Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Ultimate Guide to Low Pressure Molding (LPM)
As electronic devices continue to develop towards miniaturization, high sensitivity and high integration, the requirements for encapsulation processes are getting higher and higher. Traditional potting and high-pressure injection molding have some disadvantages, such as long processing cycles, excessive material waste, complex operations, and a tendency to cause thermal shock or mechanical damage to electronic components. In this case, low pressure molding (LPM) has become a more suitable encapsulation solution.
This article will introduce low pressure molding working principles, common LPMS platforms (low pressure molding systems) and equipment types, the main materials used, typical application directions, and other contents. Meanwhile, we will also explain the core features of low pressure molding machine and the low pressure molding compound. Whether you are an engineer, a purchaser, or a product developer, this guide will help you gain a comprehensive understanding of the value and application of low pressure molding technology.
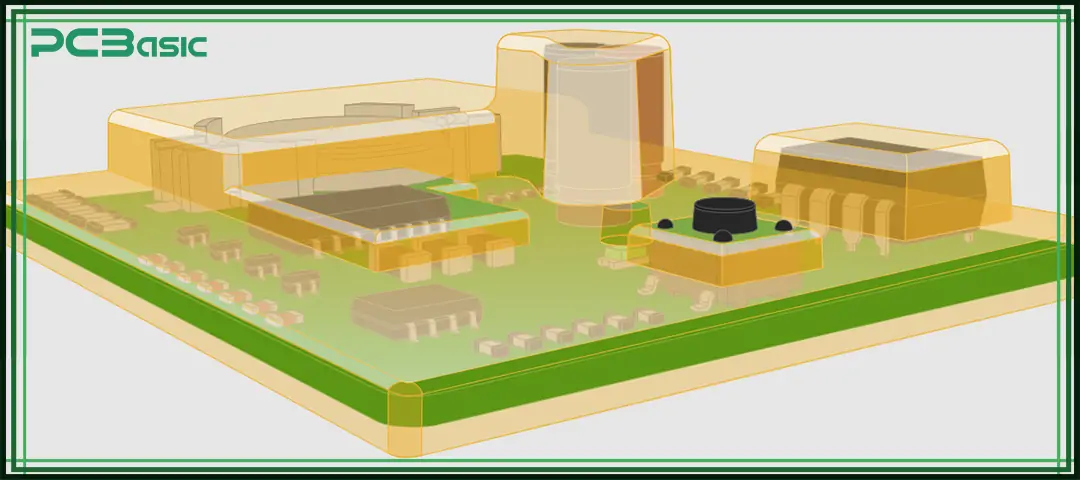
Low pressure molding (LPM) is an electronic component encapsulation process. It adopts low pressure injection molding technology and hot-melt adhesive materials to encapsulate and protect sensitive components such as PCBs, sensors, and wiring harnesses.
Unlike traditional injection molding, which requires high temperature and high pressure and may easily cause damage to components, low pressure molding systems work under much gentler conditions, typically ranging from 1.5 to 40 bar, and the temperature range is 180 to 240 °C. It is gentler and will not cause thermal or mechanical stress to the components.
This process uses thermoplastic low pressure molding materials, such as polyamide and polyolefin. These materials have excellent flowability and can easily fill molds even under low pressure. As low pressure molding compounds, they can evenly coat components and form a protective seal to prevent moisture, dust or other environmental factors from affecting the components.
Overall, low pressure molding is a cleaner, more efficient and more environmentally friendly encapsulation method. It can serve as an alternative to epoxy potting, silicone encapsulation and high-pressure injection molding, and is particularly suitable for electronic products that require precise protection.
To ensure stable and consistent molding results, low pressure molding usually employs dedicated low pressure molding machines. These machines are generally part of a low pressure molding system (LPMS). A system typically includes a raw material reservoir, gear pumps, a heating unit and a mold clamping mechanism.
Traditional injection molding equipment uses screw feeders, which involve high pressure and complex control. The low pressure molding machine uses gear pumps for feeding, which can control the flow rate and pressure of the low pressure molding material more precisely. This way, the components can be encapsulated more gently, avoiding damage caused by high temperature or high pressure.
The leading LPMS platform suppliers currently available on the market include:
• LPMS USA
• Henkel TECHNOMELT® Platform
• Cavist Manufacturing
• MoldMan Systems™
These companies offer a variety of low pressure molding systems, suitable for the demands of different production needs. From small-batch prototype development to large-scale manufacturing, they are widely used in multiple industries such as automotive and healthcare.
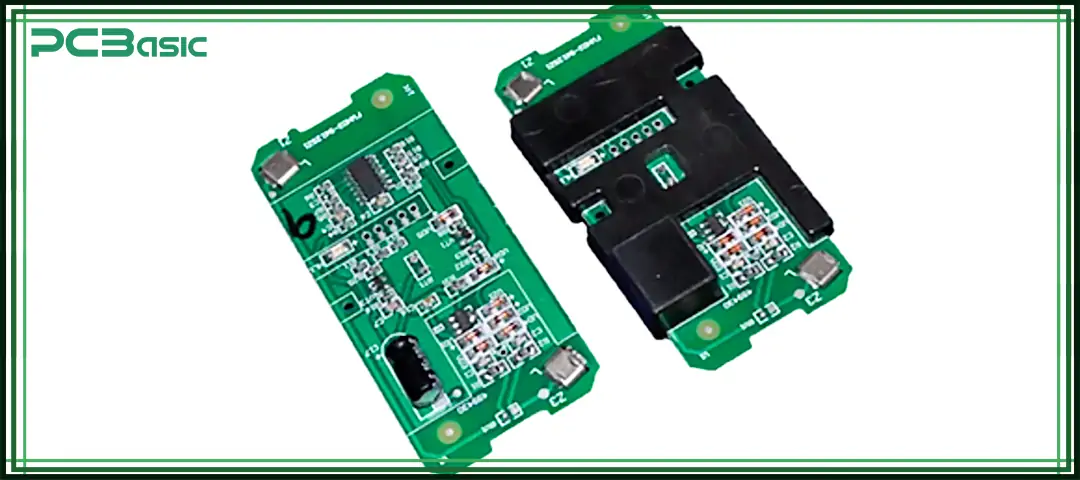
The success of low pressure molding largely depends on the low pressure molding materials selected. These low-pressure molding compounds must possess excellent comprehensive performance, including good flowability under low pressure, strong adhesion to electronic components, thermal stability during heating, as well as strong environmental resistance, such as waterproofing, dustproofing, and chemical resistance. Only by meeting these requirements can the stability of the low pressure injection molding process and the reliability of the finished products be ensured.
Common low pressure molding materials are shown in the following table:
|
Materials |
Key Properties |
Typical Applications |
|
Polyamide (PA) |
Excellent chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength |
Encapsulation of electronic components, sensor protection |
|
Polyolefin (PO) |
Soft, flexible, and provides good sealing performance |
Cable protection, connector sealing, flexible overmolding |
|
Bio-based Polyamides |
Sustainable, plant-based material with good thermoplastic performance |
Eco-friendly electronic packaging, sustainable solutions |
|
Co-polyesters |
High clarity and softness |
Medical device encapsulation, high-end consumer products |
All the above-mentioned low pressure molding materials are thermoplastic. They can soften and flow when heated and solidify and set when cooled. Most materials are UL 94 V-0 flame retardant certified and comply with the RoHS and REACH environmental protection standards. They are currently the most widely used materials in low pressure injection molding.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Low pressure injection molding is a rapid and gentle electronic encapsulation process. The entire process usually includes the following steps:
Accurately place the electronic components that need to be encapsulated-such as exposed PCBs, connectors or wire harness assemblies-into the mold cavity. The mold design must ensure stable positioning of components to avoid offset or mechanical damage.
The low pressure molding compound that has been preheated to a molten state is injected into the mold using a specialized low pressure molding machine. The injection pressure is controlled between 1.5 and 40 bar. The injection process is gentle and stable to ensure that the components are not damaged.
Low-pressure molding materials flow evenly in the mold and gently encapsulate the entire electronic component. Due to their natural adhesion properties, they automatically adhere to the surface of components, achieving excellent sealing and structural protection effects, and preventing the invasion of external factors such as moisture, dust, and mechanical shock.
After the material is injected, it cools and solidifies rapidly in the mold. As the material used is thermoplastics, it can flow after heating and quickly harden when cooled, without the need for a long wait.
After the cooling is completed, open the mold and take out the finished product. The surface of the product is clean and tidy, requiring no subsequent finishing, and can immediately enter the functional testing or assembly stage.
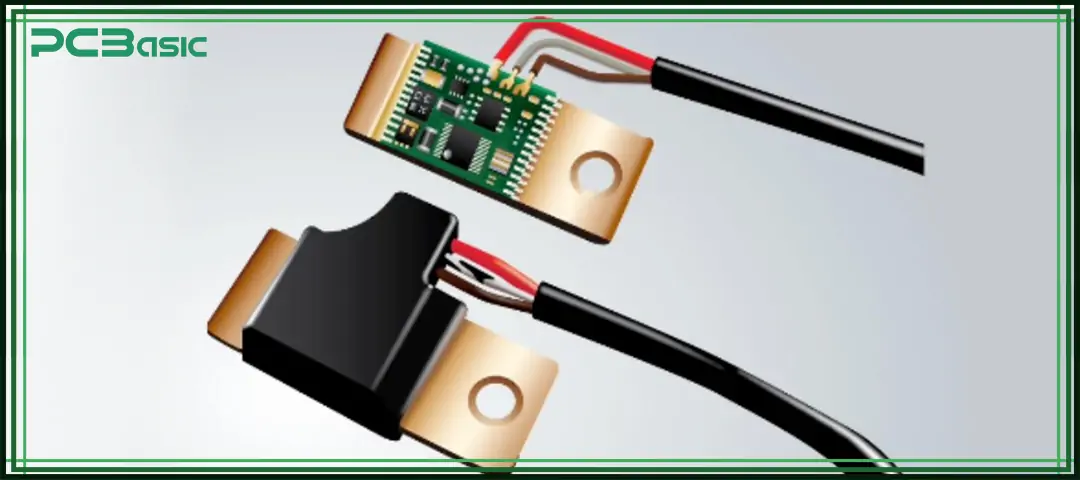
Low Pressure Molding (LPM) is an efficient and safe electronic encapsulation process. It is especially suitable for protecting precision electronic components such as PCBs, sensors, antennas, and wire harnesses. Compared with traditional epoxy potting or high-pressure injection molding, low pressure injection molding is gentler, faster, and more efficient overall.
Here are the key technical features and practical benefits of low pressure molding:
Low Pressure Operation: Low pressure molding systems operate at 1.5–40 bar, which prevents mechanical damage to fragile components.
Low Temperature Processing: Low pressure molding materials melt and flow at 180–240°C, avoiding damage to solder joints or heat-sensitive parts.
Strong Adhesion: Low pressure molding compounds bond directly to component surfaces without primers or surface treatment.
High Protection Rating: The molded parts can reach IP67–IP69 protection levels, offering excellent resistance to water, dust, and chemicals—ideal for automotive, medical, and other demanding environments.
Supports Complex Structures: Suitable for encapsulating 3D shapes and fine features, meeting high-precision packaging needs.
Fast Molding Cycle: The entire process takes only 20–60 seconds, much faster than epoxy potting, which requires hours to cure.
Low Material Waste: Low pressure molding machines use gear pumps to precisely control flow, minimizing material waste.
Immediate Next Step: Once cooled, the material solidifies quickly, and the product can go straight to testing or assembly—no waiting required.
Material Becomes Housing: Low pressure molding materials themselves form the final protective shell, so no additional casing is needed.
Lower Long-Term Cost: Although low pressure molding machines require a higher initial investment, they reduce labor, material use, and time in the long run—lowering the total cost of ownership.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable: The thermoplastic materials used are recyclable, and the process produces minimal emissions. It also complies with RoHS and REACH environmental standards.
All in all, low pressure molding technology provides both excellent component protection and greater production efficiency, making it one of the best encapsulation choices in modern electronics manufacturing.

Low pressure molding, due to its gentle process and excellent protective performance, is widely used in many industries, especially suitable for scenarios where the protection of precision electronic components is required.
Electronics & PCB Injection Molding (pcb injection molding)
Encapsulation of circuit boards
Waterproofing modules like USB drives, power modules, and RFID tags
General PCB protection from moisture, dust, and vibration
Automotive Industry
Encapsulation of under-hood electronics to resist heat and oil
Protection of in-cabin sensors from dust and shock
Overmolding components of EV batteries for insulation and safety
Medical Devices
Used in oximeters, monitors, and diagnostic sensors
Ensures safety and protection for sensitive electronics
Industrial & Consumer Electronics
Smart home products like locks and sensors
Drones, GPS trackers, wearables
Wire harness and cable assemblies for better durability and strain relief
Low pressure molding is highly suitable for small-batch and medium-scale production, and is also very suitable for rapidly developing industries such as electric vehicles (EVs) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Low pressure molding is changing the way electronic components are encapsulated. Compared with traditional process, it is faster, more accurate and more environmentally friendly. Low pressure injection molding has become an ideal alternative to epoxy potting and high-pressure injection molding.
This process uses optimized low pressure molding materials and is combined with advanced LPMS equipment, which can help manufacturers reduce production costs and improve product reliability. And accelerate the overall production speed.
If you need to package sensitive electronic components or want to make the production process simpler and more efficient, then adopting low pressure molding technology is a solution worth considering.
1. What is the best low pressure molding material for PCB encapsulation?
Polyamide-based materials are commonly used for PCB injection molding due to their excellent adhesion, moisture resistance, and thermal stability. For sustainable applications, bio-based polyamides are also gaining traction.
2. How do LPMS machines differ from traditional injection molding machines?
Low pressure molding machines use gear pumps and require significantly lower pressure (1.5–40 bar) compared to traditional screw systems (350–1300 bar). They’re optimized for low pressure molding compounds and sensitive components.
3. Can low pressure molding replace potting entirely?
Yes, in many applications. Low pressure injection molding offers better cycle times, easier automation, and less material waste compared to potting, while delivering equal or superior protection.
4. Is LPIM suitable for high-volume production?
Yes. While originally used for low-volume runs, modern low pressure molding systems and automation platforms now support high-throughput environments.
5. What’s the life cycle of low pressure molding compounds?
Most low pressure molding materials have a shelf life of 2+ years when stored properly. Once molded, they provide long-lasting protection and stability under harsh operating conditions.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
