Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > BGA Rework Explained: Tools, Process, Mistakes, and Best Tips
With the development of integrated circuit packaging technology, BGA (Ball Grid Array) is widely used in various modern electronic products due to its compact structure and excellent performance. However, the solder joints of BGA chips are located at the bottom of the chip and cannot be directly seen with the naked eye. Traditional soldering tools also cannot operate them. Therefore, BGA Rework has become one of the most difficult and crucial steps in circuit board repair.
In practical use, BGA chips may encounter various problems, such as poor solder joints, chip damage, or defects during the production process. At this point, if BGA repair can be carried out promptly and accurately, the circuit function can be effectively restored, the entire circuit board can be avoided from being scrapped, and the maintenance cost can also be reduced.
For engineers, maintenance technicians and electronic manufacturing enterprises, it is very important to master BGA repair technology. If the BGA rework machine or BGA rework station is used correctly, the success rate of maintenance can be significantly improved, and the service life of the product can be prolonged.
This article will systematically introduce the relevant knowledge of BGA rework, including basic principles, tool preparation, operation procedures, comparison between hot air and infrared heating methods, common mistakes, and practical rework techniques. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced technician, this technical guide will provide you with reliable references.
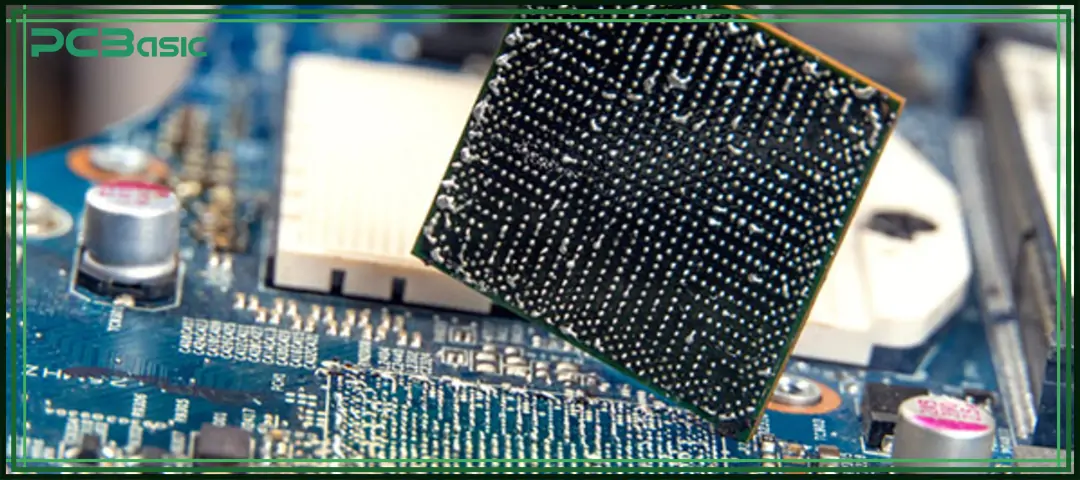
BGA rework refers to the process of removing, reballing and resoldering the BGA packaged chips on a printed circuit board (PCB). BGA (Ball Grid Array) is a common surface mount packaging form. It connects the integrated circuits (ICs) to the circuit board through tiny solder balls arranged at the bottom of the chip.
Since these solder balls are located at the bottom of the chip, they cannot be directly seen by the naked eye and cannot be operated with a regular soldering iron. Therefore, BGA repair is more complex than the maintenance of traditional devices and has higher requirements for equipment and operational techniques.
Common situations that require BGA rework include:
• Some solder joints fail, or the connection is unstable, and resoldering is required
• If the chip malfunctions or has aged, a new BGA chip needs to be replaced
• The original chip needs to be upgraded to a newer version
• Poor soldering or other defects during the production process need to be repaired
In all these cases, using professional BGA rework machines or BGA rework stations can effectively restore the circuit function, prevent the entire board from being scrapped, and reduce the overall repair cost.
In modern electronic products, such as smartphones, laptops and communication equipment, BGA components are widely used on PCBs. This is because BGA packaging has the advantages of small size and high pin density, making it highly suitable for high-performance and compact electronic designs.
However, in actual use, due to thermal stress caused by repeated heating and cooling processes, mechanical vibration during equipment operation, or poor soldering quality during production, BGA solder joints are prone to cracking, cold solder joints or disconnection. These problems can lead to unstable chip connections, which in turn affect the functionality of the entire circuit board.
If timely and effective BGA rework is not carried out, a single damaged BGA chip may cause the entire PCB to become unusable. This not only increases the cost of repair or replacement but also leads to waste of components and loss of resources.
By using professional BGA rework stations and following the correct operation procedures and process standards, technicians can quickly identify and repair BGA solder joint problems. This helps prevent scrapping entire boards, reduces maintenance costs, extends the overall product lifespan, and improves production efficiency and product reliability.
When conducting BGA rework, it is necessary to be equipped with basic but professional tools, whether in the repair workshop or on the production line. These tools help to enhance the efficiency of rework and soldering quality, ensuring a stable and reliable operation process.
A professional BGA rework station is equipped with a bottom heater, a top heater and a vision alignment system. It can precisely heat and position the chip, ensuring the accuracy and safety of the soldering process, and is suitable for the remove and installation of most BGA components.
The BGA rework machine typically uses either hot air or infrared heating. The hot air system uses airflow to heat the chip and has strong adaptability. The infrared system heats by radiation, operates quietly and heats evenly. Both methods have their own advantages and can be chosen based on actual needs.
Common soldering materials include lead-free solder paste (such as SAC305), flux (liquid or gel), and new solder balls for reballing. These materials determine the quality of the solder joints and the reliability of the rework.
These include solder wick, microscopes, tweezers, positioning tools, and X-ray inspection equipment. They are used to assist with soldering, remove residual solder, align and detect hidden solder joints, ensuring that the entire rework process is precise and efficient.
Choosing a reliable BGA rework station and matching it with appropriate tools is the key to improving the success rate of rework and the quality of soldering.
Choosing the appropriate heating method is crucial to the effectiveness of BGA Rework. The following is a comparison of two common heating methods:
|
Feature |
Hot Air BGA Rework Station |
IR BGA Rework Station |
|
Heating Method |
Heated air directed through nozzles |
Infrared light or ceramic heating plates |
|
Heating Speed |
Fast and efficient heating |
Slower but more stable heating |
|
Noise Level |
Noisy due to air pumps |
Silent operation |
|
Heat Area Control |
Controlled by interchangeable nozzles |
Controlled by beam focus or diffusion |
|
Nozzle Requirement |
Requires changing nozzles for different chip sizes |
No nozzles needed; beam size can be adjusted |
|
Effect on Shiny/Silver Parts |
Effective on most surfaces |
Less effective unless black tape is applied |
|
Cost |
Medium to high, depending on nozzle types and brand |
Higher for precise IR systems; entry-level less precise |
|
Application Suitability |
Versatile and flexible for general BGA rework |
Better for precision work and quiet environments |
Depending on different repair requirements, product types and budget conditions, a more suitable type of BGA rework machine can be selected to achieve better repair results and work experience.
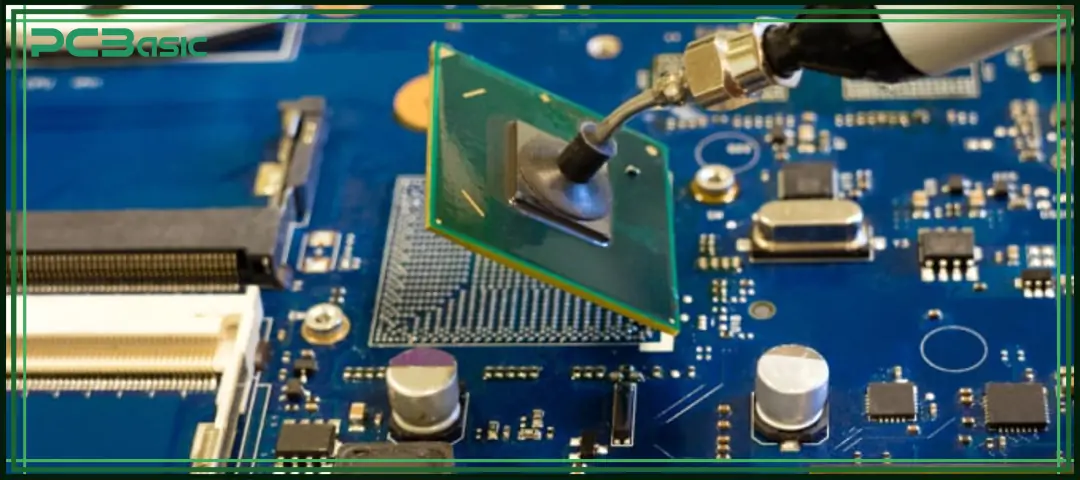
To successfully complete a BGA repair, the following steps must be followed. Each step requires the use of appropriate tools and standard procedures to ensure soldering quality and reliability.
First, clean the surface of the circuit board using isopropyl alcohol to remove dust, grease, and other contaminants. Then, apply flux around the BGA chip to help the solder joints wet properly during heating. Next, secure the PCB on the BGA rework machine to prevent movement during operation. ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection must also be in place to avoid damaging the chip.
Use the bottom heater to preheat the board, typically to around 150°C. Then apply top heat directly over the BGA chip, typically around 350°C. Once the solder balls reach reflow temperature (about 250°C), gently remove the BGA chip using a vacuum pen or tweezers. Be careful not to pull or damage the pads.
Use solder wick to clean up the residual solder on the pads. Use a microscope to inspect the pads for any lifting, peeling, or scratches. If pad damage is found, it should be repaired or replaced before proceeding. After removing the solder, use alcohol to thoroughly clean off any flux residue, keeping the surface clean and flat.
Place the BGA chip on a reballing stencil. Apply a small amount of solder paste to the pad locations. Then, place new solder balls into the stencil holes in the correct array. Apply gentle preheating to tack the balls into place. Full reflow is not necessary at this stage—only ball positioning.
Place the reballed BGA chip back onto the PCB and use the vision alignment system to align it precisely with the pads. Once aligned, perform reflow soldering according to the recommended temperature profile. Hold the temperature until all solder balls are fully melted and properly wetted. After reflow, allow the board to cool down naturally.
After soldering is complete, use an optical microscope to inspect the visible joints. Then use an X-ray inspection system to check the hidden joints under the BGA. Look for defects such as shorts, opens, or voids. Ensure all joints are well-formed and reliable.
Finally, perform in-circuit testing (ICT) or full system functional tests on the repaired board. Confirm the BGA chip is working properly and that signal and power connections are functioning correctly. Only after passing the testing should the board proceed to final assembly.
Throughout the entire process, using a professional BGA rework station (BGA Rework Station) ensures more accurate temperature control and better operational stability. This greatly improves the success rate and consistency of BGA rework and is essential for high-quality repairs.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Even with a high-end BGA rework station, improper operation can still lead to rework failure. Below are some of the most common mistakes during the rework process and suggestions on how to avoid them:
If the technician lacks professional training, issues can easily occur during the operation. For example, poor temperature control may cause the PCB to overheat or even damage the pads. To prevent this, operators should receive standardized training and strictly follow the IPC-7095 rework guidelines.
Each BGA chip has a specific reflow temperature profile. If not set correctly, it may result in cold solder joints or weak connections. It is recommended to use the thermocouples and data logging features of the BGA rework machine to monitor and optimize the heating parameters in real time.
If flux residues or old solder remain on the pads, they can cause short circuits or poor solder joints. After removing the chip, thoroughly clean the pad area to ensure a smooth and clean surface before the next soldering step.
Incorrect solder ball size or inaccurate placement can lead to misaligned or failed solder connections. During BGA reballing, use standard stencil templates and select solder balls and alloys that match the original manufacturer specifications to ensure soldering accuracy.
During rework, if nearby components are not well protected, they may be damaged by excessive heat. Use aluminum foil, heat shields, or other thermal protection materials to safeguard adjacent components. If using an infrared system, enable the focused heating function to apply heat only to the target area.
1. Always use X-ray inspection equipment before powering on the board to verify solder joint quality and ensure there are no shorts, cold joints, or voids.
2. Practice thermal profile setup and rework techniques on scrap PCBs to build experience.
3. Record detailed steps for each rework, including temperature settings, operation time, and materials used. This helps with quality control and future troubleshooting.
By avoiding these common mistakes and using a reliable BGA rework station along with standardized procedures, you can significantly improve the success rate and reliability of BGA rework.
BGA rework is a very important technique in modern electronics repair and manufacturing. Although this process is complex, it can be performed safely and reliably as long as you have proper training, the right tools, and follow standardized procedures.
Whether you are using DIY tools or a professional BGA rework machine, as long as you understand each step clearly, avoid common mistakes, and follow best practices, you can greatly improve the success rate of BGA repair while reducing the risks during the operation.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
