Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCB Delamination: Causes, Prevention, and Solutions
As you know, PCBs are the backbone of many electronic devices. However, printed circuit boards need protection from delamination. Usually, PCB delamination happens due to manufacturing faults. It's a potentially harmful condition during the manufacturing process and usually results from humidity. Humidity substantially damages the adhesive material and separates the base layers.
Well, a small delamination is bearable but the large scale is what causes real trouble. This article will thoroughly analyze PCB delamination, how to prevent it, and why it happens. So, read it carefully till the end to learn everything about it. Let's get going!
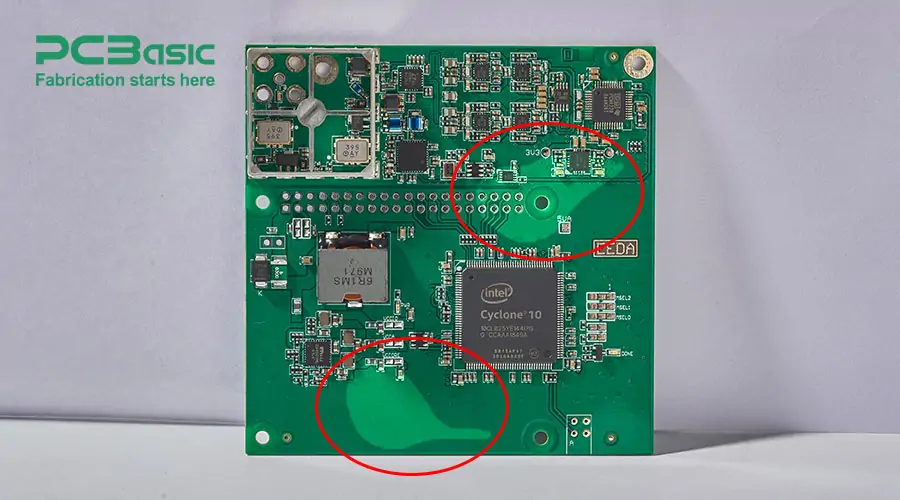
Related forms of delamination are also known as PCB measling and PCB crazing. PCB measling is the formation of very small delaminated white spots. While, crazing is a condition when the fibers in the glass cloth and resin material of a PCB separate.
The following example illustrates the delamination on the surface layer of a PCB. The circular discolored area is where the top layers of material are starting to separate from the base material.
Excess Moisture
The most common reason for delamination is the moisture trapped in the PCB base materials. The unfavorable storage conditions of laminate materials can lead to an uptake in humidity. And, excess humidity in the PCB substrate can cause delamination during fabrication. Furthermore, PCB base materials are hygroscopic. So, they can easily absorb water. Excess moisture in the printed circuit board doesn't always cause delamination, but it'll contribute to CAF (conductive anodic filamentation).
Thermal Stress
The other common factor is the period at which a board is help at high temperatures. Repeated thermal stress can up to high temperatures can cause delamination during assembly. Even after assembly, if the PCB undergoes repeated thermal stress above it's glass transition temperature, the delamination can occur. Delamination due to thermal stress might start in the internal layers without impacting the external layers.
Poor Manufacturing Processes
Poor manufacturing processes can also lead to PCB delamination. PCB has to go through a series of steps during manufacturing such as etching, printing, and plating. If all these steps are completely taken care of, and high-quality materials and equipment are used, there is a significant reduction in the delamination.
Low-Quality Materials
The most significant factor of PCB delamination is the use of low-quality materials. When the quality of materials used in your PCB is not up to the mark, the chances of delamination are higher. Moreover, the use of proper handling techniques for the PCB materials also reduces the delamination process significantly.
Incorrect Type of FR-4 Tg Materials
If you are using FR-4 material with the incorrect type of Tg, than you may face delamination. It can also cause problems with their longevity and reliability. So, it's important to use the correct type of FR-4 Tg materials when manufacturing PCBs. Because, it can affect how well your PCBs hold up over time.
Delamination can impact the optimal performance of the printed circuit boards. Its effects and consequences are:
Electrical Performance Issues
Delamination can peel the copper traces from the dielectric. As a result, it can cause crosstalk, signal reflections, impedance variations, and noise that downgrade the board's electrical performance.
High Risk of Failure
Delamination can weaken the PCB's physical structure, making it vulnerable to mechanical stress and mechanical issues.
Reduced Lifespan
Heat issues, weakened structure, and electrical problems reduce the PCB's lifespan and reliability.
Heat Dissipation Problems
Air is not a good conductor of heat as other board materials. And, delamination creates air gaps that develop regions with thermal resistance that can stress active components on the board.
PCB Delamination vs Measling
As I've discussed earlier in this blog post, delamination is the separation of layers of your PCB base materials, which creates bubbles or gaps that look like blisters. This happens in the manufacturing process when humidity or heat are present in your PCB.
On the other hand, PCB measling is the disintegration of pieces in the weaves inside of the board. It can be tolerable and minor until it's not frequent or if it doesn't bridge soldering eyes and conductors. Furthermore, stress during manufacturing process might cause measling.
Keep a Dry Environment
As mentioned above, delamination occurs when the board is exposed to humidity or moisture. So, if you're storing your PCB for a long time, then make sure to keep it dry. The best way is to keep the board in an enclosed container with no cracks or holes.
Proper Baking
Baking of board before thermal processing is a common practice in the PCB industry. This is required because humidity can be trapped between the dielectric and copper layers and cause delamination. Baking of boards before thermal processing helps to eliminate moisture from the board surface. Thus, it'll help to prevent delamination of PCB.
Use High-Quality Components
As mentioned above, the quality of materials and components can impact the performance of the PCB. So, if you make sure to use the high quality materials and components than you PCB will work properly and you'll prevent it's delamination.
Proper Handling
Another common factor to prevent delamination is proper handling. It starts with choosing a supplier that can pass all qualification tests and can meet your needs. Adding more, must store your PCB at optimal conditions that'll not impact it's performance.
First of all, clean the board's surface by using wipes.
Drill at least two holes into the delamination blister by using the micro drill. Don't drill too deep to expose the circuits or inner planes.
Bake the PCB in the oven to eliminate any moisture if present.
Then, pour the epoxy into the cartridge and inject it into one of the drilled holes.
Apply light pressure on the board if the blister isn't filled properly.
Cure the epoxy at room temperature for 24 hours or at 74°C (165°F) for one hour.
Scrape off any excess epoxy by using a knife or scraper.
Evaluation
After drying, must do a visual examination to check the color and texture. Additionally, do electrical tests on conductors around the repaired areas to see if everything works properly.
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)
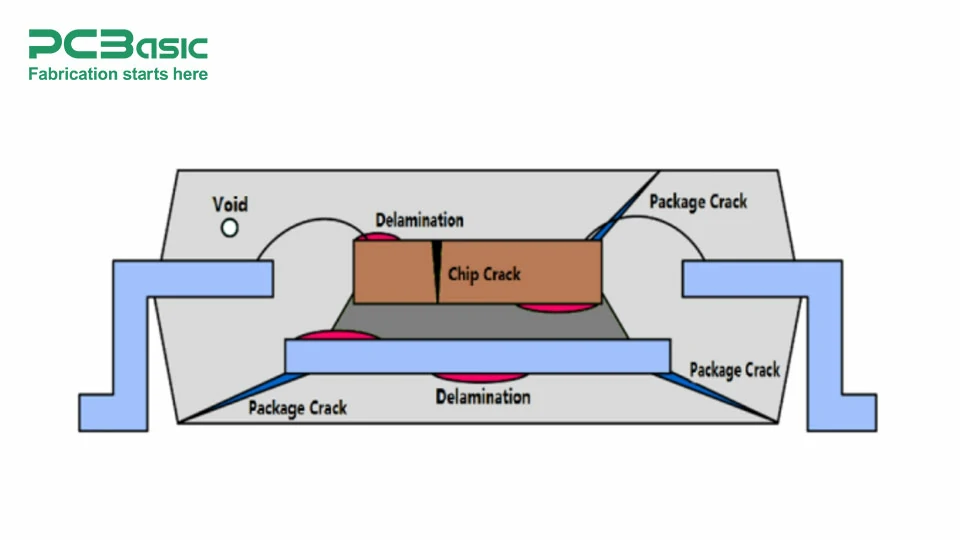
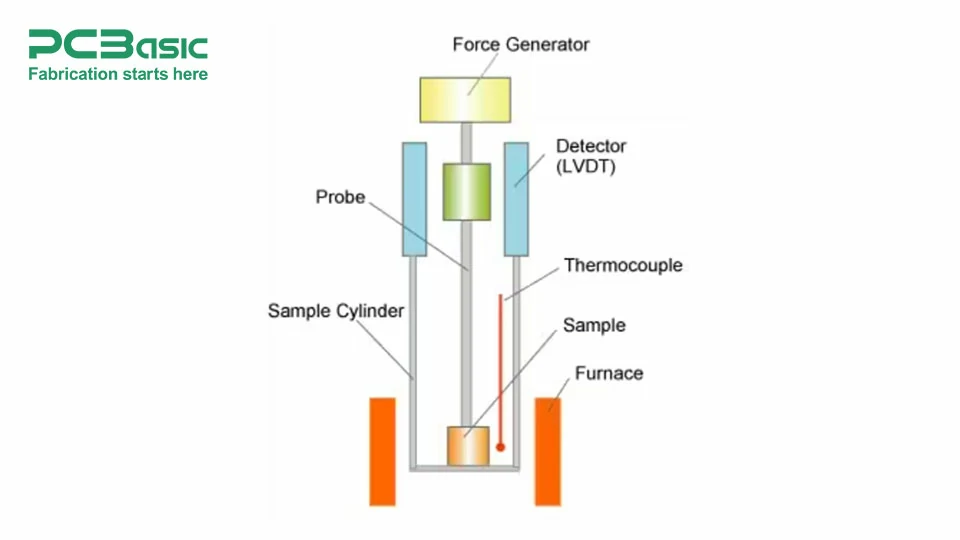
Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA)
This test measures how much energy is required to break a sample. It applies pressure to the sample and then measures how much energy is utilized to break it. If there's no delamination present, then it shouldn't reveal any changes in braking force.
It is very important to have clear parameters to get an accurate PCB to withstand periods of high demand. Following are the stress testing parameters to avoid PCB delamination.
Solder Float Test
It's a stress testing parameter and an accelerated lifetime test. It simulates the effects of a solder joint subjected to thermal cycling. This test is performed at 288°C.
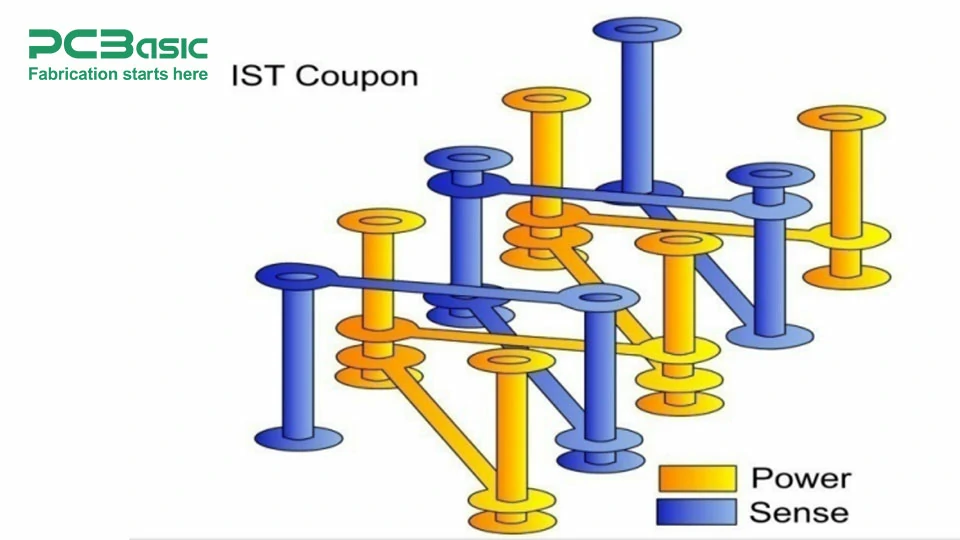
Interconnect Stress Test (IST)
This test allow engineers to pull out common modes and thereby reduce problems. This test allows to identify if the PCBs are at risk and that too prior to manufacture. In this test, a static force is applied to the PCB. The static force is applied for ten seconds and then released for 30 seconds. This cycle is repeated for one minute.
This test involves stimulating the high-temperature reflow process by heating up and cooling down the PCB multiple times. Each time the PCB is heated up and cooled down is referred to as "N-pass". the number of N-passes in which you can observe no delamination is your max allowable number of N-passes.
Time at 260°C
Do you want to make sure that your PCB will not delaminate? Then make sure that the time at 260°C is greater than ten minutes. Furthermore, the time of temperature of the PCB during testing depends on the type of epoxy used in it's manufacture. Few epoxies are more heat resistant that others. So, they require less time at a high temperature.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote





Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
