Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > IPC 6012 Standard: A Comprehensive Guide
In many critical applications, such as medical, military, automotive electronics and aerospace, any minor defect can lead to system failure and even pose safety hazards. Therefore, ensuring the manufacturing quality, structural stability and electrical performance of PCBs has become a key factor for the success of electronic products. Against this background, the IPC 6012 standard was developed.
IPC 6012 not only clarifies the technical requirements of PCBs in terms of materials, electroplating, dimensions, tolerances, lamination and inspection, but also subdivides the product grades. Understanding the structure and application of the IPC 6012 standard is the basis for ensuring product compliance, reducing failure rate and improving customer satisfaction.
In this article, we will comprehensively analyze the definition, scope of application, technical requirements, grade classification of the IPC 6012 standard, as well as its relationship with other IPC standards. This article can help you gain a deep understanding of this core industry norm and guide you on how to effectively apply it in actual projects. So, what exactly is IPC 6012?

IPC 6012 is a widely recognized standard in the electronics manufacturing industry regarding the certification and acceptance performance specifications of rigid printed circuit boards. This standard was released and issued by the Electronic Industry Connectivity Association. The basic requirements for PCBs in terms of quality, durability and reliability have been clearly stipulated. For enterprises engaged in PCB manufacturing, inspection or quality control, the IPC 6012 standard is an indispensable basic specification.
IPC 6012 can provide a clear performance benchmark for production, ensuring consistency and traceability during the manufacturing process. It is a standard specifically applicable to rigid PCBs, including single-sided boards, double-sided boards and multi-layer boards. Although IPC 6012 is a widely recognized standard in the industry, it is not legally mandatory. Many OEM manufacturers will require their suppliers to comply with or obtain IPC 6012 certification. So, what are its requirements?
The IPC 6012 standard divides rigid PCBs into three performance grades. Each grade corresponds to different quality, reliability and functional requirements. Next, we will explain these three levels. Understanding the IPC 6012 class is crucial for material selection, layout design and finding qualified manufacturers.
IPC 6012 class 1 is applicable to general-purpose electronic products that do not require high reliability. Such products are usually low-cost and non-critical equipment. Even if there are appearance defects, it is fine as long as the basic functions are normal. Typical applications include:

Toys and gift electronic products
Simple consumer electronic devices
Disposable or short-life-cycle equipment
Although such products are not mandatory to undergo IPC 6012 certification, some low-volume manufacturers still refer to the IPC 6012 standard for basic process control.
IPC 6012 class 2 is the most widely used performance grade in the industry. It is applicable to products that require continuous and stable operation but are not critical safety tasks. The requirements of IPC 6012 class 2 include:
Medium-level solder joint control
Minor defects in appearance are allowed as long as they do not affect the functionality
Control the thickness, size and thickness of the hole copper
It has good functional reliability, but does not require continuous operation under full load or extreme conditions. Typical applications include industrial automation control equipment, consumer electronic products (such as mobile phones and tablet computers), household appliances, office electronic equipment, etc.
IPC 6012 class 2 strikes a balance between performance and cost and is the preferred grade for most commercial products.
IPC 6012 class 3 is the most stringent grade in the IPC 6012 standard. This level is applicable to critical mission scenarios. It does not allow for any malfunctions, as any malfunction could pose security risks or cause significant losses to the application. The requirements of IPC 6012 class 3 include:
Higher standard annular ring dimensions and hole copper thickness
Stricter wire spacing and wire width tolerances
There is almost zero tolerance for appearance and structural defects
Intensive tests such as thermal cycling and cross-section (microsection) analysis must be carried out
Typical applications include aerospace electronic equipment (flight control systems), military products and defense systems, medical electronic equipment (such as pacemakers and imaging systems), automotive safety systems (such as autonomous driving and airbag controllers), etc. Due to the high reliability requirements of IPC 6012 class 3, manufacturers often need to undergo strict IPC 6012 certification and accept quality audits.
The key differences between IPC 6012 class 2 and class 3 are summarized in the table below:
|
Item |
IPC 6012 Class 2 |
IPC 6012 Class 3 |
|
Application Type |
Commercial / Industrial Products |
Critical / Safety-Critical Electronic Products |
|
Inspection Criteria |
Focus on functional reliability, minor defects allowed |
Near-perfect manufacturing quality required |
|
Annular Ring Dimensions / Hole Plating Thickness |
Standard requirements |
Stricter control of geometry and plating thickness |
|
Testing and Validation |
Functional and continuity testing |
Includes thermal, environmental, and structural integrity testing |
|
Documentation & Traceability |
Moderate requirements |
High-level traceability and detailed documentation required |
Usually, IPC 6012 class 1 is less used in practical applications. It is only applicable to general electronic products with extremely low reliability requirements. This is why in the actual project evaluation and standard setting, class 2 and class 3 are usually compared with emphasis only. When choosing IPC 6012 class 2 vs. class 3, it needs to be determined based on the purpose of the product, the expected lifespan and whether it is a critical mission.
After understanding the grade classification of IPC 6012, next we will focus on introducing several key technical requirements in this standard. These requirements are directly related to the electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, solderability and long-term reliability of PCBs, and are the core basis for achieving class 2 and class 3 quality grades.
The IPC 6012 standard defines the certification and performance evaluation criteria for rigid PCBs, including but not limited to:
Mechanical dimensions and structural tolerances
Electrical connectivity and insulation requirements
Welding performance and electroplating quality
Specifications for base materials, inner layer structures, surface treatments and protective coatings
The goal of the IPC 6012 certification is to ensure that PCBs have consistent manufacturing quality and reliable operational capabilities in different application environments. It mainly targets the following aspects:
1. Copper Thickness
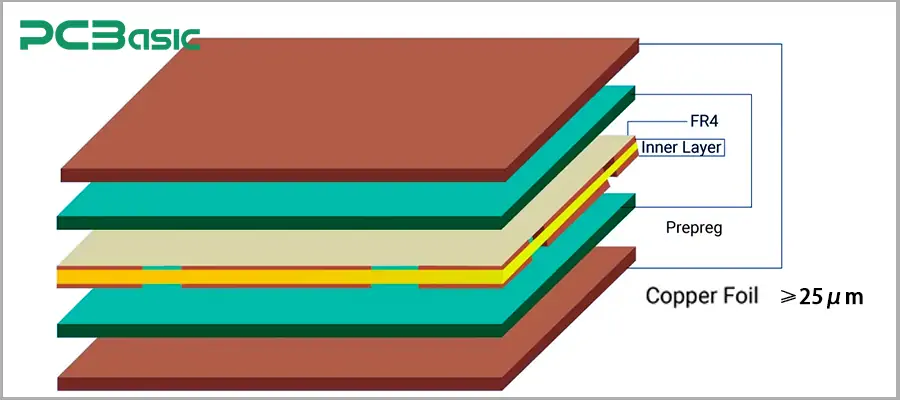
The copper layer on the PCB determines the current-carrying capacity.
The IPC 6012 class 2 requirements apply to common industrial or consumer electronic products. It only requires that the thickness of the copper layer meet the basic performance requirements.
The IPC 6012 class 3 requirements are often used in high-reliability products. It requires the copper to be thicker, especially for through-hole plating, where the copper thickness must be ≥25μm, to ensure it can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress.
2. Solder Mask
The solder mask layer is a green (or other colored) coating used to protect the circuit and prevent short circuits. Requirements include:
It adheres firmly and does not fall off
There are no pinholes, bubbles or delamination on the surface
It can be accurately aligned with the solder pad
In class 3, the solder mask layer must be almost defect-free; otherwise, it may affect the long-term reliability of the product.
3. Annular Ring
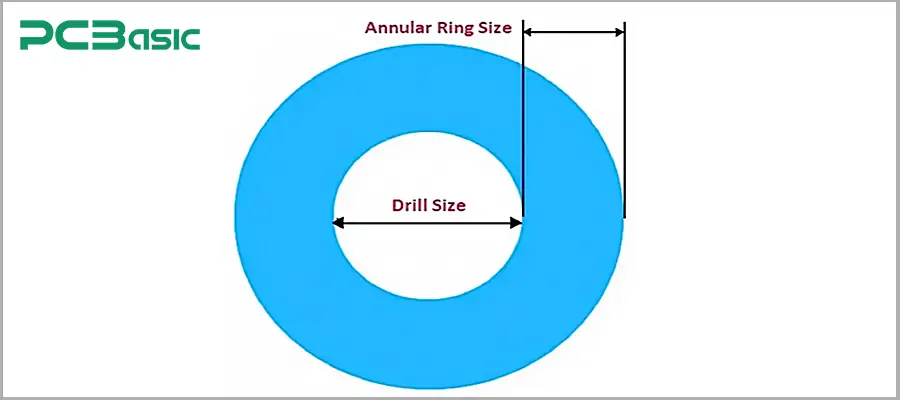
When we drill holes in a PCB, there will be a circle of copper around the holes, and this is the annular ring. It is responsible for connecting the circuits of different layers.
At non-critical positions, class 2 allows for slight damage (breakage). Class 3 requires that no fracture is allowed at any position; otherwise, it may lead to welding failure.
4. PTH - Plated Through Hole
A layer of copper should be plated inside the through hole to form a connection between the upper and lower layers. IPC 6012 requires that this layer of copper should have a certain thickness and adhesion:
Class 3 requires copper with a thickness of ≥25μm to ensure reliability under high temperatures or repeated plugging and unplugging.
The core differences between IPC 6012 class 2 and class 3 lie in tolerance control, defect tolerance and detection strictness, as shown in the following table:
|
Item |
IPC 6012 Class 2 |
IPC 6012 Class 3 |
|
Plated Through-Hole Thickness |
Standard requirement (some deviation allowed) |
≥25μm, consistent and tightly controlled |
|
Annular Ring Break Tolerance |
Acceptable in non-critical areas |
Completely prohibited |
|
Solder Mask Defects |
Minor defects acceptable |
Near-zero defects required |
|
Dimensional and Positional Tolerance |
Standard precision |
High-precision control |
|
Inspection Methods |
Standard electrical + visual inspection |
Includes cross-section analysis and X-ray inspection |
By following the IPC 6012 standard and choosing the appropriate grade based on the actual needs of the products, manufacturers can effectively control risks, improve product quality and meet customer expectations. In conclusion, understanding these key requirements is not only the basis of product compliance, but also a powerful guarantee for obtaining IPC 6012 certification and winning the trust of high-end customers.
After mastering the key technical requirements of IPC 6012, we also need to understand another important standard that is often used in combination with it - IPC-A-600. Many people often confuse IPC 6012 with IPC-A-600. Although they are both related to the quality assessment of PCBs, their uses and emphases are different.
|
Item |
IPC 6012 |
IPC-A-600 |
|
Type |
Performance Specification |
Acceptability Standard |
|
Purpose |
Defines structural, electrical, and mechanical requirements for PCBs |
Provides visual criteria for acceptable and non-acceptable PCB defects |
|
Key Focus |
Plating thickness, copper layers, dimensional tolerances, hole quality, electrical testing |
Solder joint appearance, hole wall defects, delamination, foreign matter, bubbles, scratches, etc. |
|
Usage Stage |
Used during design evaluation and manufacturing process control |
Used during final inspection and quality acceptance |
|
Target Audience |
Engineers, manufacturers |
Inspectors, customers, auditors |
|
Relationship |
Specifies “what the board must do” |
Shows “what the board should look like” |
IPC 6012 and IPC-A-600 complement each other. IPC 6012 defines "the standards that must be met", while IPC-A-600 shows "what these standards look like". Usually, IPC 6012 is used in the manufacturing process, and IPC-A-600 is referred to in the inspection process. Then, let us learn how to comply with IPC 6012. Learn more about IPC-A-600 standard:https://www.pcbasic.com/blog/ipc-a-600.html
Ensuring compliance with the IPC 6012 standard is an important responsibility for rigid PCB manufacturers. The following are some steps we have summarized that can help you achieve compliance.
1. Understand the IPC 6012 standard
The first step to ensuring compliance is, of course, to understand the standards first. IPC 6012 stipulates the minimum acceptance criteria in the following aspects:
Structural integrity
Conductor spacing
Insulation performance
Copper plating thickness
Quality of the solder mask
Before applying for IPC 6012 certification, we must study the entire specification in detail and understand the required test processes, documentation requirements and production control requirements.
2. Determine the required product grade
After understanding the IPC 6012 standard clearly, it is necessary to select the required level. Determining the appropriate level is a crucial step to ensure compliance. We often make comparisons between IPC 6012 class 2 and class 3. The differences between IPC 6012 class 2 and class 3 have been clearly expounded above, so there is no need to repeat them here.
3. Adjust and optimize the manufacturing process
The third step is to adjust and optimize the manufacturing process. In order to meet the IPC 6012 class 2 requirements or class 3 requirements, manufacturers must optimize the entire PCB production process. This can better ensure that everything from material selection to process control complies with the standards.
First of all, the electroplating thickness of the through holes must meet the requirements. If it is the requirement of IPC 6012 class 3, the copper thickness of the through hole needs to reach ≥25μm and maintain consistency. Secondly, the circular rings on the PCB should be strictly controlled to prevent problems such as breakage and misalignment. For the solder mask layer, class 2 can accept minor defects, but class 3 requires almost no flaws. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the hole positioning, plate dimensions, etc., comply with strict tolerance ranges. All these items are the key contents to be inspected during the review. Therefore, the entire manufacturing process needs to be adjusted and optimized.
4. Implement a comprehensive testing and inspection process
To meet the IPC 6012 standard, it is not only necessary for the production process to be qualified, but also for the inspection and testing to reach the standard. Enterprises must conduct visual inspections in accordance with IPC-A-600 to ensure that the appearance of the products meets the requirements.
For high-reliability applications, additional cross-sectional analysis is required to check the integrity of the inner layer structure. Electrical connectivity tests are still required to verify the performance of the lines. For the class 3 products with extremely high requirements, equipment such as X-ray inspection and AOI automatic optical inspection must be equipped to identify minor defects such as solder joint bubbles, false soldering and offset.
5. Cooperate with certified manufacturers
For enterprises without an internal IPC-certified engineering team, choosing to cooperate with PCB manufacturers that have IPC 6012 certification is one of the most ideal paths to ensure quality and compliance.
Note: Before cooperation, it should be confirmed whether the PCB manufacturer supports the requirements of different levels such as IPC 6012 class 2 or IPC 6012 class 3. Qualified manufacturers usually have a mature process control system and complete testing capabilities.

The clear acceptance criteria of IPC 6012 effectively prevent the occurrence of various common PCB defects:
1. The coating on the through holes is too thin, causing unstable current, open circuits within the board, and even thermal failure. However, IPC 6012 can effectively prevent electrical failure caused by insufficient copper thickness in through-holes by setting a lower limit requirement for the thickness of the electroplated copper layer in through-holes. This standard also requires manufacturers to verify by means such as microsection inspection to control the reliability of conduction from the source.
2. IPC 6012’s control over annular ring dimensions and hole alignment helps prevent breakout-related soldering failures.
3. In thermal cycling or humid environments, layer separation and voids can cause signal interruption or mechanical fatigue. The IPC 6012 standard stipulates requirements such as lamination strength, material consistency, and the proportion of void area, which can effectively prevent structural defects caused by delamination and material voids.
4. Offset of the solder mask layer or pinhole detachment may cause bridging, oxidation or electrical short circuits. In IPC 6012 class 3 requirements, the solder mask must be tight, accurately aligned and have no obvious defects. This can effectively reduce the impact of solder mask defects on reliability.
5. If the size deviation of the circuit board is too large or the hole positions are inaccurate, it will lead to assembly failure or mechanical stress concentration. The IPC 6012 standard has detailed tolerance specifications for contour dimensions, drilling accuracy and center distance of holes. The dimensional and hole position tolerances of the control board can ensure assembly consistency.
The above only lists a few examples of how the IPC 6012 standard effectively prevents PCB defects. Besides, IPC 6012 has more benefits. So, when should we use the IPC 6012 standard?
When your project has requirements for the reliability, consistency or compliance with industry standards of rigid PCBs, the IPC 6012 standard should be used. Typical applicable scenarios include:
Class 2 Applications: such as consumer electronics or general industrial products. These products are function-oriented and can allow for minor appearance defects.
Class 3 applications: such as aerospace, automotive safety systems, medical equipment, etc. These products have extremely high requirements for durability and zero defects and must strictly comply with the IPC 6012 class 3 requirements.
Supplier quality control: By requiring IPC 6012 certification, ensure that suppliers comply with the standards in terms of materials, structures and testing.
Unified internal inspection standards: Establish clear acceptance criteria in combination with IPC-A-600.
|
Standard / Resource Name |
Description |
Relevance to IPC 6012 |
|
IPC-A-600 |
Acceptability of Printed Boards with visual examples of defects |
Used alongside IPC 6012 to judge accept/reject conditions |
|
IPC-2221 |
Generic standard for PCB design, covering layout, spacing, and rules |
Complements IPC 6012 by ensuring design aligns with manufacturing |
|
IPC-T-50 |
IPC glossary of terms and definitions |
Helps clarify terminology used in IPC 6012 certification and related standards |
|
IPC-6011 |
Generic performance specification for the IPC-601x series |
Serves as the base document for understanding class 2 and class 3 requirements |
|
IPC Training & Certification Programs |
Official training and exams from IPC |
Supports proper application and understanding of IPC 6012 class 2 / class 3 requirements |
The IPC 6012 standard is one of the core standards in the field of PCB manufacturing. Today, with the continuous upgrading of electronic products, applying the IPC 6012 standard remains the best industry practice for creating high-quality PCBs. Whether it is PCB manufacturers, system integrators, or quality control personnel, understanding and applying this standard can significantly enhance the reliability of PCBs and reduce product failure rates. For applications in key fields, the requirements of IPC 6012 class 3 should be strictly implemented. For most industrial-grade products, the requirements of IPC 6012 class 2 can be adopted. In conclusion, choosing the appropriate standards is like buying an insurance policy for product quality.
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
