Have you ever wondered what makes your smartphone smarter and laptops lightning-fast? That's different types of PCBs working together to give you the end product. In today's modern technology world, Printed Circuit Boards are the unsung heroes!
PCBs come in different colors, shapes, and sizes, but what also differentiates PCB types is layers, design, and purpose. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a budding engineer, or simply someone curious about the inner workings of your gadget, hold onto your belts since we're going to unveil the PCB's insights. This guide will uncover different types of circuit boards, their applications, and how they work. So, let's get started.
1. Single Layer PCB
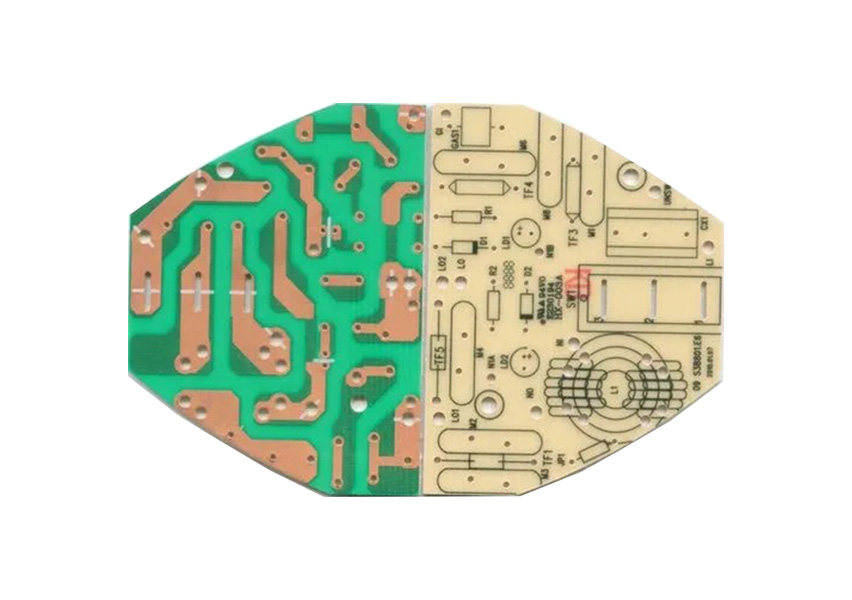
Single layer printed circuit board is the most basic type of PCB design. As the name suggests, a single-layer board is made with only one layer that includes 2 sides: one side is the conductor and the other one is for parts placement.
Single layer PCB comes with different types of PCB materials such as resin copper, glass fiber, and others.
There are vast advantages to a single-layer PCB design such as:
-
1. Easy installation which saves cost on PCB assembly.
-
2. Simple design, less time-consuming for a company to create.
-
3. Effective and easy to be tested.
-
4. Low noise that could interfere with the board functionality.
-
5. Easy and quick soldering for samples and fast and cheap in mass production.
Single layer PCB is very suitable for different types of PCB testing as it’s easy to design, assemble and ensure the components are working as they are supposed to. Single layer will often be used in prototyping and testing types of circuit boards although it’s common that such boards will mass produce as well if the design is simple enough to fit the application needs.
Except for prototyping and testing purposes, the single board can be used in applications such as:
-
1. Surveillance and personal cameras
-
2. LED lighting
-
3. Consumer goods such as Coffee machines, Radio devices, Printers, etc …
-
4. Industrial machinery such as vending machines, multimedia systems, and more …
If you need a quick solution for low-cost quick and easy types of PCB fabrication, a single-layer PCB board might be the right solution for your needs.
2. Double Layer PCB
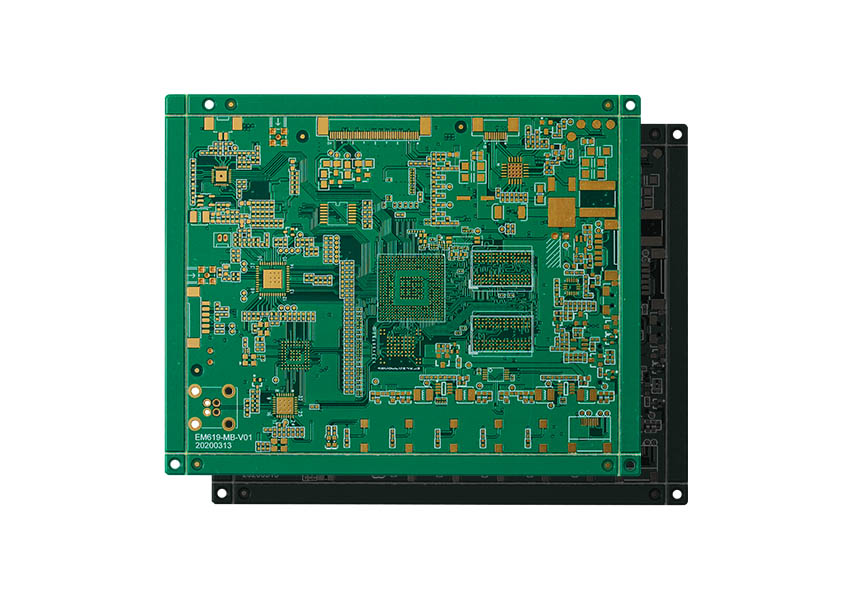
Double layer PCB (sometimes called double-sided or dual layer PCB) are considered popular types of circuit board when it comes to mass production of PCB designs. The Double layer PCB consists of two sides, top and bottom, that sandwich cooper, insulating materials, and other different types of PCB materials.
Double layer PCBs are a very popular choice among hardware enthusiasts due to their low cost, ease of design, and speed of production. The double layer consists of connectors called “vias”, small holes which connect and bridge circuits from one layer to another. Single-sided PCBs can only be assembled on one side and don’t require vias or complex wiring schemes. The vias allow engineers to efficiently bridge one side of the board to another, ultimately connecting multiple components as a single circuit in a particular design.
Double layers are often used in applications such as:
-
1. Industrial applications and controllers.
-
2. Power monitoring equipment and supplies.
-
3. Power converters AC-DC or DC-DC.
-
4. Relays and bridges to open and close circuits.
-
5. Uninterrupted power supply (UPS) systems
-
6. Other types of PCB applications …
Whenever you are an experienced hardware engineer/designer, double layer PCB should get the work done on most occasions. A double layer is often considered the best choice when designing a brand new PCB project.
3. Multi-Layer PCB
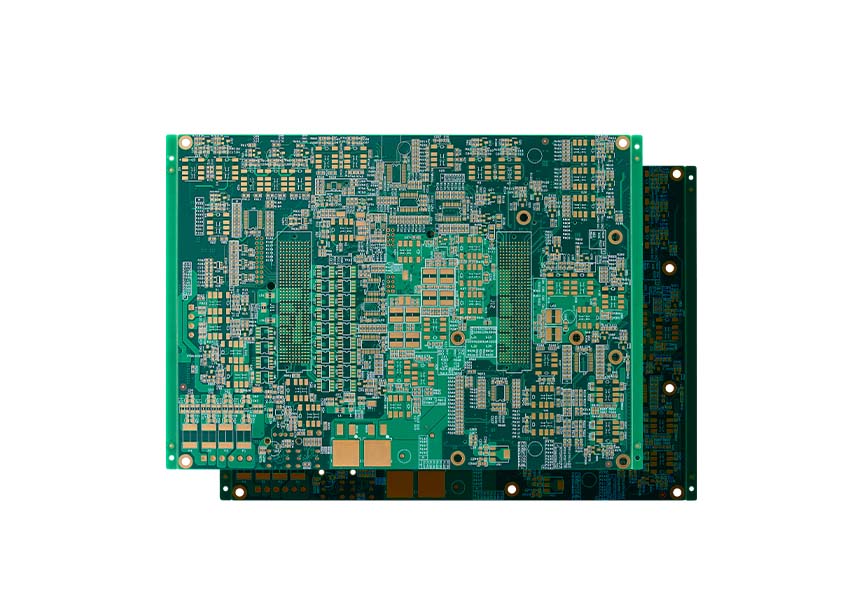
Multi-layer PCB refers to any other PCB that is above 2 layers threshold. Some complex designs require a lot of plugged vias and information transfers, which will result in a multi-layer PCB design. Multi-layer PCB can go anywhere from 4 up to 16 layers on a single PCB.
Unlike the other designs such as Double-Sided or single-layer PCBs which only contains two conductive layers incorporated between the copper boards, a Multi-layer PCB (a PCB with > 2 layers) has no less than three layers of conductive material sandwiched in the center of the PCB material.
One thing to consider is that the higher the number of layers and the density in different types of PCB, the more complex the design will be and will often require more resources and time in PCB designing, producing, and testing.
Now that you're well aware of what a multilayer PCB is. Let us move to its benefits. Here are some of the advantages of multilayer PCB boards.
● High component density enables compact, feature-rich devices.
● Minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI).
● Ideal for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
● Provides stable ground references for components.
● Despite being multilayer, it helps to create sleek, lightweight devices.
To manufacture a multilayer PCB, we use laminating alternating layers of substrate material and prepreg with copper foils. Then, we etch away unwanted copper to create the desired circuit traces. The amount of layers between the multilayer PCBs can vary widely from 4 to 20 layers or more, depending on the complexity of the devices.
Let's look into some key areas where multilayer PCB boards are commonly used.
● You can find them on smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart TVs.
● They are the backbone of computer servers and data centers.
● In networking equipment, routers, and communication devices.
● Medical equipment such as MRI machines and CT scanners leverages multilayer PCBs.
● They also play an important role in automation and control systems used in factories and industrial machinery.
4. Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs, or rigid printed circuit boards, are a fundamental type of electronic circuit board known for their inflexibility and durability. You can find them in most daily-use items because of their robust structure.
As their name suggests rigidity, you can not bent or deformed them. If we talk about their making, various layers, such as a substrate layer, a silk screen layer, a copper layer, and solder mask layers, are used. To bind these layers together, we use heat and glue.
What sets rigid PCBs apart is their versatility, making them single-sided, double-sided, or even multilayered. Unlike other boards that can be single or double-sided, you can alter rigid boards to your liking while remaining within your budget.
Let's dive into what benefits it holds:
● They are ideal for intricate electronic devices, which can accommodate many components.
● Regarding cost, rigid PCBs are more economical than flexible or rigid-flex ones.
● They have many applications ranging from electronics to industrial control systems.
● With their rigid structure, you can expect them to work longer without wear and tear.
Rigid PCBs are a fantastic choice if you're searching for an affordable solution that can be manufactured in large quantities. The most common materials used in its manufacturing include FR-4 (Fire Retardant-4) and other substrates such as ceramic, metal core, and composite materials to give the device its unique properties.
Let's now hop onto its industrial and everyday use applications:
● They are most commonly used in engine control units (ECUs) and vehicle sensors.
● Critical for radar systems and military communication equipment.
● Found in medical imaging equipment and diagnostic instruments.
● Employed in power distribution systems and renewable energy equipment.
5. Flex PCBs
A flexible circuit board is made from a naturally flexible substrate, such as polyamide Kapton. These boards are known for their flexibility and versatility, making them bent or deformed. Their flexibility makes them suitable for applications where traditional rigid PCBs won't be practical.
The key materials used in their formation include polyamide and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) for flexibility. Besides this, just like rigid PCBs, flex PCBs use copper foils for conductive traces.
Here are some of its benefits:
● Their flexibility allows them to fit into smaller spaces.
● Fewer connectors and interconnectors reduce the risk of connection failure.
● It is ideal for applications where weight is critical, such as portable devices.
● Flex PCBs are less prone to mechanical stress and vibrations.
● They can adapt specific shapes and contours, enabling innovative product designs.
Now, let's see where we can find flex PCBs:
● Used in digital cameras for their compact design.
● Employed in airbags and automotive control systems.
● It is found in wearable health monitors and surgical instruments.
● Used in sensors in automation and robotics.
● Integral in developing flexible and rollable displays for next-generation screens.
6. Rigid-Flex PCBs
A rigid-flexible printed circuit board is a specialized class of PCBs that blends the features of both flexible and rigid PCBs into a single unit. They feature rigid sections, which do not bend, and flexible units that allow for folding and bending. This unique design makes them exceptionally versatile for various applications.
To dive deep into their structures, you'll find they are constructed using a combination of materials. For instance, the rigid one often uses traditional materials like FR4. In contrast, the flexible sections consist of polyamide that can withstand bending and folding.
The best part about these PCBs is they can replace multiple traditional PCBs and connectors, saving room in compact devices. Moreover, these boards can accommodate high-density components, making them suitable for complex electronic systems.
Like rigid and flexible PCBs, they also have similar advantages with some additions. Let's have a wider picture of it.
● Reduction in connectors and assembly complexity often results in cost savings in the long run.
● Engineers have more design freedom as they create 3D designs, reduce weight, and optimize layout.
● Their flexible shape saves space.
● They are employed in industrial control systems for their resilience and space efficiency.
If we talk about its applications in industries, you can find them in everything from small gadgets to bigger medical equipment and everything in between. Here are some of its common applications.
● Rigid-flex PCBs are essential in medical devices like pacemakers and diagnostic equipment.
● Used in aerospace systems where weight reduction, reliability, and flexibility are critical.
● They can also be found in airbags and infotainment systems.
7. High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCB
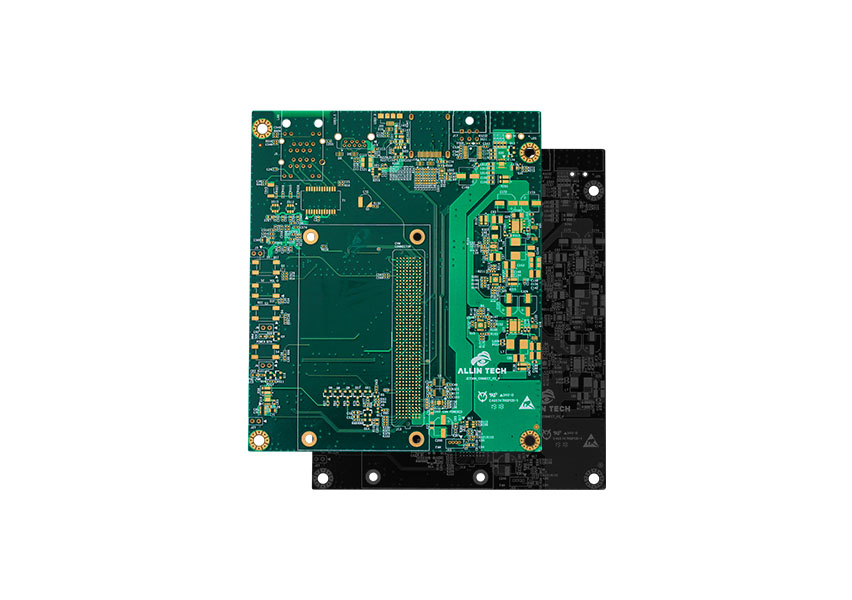
High density interconnects, on in short, HDI stands for the type of circuit board that comes with a higher density of wires. HDI board has a limited amount of space which results in tight spaces and lines.
Compared to normal PCB designs, HDI designs are the way to go when it comes to multi-layer designs with expensive finishes. HDI designs can offer multiple benefits compared to conventional designs, such as lighter weight PCB in smaller dimensions and better electrical performance.
The inspiration for HDI board design came from the semiconductors industry. Semiconductors use a very small surface area while managing to pack a lot of transistors and micro-electrical components.
HDI boards are especially suitable and optimized for high-speed electrical signal transmissions. Those boards support multiple features including HF (high frequency) transition and blockade control. The reason that HDI boards are designed with better density is due to their miniaturized design which comes with tiny electronics parts located in high density across the board, which is why we call this type of board a high-density interconnect PCB.
The applications of HDI boards include:
-
1. Personal computers (laptops, PCs)
-
2. Mobile phones
-
3. Health care equipment
-
4. Automotive industry
-
5. Game consoles
-
6. Wearables, smartwatches, and more …
The technology used in the production of HDI boards allows amplification of the original PCB design but in smaller, lighter, and denser spaces. The process of placing components over an HDI board requires advanced PCBA and SMT technology due to the high precision requirements and tight surface space. Repairing such boards manually can be a difficult task for engineers due to the density of the HDI board.
HDI board is a great option for designs that require fast electrical transmission while packing components in a small space.
8. High-Frequency PCB
High-frequency PCB boards are defined as types of PCB that operate in frequencies above 1GHz. There are multiple materials that can be used for pthe roduction of such boards such as PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). This material is often called Teflon, in short. Most of the high-frequency PCB types and designs can reach a frequency beyond 5GHz. There are other types of materials such as FR4 (glass-reinforced epoxy) and PPO (polyphenylene oxide). Those types of materials can reach up to 10GHz when used correctly.
The purpose of High-frequency types of PCB, or HFP in short, is to meet the demands for advanced PCB designs. Those types of designs require fast signal transmission at a high-frequency range. This kind of ability allows the HFP to deliver signals at a high rate and great speed.
Some of the high-frequency PCB types are used in critical applications such as:
-
1. Communication systems, network stations, high-frequency radio transmitters, etc …
-
2. Military industry and its applications including weapons, missiles, and tracking devices.
-
3. Radar systems and applications in aerospace and aviation
-
4. Medical and health care applications for diagnostics and monitoring purposes.
High-frequency PCB types are crucial for industrial and critical systems use, due to their ability to transmit high-frequency fast signals across multiple circuits. For consumer use, other options might be a better choice such as a double layer or multilayer PCB.
9. LED PCBs
With the name LED, you must be thinking of some lights. Then, you're right! LED PCBs are engineered to provide the necessary electrical connections, thermal management, and mechanical support for LEDs.
They are typically constructed using materials optimized for heat dissipation and light transmission. For instance, it employs aluminum for its excellent thermal conductivity, copper for conducting heat, and FR4 for good electrical insulation.
These boards have specially designed pads for soldering or mounting LEDs, ensuring electrical connections. This PCB layout considers light diffusion and reflection to maximize the LED's luminous output.
With all these remarkable features, it holds a great number of benefits. For example:
● They are excellent at dissipating heat for maintaining LED performance and longevity.
● Optimized Light Output maximizes the distribution of LEDs.
● These boards offer reliable electrical connections, reducing the risk of LED failure.
● They are also compact, making them flexible to adjust in compact spaces.
Let's now have a look at some of its applications:
● They are the foundation of LED lighting systems for homes, offices, and streetlights.
● Used in vehicle headlights, taillights, and interior lightning.
● Found in TVs, monitors, and small display screens in devices like smartphones.
● It is located in LED PCBs powered by illuminated signs and billboards.
Summary
In this article, we covered the different PCB types and their applications. No matter if you have a single layer or multilayer design requirements, PCBasic is here to help.
By understanding the application’s needs, we can turn your idea into reality. With over 15 years of knowledge, we are able to handle any type of PCB including HFP and HDI complex designs.









