototype boards and complete the assembly of components and the debugging of prototypes. This step is used to verify the function of the circuit design and confirm the feasibility of the production process. After that, the engineering team optimized the design based on the feedback and confirmed the final version. This stage determines the function, size and structure of the final product and is the foundation of the entire electronics manufacturing process.
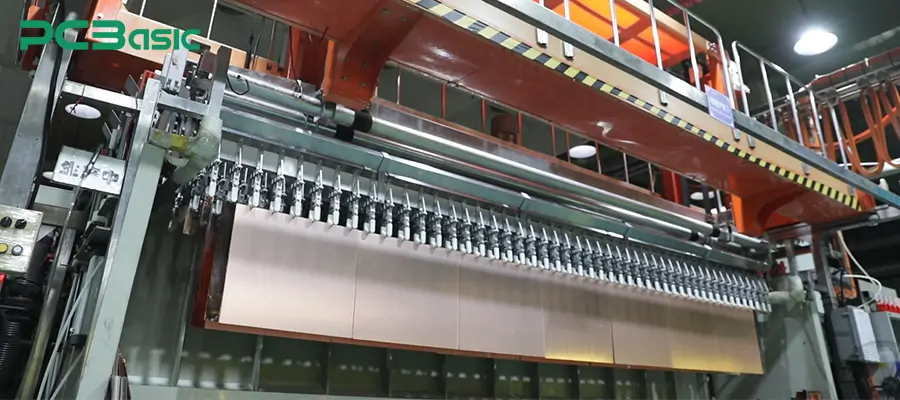

After the design is confirmed, the PCB manufacturing stage begins. In this stage, the design will be transformed into a physical circuit board, which is the carrier of electronic components. According to product requirements, rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs or rigid-flexible PCBs can be selected to adapt to different structures and application scenarios. The PCB manufacturing involves key processes such as pattern transfer, etching, drilling, electroplating, lamination, solder mask printing and surface treatment. The number of layers of a PCB, the type of board, the thickness of copper, and the design of vias will all affect the electrical performance and reliability of the product.
The output of this stage will be directly used for the subsequent component assembly, so manufacturing accuracy and quality control are particularly important.
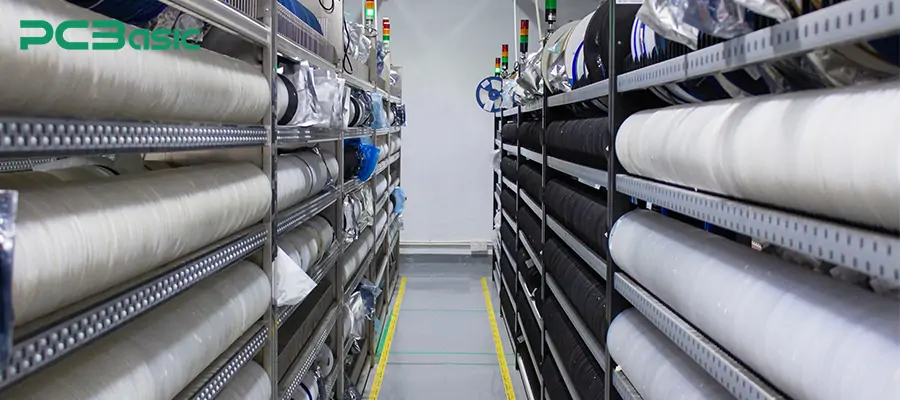

At the stage of PCB prototyping or mass production preparation, the manufacturer will start to purchase components based on the BOM list output by the design. This includes active components (such as ICs, crystal oscillators, modules) and passive components (such as resistors, capacitors, inductors), etc.
Reliable components suppliers are crucial for the procurement of components. When purchasing, it is necessary to ensure that the components are genuine products from the original factory and have good traceability. At the same time, it is necessary to carry out overall management based on factors such as delivery dates, inventory status, and life cycles to prevent the risk of material shortage or production suspension. Component sourcing directly impacts both delivery schedules and product quality, serving as the critical link between design and production. High-quality components are the key to ensuring the long-term reliability of the product.
After the PCB manufacturing and material preparation are completed, the PCB assembly manufacturing stage begins. This stage mainly includes two major processes: surface mount technology (SMT) and through-hole mounting technology (THT).
SMT precisely places micro-components on the surface of a PCB through a placement machine and then completes the soldering through reflow soldering. It is suitable for most modern electronic products. THT involves inserting components with pins into preset holes and fixing them through wave soldering. It is often used for high-current and large-sized devices. According to the product structure and functional requirements, SMT and THT can be used separately or in combination. The accuracy and stability of the mounting process will directly affect the overall performance and yield of the machine.
After the components are mounted or inserted, they enter the crucial soldering process stage. For SMT components, reflow soldering is usually adopted. The solder paste is melted in a precisely temperature-controlled reflow oven to form reliable solder joints. THT components, on the other hand, use wave soldering, allowing liquid tin waves to pass through the bottom of the PCB to achieve overall soldering of the pins.
In addition, the printing quality of solder paste is also of vital importance. Usually, laser steel mesh is used for precise printing to ensure uniform solder paste volume and avoid problems such as solder bonding or false soldering.
High-quality soldering techniques are a key link in ensuring the stability of the electronic manufacturing process. Precision at this stage is critical to ensuring high yield and product reliability.
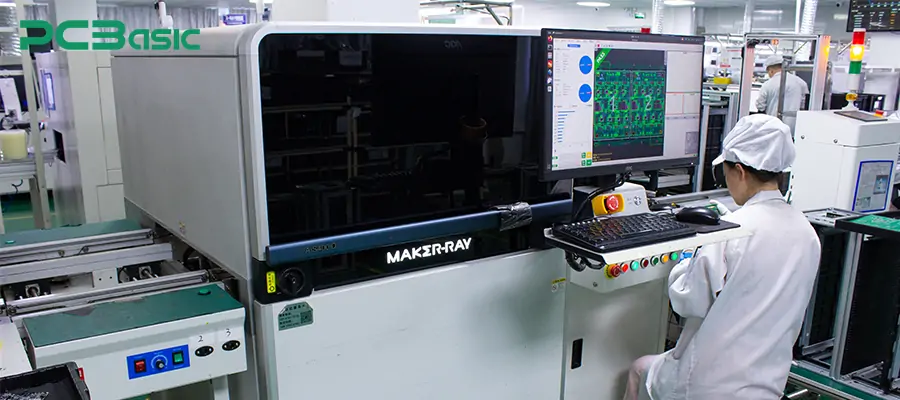

To ensure that the products meet the standards, manufacturers will conduct multiple tests, including:
Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI)
X-ray Inspection
Functional testing
This stage is to ensure that the quality of electronic component assembly meets the requirements of the electronics manufacturing industry.
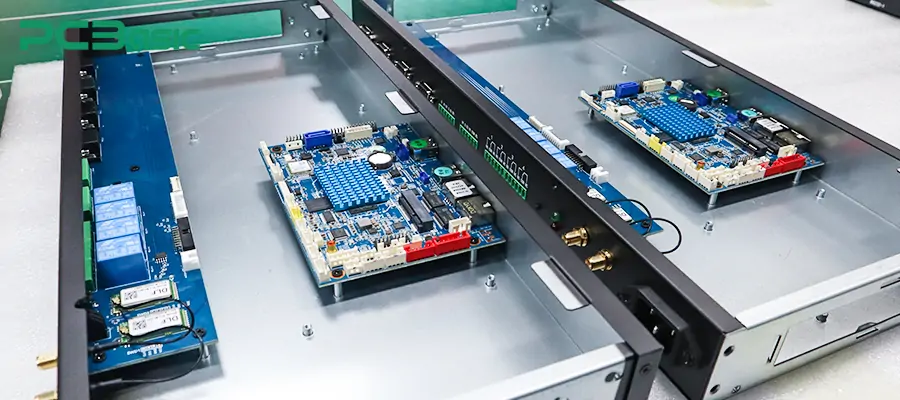

PCBA that passes the test will enter the final assembly stage of the entire machine. By integrating it with structural components, screens, batteries, casings, buttons, antennas and other modules, a complete electronic device can be completed.
This process includes steps such as structural assembly, cable arrangement and insertion, and screw fixation. Sometimes it also involves the bonding of thermal conductive materials, waterproof encapsulation or shock-resistant treatment. During the assembly process, standard operating procedures must be followed to ensure consistency and assembly efficiency.
Subsequently, the product will undergo another functional check and overall machine aging test to ensure that it meets the shipment standards in terms of appearance, performance and operation experience. This stage, which transforms electronic systems from circuit boards into electronic products, marks the imminent completion of the manufacturing process.
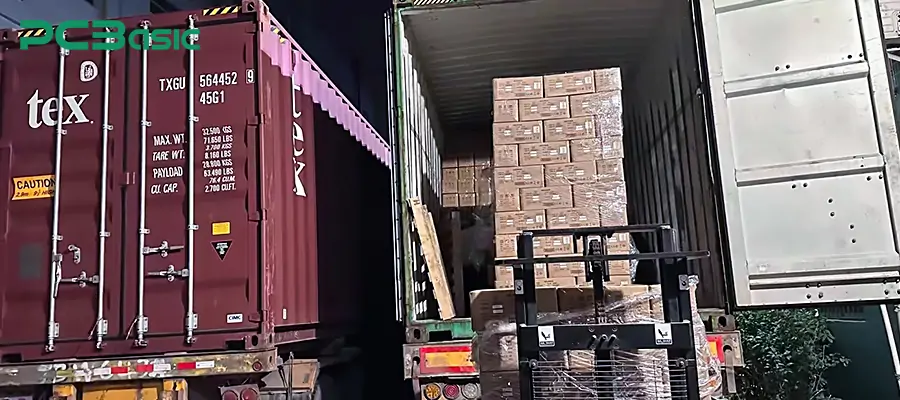

After the entire machine is assembled and passes the final inspection, the product enters the packaging and logistics stage. First, apply labels (such as serial numbers, certificates of conformity, certification marks, etc.), and then select materials like anti-static bags, blister boxes, foam, and paper boxes for protective packaging based on the product characteristics.
Subsequently, the products will be packed into outer boxes, labeled with barcodes or shipping labels, and then enter the storage area to wait for shipment. According to customer requirements, operations such as moisture-proofing, shock-proofing, custom outer boxes, and accessory packaging may also be carried out.
Finally, the logistics team will arrange for the shipment, delivering the products safely and efficiently to the customers or sales channels. This stage not only affects the delivery efficiency but also directly relates to the user's first impression. Packaging and logistics are the final stages of the entire electronics manufacturing process.
|
Stage |
Tools / Technologies |
Brief Description |
|
Design & Prototyping |
EDA tools (e.g., Altium, Eagle), manual soldering |
Define functions, electrical connectivity, and structure; validate initial feasibility |
|
Component Sourcing |
ERP systems, sourcing platforms (Digi-Key, Mouser) |
Ensure component quality and delivery; avoid supply shortages |
|
PCB Fabrication |
CNC drilling machine, plating line, OSP/ENIG process line |
Produce high-quality PCBs per design, including rigid, flex, or rigid-flex types |
|
PCB Assembly (PCBA) |
Pick-and-place machines, insertion machines, reflow ovens, assembly line |
Accurately and efficiently mount components onto PCBs |
|
Soldering Process |
Reflow oven, wave soldering machine, solder paste printer |
Establish electrical connections and ensure soldering reliability |
|
Testing & Quality Control |
AOI system, ICT fixtures, programmers, burn-in chambers |
Verify electrical performance and screen for potential defects |
|
Final Assembly & Packaging |
Electric screwdrivers, heat shrink machine, packing tools, label printer |
Complete full product integration and prepare for shipment |

With the continuous upgrading of manufacturing technology, modern electronics manufacturing is gradually moving towards intelligence, precision and high automation. The following are several advanced technologies in the digital electronics manufacturing process:
1. High Speed SMT Line
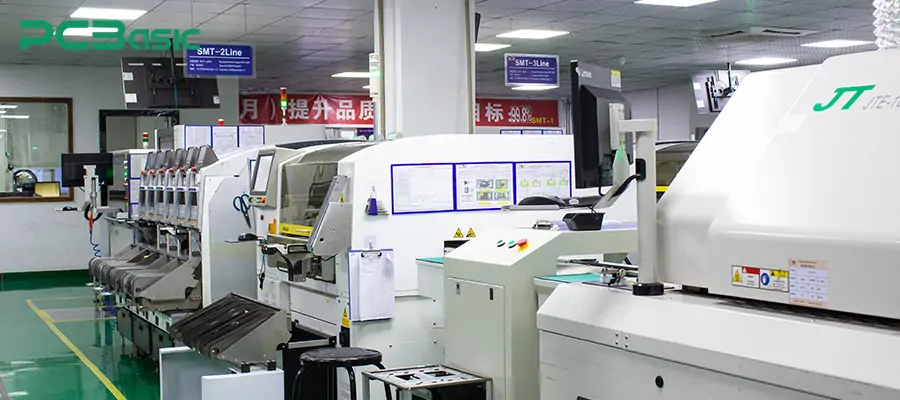

One of the most crucial advancements is the application of high-speed SMT production lines. Advanced SMT machines can mount tens of thousands of components per hour. This can significantly enhance the efficiency of electronic component assembly, and is particularly suitable for high-density and high-precision circuit boards.
2. Laser marking and 3D AOI inspection
Another key technology is laser marking and 3D inspection. Laser equipment can mark each PCB with a QR code and serial number, achieving full-process traceability throughout the entire electronics manufacturing process. The 3D AOI system can precisely detect the height of solder joints, the coplanarity of components and mounting deviations. It is an important guarantee in the digital electronics manufacturing process.
3. MES system
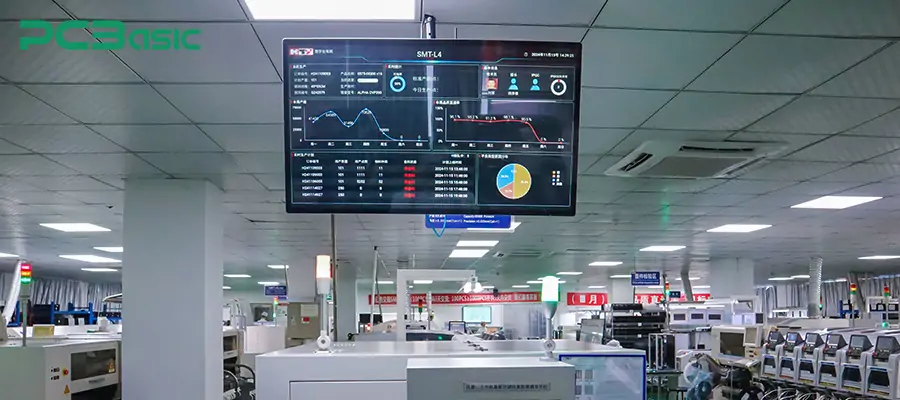

To achieve intelligent production management, many manufacturing enterprises have deployed self-developed or customized MES systems. This system can monitor the production status, process path and quality data of each circuit board in real time. It can also be integrated with ERP systems, production equipment and warehousing systems to achieve transparent and information-based intelligent factory operations.
4. Advanced equipment
Advanced technology cannot do without advanced equipment. For example, in the testing phase, Flying probe testing technology is an important tool in prototype boards and small-batch production. This method enables the rapid detection of open circuits, short circuits, polarity errors, etc., in circuits by directly contacting the test point with a movable probe without the need for custom fixtures. This device was a fast and efficient testing method in the early electronic manufacturing process verification.
In addition, advanced deionized water spray washing machines are also widely used in the cleaning process after soldering. This equipment uses high-pressure pure water for spraying and washing, effectively removing flux residues and ionic contaminants. This equipment is often used in application fields with extremely high reliability requirements, such as medical devices, automobiles, and aviation.
The wide application of these advanced technologies is driving the electronics manufacturing industry to continuously evolve in a more efficient, intelligent and reliable direction.
Advanced technology has injected unprecedented efficiency and flexibility into electronic manufacturing, but at the same time, it has also put forward higher requirements for the consistency and reliability of products. For this reason, enterprises must cooperate in implementing systematic quality control processes and standardized norms.
|
Item |
Category |
Purpose |
|
AOI(Automated Optical Inspection) |
Quality Assurance |
Detect placement defects, soldering issues, and component misalignments |
|
ICT (In-Circuit Test) |
Quality Assurance |
Verify circuit continuity, component values, and electrical performance |
|
Functional Test (FCT) |
Quality Assurance |
Simulate real-world operation to ensure board functionality |
|
Burn-in Test |
Quality Assurance |
Run boards under stress to identify early-life component failures |
|
IPC-A-610 |
Industry Standard |
Defines the acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies |
|
IPC-2221 |
Industry Standard |
Provides generic standards for PCB design |
|
IPC-6012 |
Industry Standard |
Specifies performance and quality requirements for rigid PCBs |
|
ISO 9001 |
Industry Standard |
Defines requirements for quality management systems |
|
ISO 13485 |
Industry Standard |
Specifies QMS requirements for medical device manufacturing |
|
RoHS |
Industry Standard |
Restricts the use of hazardous substances in electronic equipment |
These standards ensure that each product complies with international norms in terms of quality, safety and environmental protection.
Understanding the electronics manufacturing process can help enterprises better carry out product design, production arrangement and supply chain management. From design to shipment, every link determines the success or failure of the product. Whether it is consumer electronics, automotive electronics, or industrial control equipment, a deep understanding of the electronic manufacturing process can bring higher quality assurance and manufacturing efficiency. Mastering every step—from component assembly to final packaging—equips you to stay ahead in the fast-evolving electronics manufacturing industry.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
