Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCBA Test: A Comprehensive Guide on PCB Assembly Testing
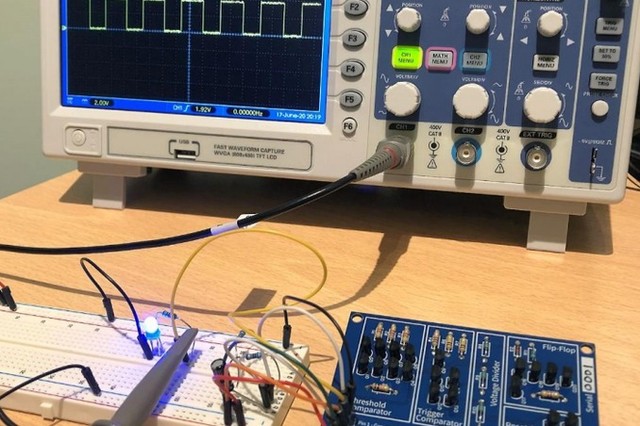
The printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) test is a quality control process used in electronic manufacturing. A PCBA refers to the assembled printed circuit board found in virtually all electronic devices, such as computers, phones, appliances, and more. During a PCBA test, the assembled printed circuit board is thoroughly tested to check for any faults or defects before the device is finished and shipped to customers.

Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is the pcb assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB Assembly Services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB Assembly Manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB Prototype Factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
● Improves quality and reliability: Testing identifies faulty boards before use, reducing failures and recalls in the field. It ensures products meet high standards for quality and reliability.
● Saves time and money: PCBA testing finds issues early when they are less expensive to fix. This prevents costly delays and expenses further down the line from faulty boards making it through to products.
● Provides peace of mind: Customers expect the products they receive to work as intended from day one. PCBA testing helps ensure this is the case by rigorously validating boards before use, providing confidence in maintaining quality standards.
● Component quality: Visually inspect all passive and active components for defects, damage, or correct values. Use specialized tools to test integrated circuits.
● Soldering quality: Examine all solder joints under a microscope to check for defects like whiskers, bridges, or uneven/cold solder. Perform pull tests on random samples.
● Circuit continuity: Use a multimeter to test that all traces and connections between components are intact without breaks or shorts. This validates proper manufacturing of the PCB.
● Functionality: Power on the board and perform functional tests by toggling inputs and checking output responses. Ensure advertised features work as specified.
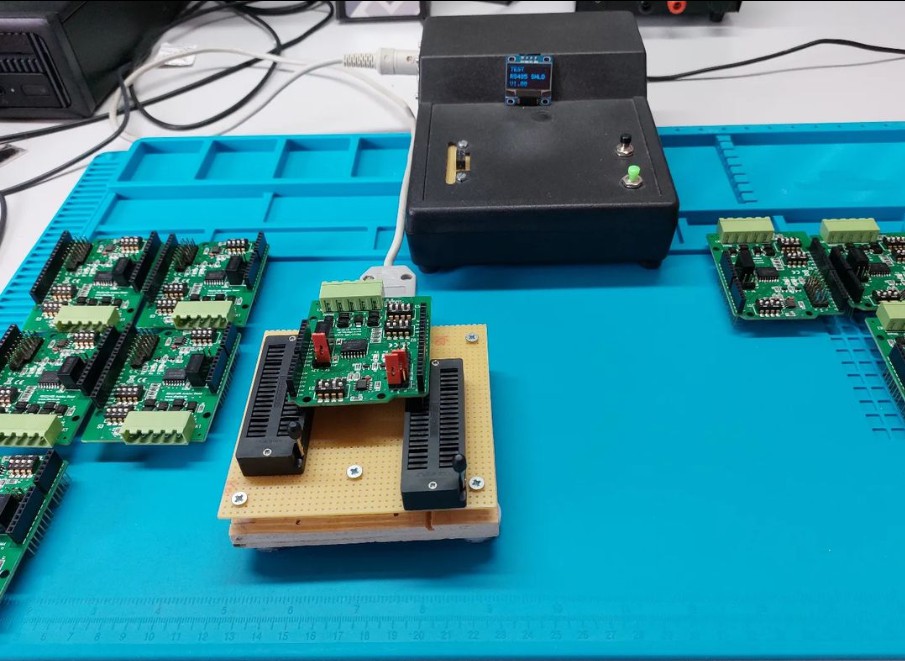

PCBA test has become increasingly important to ensure product quality and reliability. Here are some of the most widely used PCBA testing methods:
Visual inspection is a standard PCBA testing method involving visual examination of PCBs. The process checks for any defects, damages, or abnormalities that may have occurred during the manufacturing process. The equipment includes magnifying lenses or microscopes, which help inspect minute component sizes and placements. Good lighting is essential.
Advantages:
● Catches gross defects
Disadvantages:
● Some issues require extra equipment.
Precaution: Ensure adequate lighting and magnification levels for visual inspection.
Advantages:
● Provides a baseline for quality checks on the subsequent production run
Disadvantages:
● Requires shutdown of production line for inspection
Precaution: Manufacturing the first article samples should utilize all planned production materials, processes, and equipment for the most accurate results.
In-circuit testing (ICT) evaluates printed circuit boards (PCBs) by testing components and connections while still installed on the board. Using automated test equipment (ATE), ICT sends test signals into the circuit board and analyzes responses to verify components, connections, and basic functionality match the design.
Advantages:
● Faster than testing components individually
Disadvantages:
● Test fixtures and ATE equipment require investment
Precaution: Take caution not to damage circuit paths during test probe connection and disconnection.
Flying probe testing is a quick and reliable way to test printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs) and printed circuit boards (PCBs). It uses a computer-controlled probe card with multiple fine needle probes that 'fly' over the board surface to contact circuit traces and test points.
Advantages:
● Finds a variety of defects, including intermittent faults
Disadvantages:
● You can only access test points; buried components require other methods
● Reduces the need for manual visual inspection
Disadvantages
● Component shadows or glare can hamper detection
Precaution: Proper lighting setup is critical for defect-free image capture.
Advantages:
● Accelerates detection of design or manufacturing flaws
Disadvantages:
● Elevated temperatures may damage components that would otherwise function properly
Precaution: Burn-in should be done carefully to monitor component temperature and avoid overheating issues.
X-ray inspection is a non-destructive testing method to evaluate printed circuit board assemblies' internal structure and composition. It works on the principle of bombarding PCBs with X-rays and analyzing the resulting pattern of beams after they pass through the material.
● Can inspect boards in a populated state
Disadvantages:
● PCBs need to be moved through the scanner, limiting throughput
Precaution: Be careful to protect yourself against X-ray radiation exposure during operation.
Advantages:
● Accelerates the effects of long-term usage
Disadvantages:
● Requires specialized fatigue testing equipment
Precaution: Components must be securely fastened during high-cycle fatigue testing to avoid detachment.
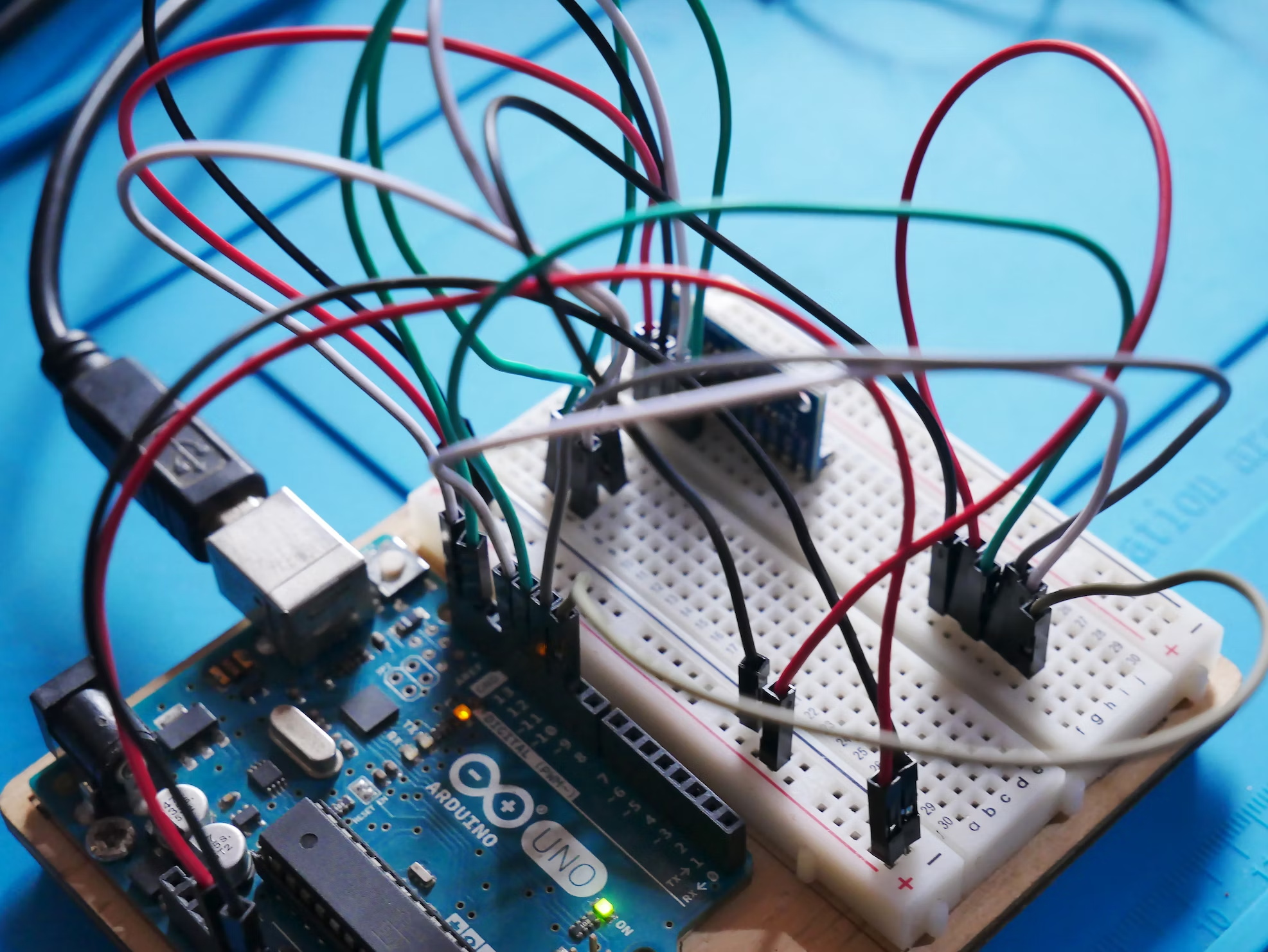
Functional testing is used to validate whether a PCBA is functioning per its design specification. In this method, test signals are given as input to the PCBA, and corresponding output signals are analyzed to check if components are working individually and as an integrated system.
Advantages:
● Ensures reliability of the design
Disadvantages:
● Requires specialized functional test equipment
Precaution: All safety protocols must be followed while handling live circuitry during functional testing.
The aging test subjects PCBAs to extreme environmental conditions such as high temperature and humidity for a period of time. This allows manufacturers to check if components can withstand hazardous environmental stresses over prolonged usage.
Advantages:
● Ensures long operational life under stressful conditions
Disadvantages:
Precaution: Be careful to prevent physical damage to PCBAs during transfer in and out of climate chambers.
The equipment used is a programmable climatic chamber that can accurately control and monitor temperature and humidity as per IEC standard testing protocols.
Advantages:
● Certifies components to work in hazardous environmental zones
Disadvantages:
● Climate chambers require large floor areas and high energy costs
Advantages:
● Provides permanent video record for traceability
Disadvantages:
Testing PCBAs often reveals the following common defects:
● Short circuits: When solder or stray metal connects components that should not be connected, which can cause boards to fail to power on or function incorrectly.
● Cold solder joints: Solder did not properly flow and bond between components and the board, resulting in weak connections that can fail over time.
● Mismatched components: The wrong resistor, capacitor, or integrated circuit may be installed due to incorrect part placement or mixing up similar-looking parts.
Addressing these typical defects is important for producing high-quality PCBAs that will reliably perform as intended. Testing catches these issues to improve product quality and reliability.
If your business needs robust, high-quality PCBA production, consider partnering with an industry leader like PCBasic. Our full-service manufacturing includes cutting-edge PCBA testing that can give you peace of mind and improve your product quality. Contact us today to discuss how they can help meet your testing needs.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
