Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > The Ultimate FR-4 PCB Guide: From Material Properties to Application Decisions
Today, with the rapid development of electronic design and manufacturing, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are used in almost all electronic devices, such as smartphones, medical instruments and aerospace systems. Among these PCBs, the most common core material is FR-4. This material offers balanced performance in terms of cost, mechanical strength, thermal stability and electrical insulation. Therefore, the FR-4 PCB has always been regarded as a reliable and economical standard choice.
As electronic products become smaller and more complex in function, the demand for high-performance and multi-purpose PCB materials is also increasing. Although high-performance materials such as aluminum PCBs and polyimide PCBs are already available on the market, FR-4 PCBs remain the preferred choice for most conventional applications.
This article will provide a comprehensive introduction to the FR-4 PCB, including its performance characteristics, common types, practical applications, and comparative analysis with other materials. Whether you are a PCB engineer or sourcing manager, understanding the FR-4 material properties, such as the thermal conductivity of FR-4 and mechanical properties, can help you make more reasonable material choices.
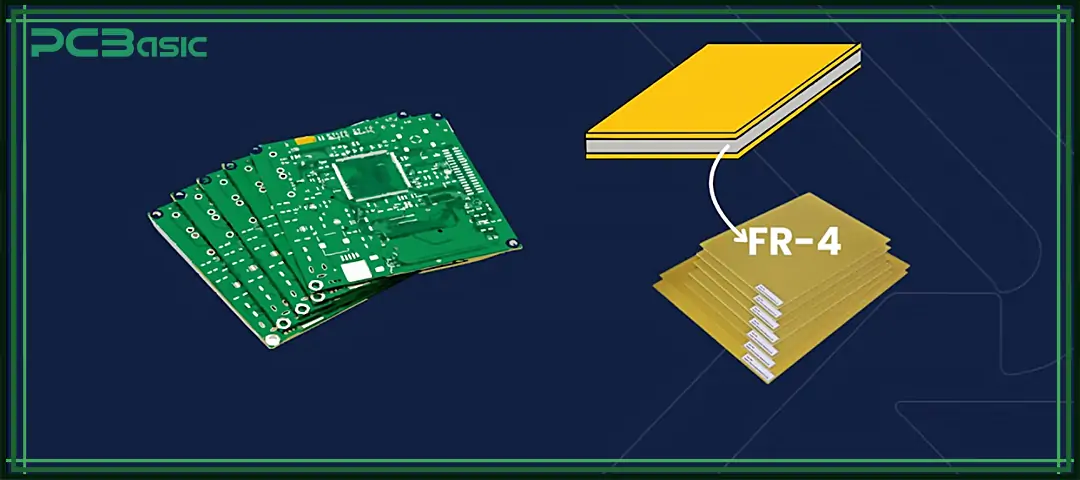
FR-4 is the abbreviation of "Flame Retardant Level 4", which is a material classification standard formulated by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) of the United States. The FR-4 substrate is made by bonding woven glass fiber cloth with epoxy resin. This material has rigidity, flame retardancy and high reliability, and is the main material for most standard FR-4 boards.
This flame-retardant epoxy laminate material complies with UL94V-0 standards, which means it can quickly extinguish when ignited. FR-4 was originally used to replace the less performant G-10 material. Because it performs stably and evenly in terms of electrical insulation, mechanical strength and cost, it soon became a commonly used material choice in various electronic products.
There are various types of FR-4 PCB materials, which are mainly classified based on the differences in their glass transition temperature (Tg) and other FR-4 material properties. Each type is suitable for different application requirements and working environments. The following are several common types of FR-4 materials:
The Tg range of the standard FR-4 is usually between 130°C and 150°C. This type of material is suitable for general electronic products, such as daily consumer electronic devices. Its price is relatively low, making it the most cost-effective choice among all FR-4 types. It is very suitable for basic circuit board applications with low performance requirements.
The glass transition temperature range of High Tg FR-4 is approximately 170°C to 200°C. Compared with the standard FR-4, it has better thermal stability and durability in high-temperature environments. This material is highly suitable for the manufacturing of multilayer PCBs and high-power circuit boards, effectively reducing the risk of material deformation or performance degradation caused by thermal stress.
Halogen-Free FR-4 does not contain brominated flame retardants, thus being more environmentally friendly and meeting green manufacturing standards such as RoHS. Because it is safer for human contact, it is often used in devices that require direct human interaction, such as wearable devices and medical electronic products. It maintains its flame-retardant performance while reducing its impact on the environment and human health.
The Comparative Tracking Index (CTI) of high CTI FR-4 is greater than 600V, featuring stronger insulation performance and better resistance to tracking. This material is suitable for circuit board design in high-voltage environments, effectively preventing breakdown problems caused by moisture or dust, and enhancing the safety and long-term stability of the product.
FR-4 Without Copper is a type of FR-4 laminate without copper layers. It is mainly used for making non-conductive structural components such as mechanical spacers, insulating plates or processing templates. Although it is not used for circuit conduction, it still retains good FR-4 mechanical properties, including high strength and dimensional stability, and is suitable for structural support or thermal isolation applications.
FR-4 PCB is widely used because it has well-balanced performance in mechanical properties, thermal properties, and electrical properties. Below are some key FR-4 material properties:
|
Property |
Value |
|
Dielectric Constant (Dk) |
3.8 – 4.7 |
|
Dissipation Factor (Df) |
0.02 – 0.03 |
|
Volume Resistivity |
>10¹³ Ω·cm |
|
FR-4 Thermal Conductivity |
0.3–0.4 W/m·K |
|
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) |
130–200°C |
|
Moisture Absorption |
~0.10% |
|
FR-4 Mechanical Properties |
Tensile: 350–500 MPa, Flexural: 400–600 MPa |
|
RoHS/REACH Compliance |
Yes |
The thermal conductivity of FR-4 is approximately 0.3 to 0.4 W/m·K. This level is suitable for low to medium-power circuit designs. However, if the circuit generates a high amount of heat, the heat dissipation capability of FR-4 may not be sufficient.
Although FR-4 PCB has certain limitations in thermal conductivity, it still has excellent mechanical strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability. These characteristics allow it to maintain reliable performance in many working environments and make it suitable for most common electronic products.
Engineers and manufacturers have continued to choose FR-4 PCBs over the long term because they have multiple obvious advantages and are suitable for the designing and manufacturing of various electronic products. The following are the main benefits:
The manufacturing process of the FR-4 board is already very mature and has high production efficiency. Compared with high-performance materials such as ceramics or polyimide, FR-4 material is cheaper and is currently one of the most cost-effective PCB substrates.
Almost all PCB manufacturers offer FR-4 material of different grades and thicknesses. Whether locally or globally, it is easy to source, and the material supply is abundant.
FR-4 PCB is suitable for various applications. From simple prototype boards to complex multilayer circuit boards, it can meet all of them. It supports the design of single-sided, double-sided and multilayer boards, and is widely used in consumer electronics, industrial control, communication equipment and other fields.
The FR-4 substrate is very stable during use. It can still maintain good performance in harsh environments such as high humidity or high temperatures. It has low moisture absorption, and it is not prone to deformation or failure due to environmental changes and is not likely to have problems even after long-term use.
The FR-4 PCB has relatively high dielectric strength and can effectively prevent electrical breakdown. At the same time, it has a relatively low dielectric loss, making it suitable for signal transmission from low to mid frequencies, ensuring the stability of the signal and the safety of the circuit.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
FR-4 PCB is recommended in the following situations:
1. The operating temperature of the project is within a moderate range and does not generate excessive heat.
2. The circuit mainly handles low-frequency signals or digital signals.
3. The design does not require high rigidity, but good electrical insulation is needed.
4. A cost-effective solution is required, and fast prototyping or production is needed.
FR-4 PCB is not recommended in the following situations:
1. The environment requires strong thermal dissipation, but FR-4 has poor thermal conductivity.
2. The circuit operates above 2GHz, or has high requirements for impedance control.
3. The product structure requires bending or folding. FR-4 is a rigid material and cannot bend.
4. The product has limited space or is subject to strong vibration. FR-4 material is not flexible or stable enough in such conditions.
5. Before design, it is recommended to confirm the FR-4 material properties with your PCB manufacturer to ensure the selected material meets the project requirements.
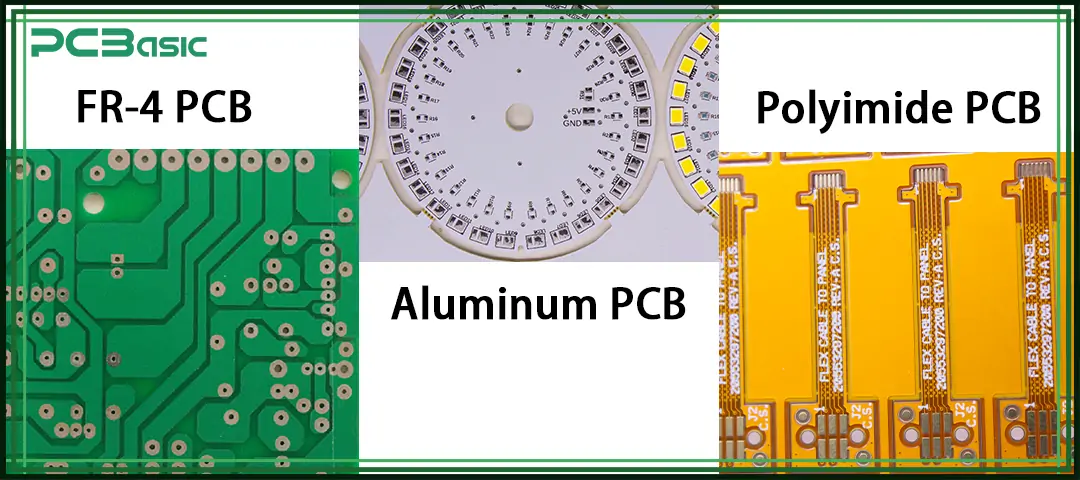
Aluminum PCB is a type of printed circuit board (PCB) that uses aluminum as the base layer. Its main advantage is good thermal performance. An aluminum PCB typically consists of three layers: the bottom layer is the aluminum base layer, the middle is the dielectric layer, and the top is the copper circuit layer.
Polyimide PCB is a PCB made from polyimide material. This material can be used to create either flexible boards (flex) or rigid-flex boards (rigid-flex). Its features include high flexibility, high-temperature resistance (up to 260°C), and excellent chemical resistance.
The table below summarizes the comparison of the three PCB materials across key performance parameters:
|
Performance Parameter |
FR-4 PCB |
Aluminum PCB |
Polyimide PCB |
|
Base Material Composition |
Fiberglass + Epoxy Resin |
Aluminum + Dielectric Layer |
Polyimide Resin (Flexible Polymer) |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
~0.3 W/m·K (thermal conductivity of FR-4) |
1–3 W/m·K |
~0.6–0.8 W/m·K |
|
Structure Type |
Supports multilayer boards |
Typically, a 3-layer structure |
Supports flexible and rigid-flex designs |
|
Flexibility |
Rigid structure |
Rigid structure |
Flexible / Bendable |
|
Max Operating Temperature |
~150–170°C |
~150–200°C (depends on construction) |
Up to 260°C |
|
Rigidity Strength |
Moderate |
High |
Flexible to medium rigidity |
|
CTE Matching (Thermal Expansion) |
Poor match with copper |
Better match with copper |
Good match, high-dimensional stability |
|
Chemical Resistance |
Good |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Durability |
Moderate |
High |
Very High |
|
Cost |
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
Typical Applications |
General electronics, digital boards |
LED lighting, power modules, high-frequency RF |
Aerospace, wearables, medical implants |
FR-4 PCB is currently the most widely used circuit board material in the electronics industry. It has high reliability, low cost and a wide application range (versatility), and is very suitable for the design of most electronic products. Its FR-4 thermal conductivity, mechanical strength and dimensional stability can also meet the requirements of conventional applications.
But as electronic devices become smaller, faster, and generate more heat, we need to understand the limitations of FR-4 material. In some applications that require higher performance, such as high-temperature or products that need flexible structures, aluminum PCBs and polyimide PCBs would be better choices.
Ultimately, which PCB substrate to choose depends on your specific requirements, such as the application environment, budget cost, and reliability requirements of the product. As long as you are clear about the FR-4 mechanical properties, advantages and disadvantages, you can make more appropriate material choices in the project.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
