Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > FR4 Material PCB-All you need to know about flame retardant circuit board
If you are here, you are probably already familiar with Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). Modern electronics consider those boards an essential component. The PCBs enable electronic components to connect and communicate with each other through lines of wires.
Determining the right material for a PCB is crucial in determining the board’s performance, durability, and functionality. The most common and well-used material for PCBs is FR4. FR4 is a type of fiberglass epoxy laminate material.
In this article, we will examine FR4, its properties and unique abilities, and the reasons for its widespread use in PCBs.
FR4 is not the only material available, so we will also compare other materials to understand which one suits the best for your application.
FR4 is a type of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. It is a type of composite material consisting of layers of fiberglass cloth clogged together with an epoxy resin binder.
This type of material provides extreme mechanical strength, while epoxy resin provides insulation and protection from moisture and different type of environmental factors.
PCB manufacturers widely use FR4 material due to its excellent electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. For new PCB designs, it is recommended to use FR4 most often. The material can handle both simple and complex PCB designs as one.
When you order PCB or PCBA, you will often be provided with FR4 as the first option. This material is very common and recommended among new designs. If you have any doubt regarding the PCB material you should use, FR4 might be your right choice.
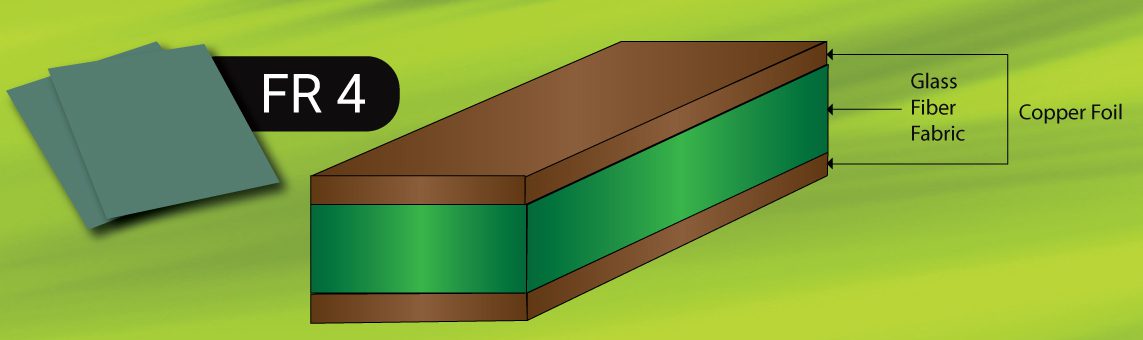
FR4 has many properties and strengths that make it an ideal material for PCB manufacturing. Here are some of the most important properties of FR4:
1. High Tensile Strength – The FR4 has a high tensile strength. This type of strength makes it extremely suitable for use in PCBs that require mechanical stability. The high tensile strength is especially useful for use in high-stress applications.
2. Low Water Absorption – FR4 has a low water absorption rate. What it means is basically it has the ability to resist moisture and humidity. This is extremely useful in high-humidity environments or outdoor and industrial applications.
3. Thermal Stability – FR4 is known to be the best material for thermal stability. It can resist high temperatures without losing its material quality. For applications such as power supplies, this is crucial. Power supplies PCB circuits can often overheat.
4. Electrical Insulation – Brilliant isolation which can prevent electrical currents from flowing between different layers of the PCB. By avoiding this, we can eliminate most causes of short circuits and other electrical problems.
Referring to the paragraph above – it’s mostly due to its strengths and properties. FR4 is a very popular choice for printed circuit board manufacturing due to its excellent electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. Its cost-effectiveness is one of the main reasons why PCB manufacturers commonly use FR4 in their boards. It is much cheaper than other materials used in PCB manufacturing, such as ceramic or Teflon. FR4 is also widely available and can be easily sourced from many PCB manufacturers.
When you are looking to produce your PCB board you might look at different factors. Factors such as price, quality, and speed of manufacturing play an important role. FR4 answers all the above and enables designers to get the highest quality at the lowest cost.
Another reason FR4 is so commonly used in PCBs is its excellent electrical properties. FR4 has a low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor, which means it can maintain a stable signal and minimize signal loss. Its high insulation resistance and breakdown voltage also make it ideal for high-voltage applications.
When we use a certain material we want to make sure it suits our application. For FR4, most of its abilities related to electrical properties can fulfill the needs of most common designs.
FR4 is also mechanically stable, with a high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand mechanical stress, vibration, and thermal shock, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. FR4’s thermal properties are also excellent, as it has a low coefficient of thermal expansion and can withstand high temperatures without degrading.
These are the main reasons why This type of PCB material is most commonly used. When you are about to choose the material for your application, you should refer to this paragraph to verify if the material can fulfill your needs.
1. Preparation of Raw Materials: The manufacturing process started with raw material preparation, which consists of epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth. The fiberglass is normally created with fin glass fiber, which is woven into the fabric structure. While epoxy is a thermosetting polymer that works on composite matrix.
2. Impregnation of Fiberglass Cloth: The prepared fiberglass cloth is impregnated with epoxy resin. It is performed in controlled conditions to uniformly distribute resin throughout the cloth. After that, cloth coated with resin is wound on a larger roll.
3. Layering and Stacking: In this phase, many layers of fiberglass coated with resin are stacked on top of each other. The layers used can be different depending on the thickness needed and the features of the final FR4 material. During this process, there is a need for more materials or substrates for certain applications.
4. Curing Process: Now the curing process is applied to the stacked layers of resin-coated cloth. In this process, pressure and heat are applied in a controlled configuration. Due to the heat applied, there is a chemical reaction done by epoxy resin, with crosslinking and hardening, to make the solid matrix. Due to the curing technique, there is a layer of the cloth that becomes strongly bonded with each other and makes a durable structure.
5. Cooling and Inspection: The composite material is now allowed to cool down after the completion of the curing process. After cooling, it faces a detailed inspection to make sure uniform structure, accurate bonding, and defects are absent. Any faults found during the inspection can be solved at that step.
6. Cutting and Shaping: According to the required parameters, cured FR4 material is cut and shaped. Accurate cutting techniques, like CNC machining, are used to make panels, sheets, or custom shapes according to projects.
7. Surface Treatment: Based on the uses, there are some other processes done on Fr4 material, like sanding or coating, to get the required features and finish.
8. Quality Control: On the final FR4 material, quality control checks are done to verify electrical, mechanical, and thermal features. It makes sure that the material fulfills industry standards and features.
9. Packaging and Distribution: When the FR4 material meets the requirements of quality control, it is packaged and ready for distribution to manufacturers and users of PCB boards and electronic devices. There must be proper handling and packaging to avoid any damage during transportation.
1. Application Requirements: There must be an understanding of electronic devices or PCB board requirements. Consider factors like the circuit complexity, components connected to the board, and the structure dimensions of the board.
2. Mechanical Considerations: Check that the PCB has the ability to handle mechanical stress like bending or vibration. Thick FR4 material can provide high durability and rigidity, which can be needed for devices that work in harsh conditions.
3. Layer Count: If you are making a multilayer board, the FR4 layer thickness has an effect on the overall thickness of the board. Make sure that the selected thickness is in alignment with design parameters and space limitations.
4. Heat Dissipation: There must be a check of the thermal requirements of the application where FR4 material has to be used. Thick FR4 can help manage heat dissipation and thermal dissipation. If your devices produce high heat, the use of thick FR4 can help dissipate heat efficiently.
5. Signal Integrity: The signal quality is very important for high-frequency applications. Thin FR4 can provide good signal performance due to less electromagnetic interference (EMI) and signal loss. Though thick FR4 offers good isolation between layers, which can be good for mixed-signal PCB boards,
6. Manufacturing Constraints: Have a discussion with the PCB manufacturers to learn about the capabilities and limitations of their manufacturing processes. Some manufacturers can have limitations on certain thicknesses that can impact your final decision.
7. Cost Considerations: There are larger raw materials used for thick FR4 material that make it costly, and its manufacturing process is complicated. Check your budget and overall expenses against the performance needed.
8. Stackup Configuration: Stack configuration for multi-layer PCB boards is used on the basis of power, number of signals, and ground layers as the configuration of these layers. Each FR4 layer's thickness contributes to the overall stack-up thickness.
9. Design Guidelines: Use the design guidelines given by the PCB manufacturer. They mostly give suggestions for FR4 thickness according to their manufacturing process.
10. Testing and Prototyping: Before selecting any FR4 thickness value for mass production, you must check testing and prototyping. Make prototypes with different thickness values and select what is best according to your needs.
11. Simulation Tools: To simulate the behavior of PCB boards with different FR4 thicknesses, use PCB design and simulation software. It will provide details on heat performance and signal integrity.
FR4 is a versatile material that is suitable for a wide range of PCB applications. Here are some situations where you should consider using FR4 for your PCB:
1. Low to Medium Frequency Applications – FR4 is an ideal material for low to medium-frequency applications. This is due to its excellent electrical insulation and low-loss tangent. Applications such as consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial controls commonly use them.
2. Cost-Sensitive Applications – Compared to other materials, FR4 is a cost-effective option. Ceramic or Teflon materials are considered expensive in comparison. If your product has a price budget, you should consider FR4 as your choice to go.
3. High-Temperature Applications – FR4 has excellent thermal stability. It can resist high temperatures without degrading. Most applications will benefit from such properties and abilities.
4. High Mechanical Stress Applications – FR4 has a high mechanical strength. if your PCB designs are located in stressful environments such as a car or industrial machine, FR4 might be a good choice for PCB fabrication.
5. General-Purpose Applications – Due to its versatility, FR4 is widely used as a material in various applications. It is an ideal material for applications such as power supplies, lighting, and control systems. IoT systems, smart homes, and other small wireless controllers are great choices as well.
1. High-Frequency Signal Loss: FR-4 PCB boards can cause signal loss and attenuation, especially for high-frequency values. They can cause lower-quality signals and affect the performance of high-speed digital and RF circuits.
2. Limited Thermal Performance: As this FR-4 has reasonable thermal conductivity, it cannot be best for projects with high heat dissipation needs. Excessive heat can cause damage to components and decrease overall reliability.
3. Mechanical Rigidity: FR4 materials have a rigid structure, so they cannot be used for projects where bending or flexibility are needed. For projects where flexibility is needed, flexible boards can be used.
4. Vulnerable to Moisture Absorption: There can be moisture absorbed by the FR4 that affects its electrical features and causes delamination of layers in humid conditions. It can affect long-term PCB board reliability.
5. Limited RF and Microwave Performance: FR-4 boards are not optimized for RF and microwave applications since they have dielectric features and signal losses. Specialized materials, like Rogers or Teflon-based substrates, are used for these projects.
6. Complex Designs can need More layers. High-density or complicated circuit designs can need more PCB layers to handle routing and signal integrity parameters. It can increase overall expenses and cause manufacturing complications.
7. Impedance Control Challenges: Getting accurate impedance control for high speed can be difficult with FR4, especially for fine traces and differential pairs. This limitation has an effect on the quality of the signal.
8. Limited Voltage Isolation: The dielectric strength of these materials is not enough for applications that need high voltage isolation. In these conditions, specialized materials with good insulation features must be used.
9. Environmental Concerns: FR-4 boards come with epoxy resins and glass fibers, which can be a hazard to the environment during disposal and recycling. Materials that are eco-friendly and sustainable must be considered.
10. Reliability Under Extreme Conditions: For devices that work in high temperatures, high humidity, or harsh chemical conditions, the reliability of FR-4 boards can be compromised with time.
11. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Constraints: FR-4 material comes with certain design rules and limitations that engineers must follow during the layout phase.
12. Size and Weight: For uses where weight and size are important, the restriction can be the FR-4 PCBs' considerably larger density when compared to other materials.
PCB manufacturers commonly use FR4 as a material, but it’s not the only material available. Each material used in PCB manufacturing possesses its own set of properties and advantages. Let’s take a look at how FR4 compares to other materials used in PCB manufacturing.
● Ceramic PCBs – Ceramic PCBs are a popular choice for high-temperature applications due to their excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. However, ceramic PCBs are more expensive to manufacture than FR4 PCBs and are not as widely available.
|
Property |
FR4 |
Ceramic Material |
|
Chemical composition |
Epoxy resin and glass fiber |
Oxide |
|
Melting point |
185 to 210°C |
1,500 to 2,000°C |
|
Curie temperature |
N/A |
Varies |
|
Electrical resistivity |
100 to 100,000 Ω·cm |
100 to 100,000 Ω·cm |
|
Dielectric constant |
4.5 to5.5 |
5 to 100 |
|
Loss tangent |
0.02 to 0.04 |
0.01 to 0.1 |
|
Thermal conductivity |
0.2 to 0.4 W/m·K |
10 to 200 W/m·K |
|
Mechanical strength |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
● Teflon PCBs – Teflon PCBs are a popular choice for high-frequency applications due to their low dielectric constant and low loss tangent. However, Teflon PCBs are more expensive to manufacture than FR4 PCBs and are not as widely available.
|
Property |
Teflon PCB |
FR4 PCB |
|
Material |
Teflon |
Epoxy resin and glass fiber |
|
Dielectric strength |
High |
Low |
|
Dielectric loss |
Low |
High |
|
Thermal stability |
Excellent |
Good |
|
Chemical resistance |
Excellent |
Good |
|
Cost |
Expensive |
Less costly |
|
Machinability |
Difficult |
Easy |
|
Mechanical strength |
Not as strong |
Good |
● Aluminum PCBs – Aluminum PCBs are a popular choice for LED applications due to their excellent thermal conductivity. However, aluminum PCBs are more expensive to manufacture than FR4 PCBs and are not suitable for applications that require high mechanical strength.
|
Feature |
FR4 PCB |
Aluminum PCB |
|
Material |
Glass fiber epoxy |
Aluminum |
|
Thermal conductivity |
0.2 W/m·K |
170-200 W/m·K |
|
Current carrying capacity |
Low |
High |
|
Anti-seismic performance |
Poor |
Good |
|
Anti-electromagnetic interference performance |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
|
Applications |
consumer electronics, General electronic circuits, |
high-frequency circuits, , railway electronics High-power, high-density, LED lighting, automotive electronics |
● Flexible PCBs – Flexible PCBs are a popular choice for applications that require a flexible form factor. However, flexible PCBs are more expensive to manufacture than FR4 PCBs and are not suitable for applications that require high mechanical strength.
|
Feature |
FR4 PCB |
Flexible PCB |
|
Material |
Glass fiber epoxy |
Polyimide, Kapton, or other flexible materials |
|
Flexibility |
Rigid |
Flexible |
|
Thickness |
2 to 125 mils |
1/2 to 3 mils |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
|
Thermal conductivity |
0.2 W/m·K |
0.03-0.4 W/m·K |
|
Current carrying capacity |
Low |
Low |
|
Dielectric constant |
4.7-5.3 |
3.5-3.7 |
|
Loss tangent |
0.02 to 0.03 |
0.001 to 0.005 |
|
Applications |
consumer electronics, General electronic circuits, |
Mobile devices, wearables, medical devices, automotive electronics |
If you read this far – you are probably an expert in FR4 PCB material. Whenever you have a doubt about which material to use for your next project, we at PCBasic are here for you. PCBasic specializes in all types of PCB materials and fabrication methods.
With years of experience, we accumulated the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools to help you manufacture from a prototype stage all the way to mass production!
By uploading the Gerber files to our quotation system, we can recommend the most suitable material for your design. Do not hesitate to contact us and receive an instant quote for your next project.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
