Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > > A Comprehensive Guide to CPU Reballing
Know everything about CPU reballing, its types, the reballing process, and CPU reballing cost. Learn why CPU reballing is needed and which is better, CPU reballing or replacement. Your complete guide to CPU reballing is here!
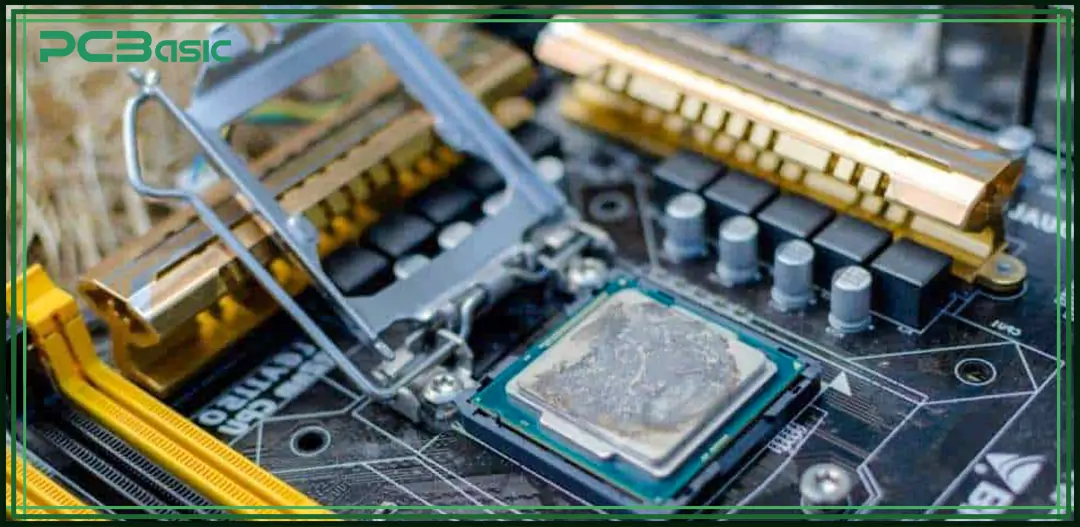

BGA (Ball Grid Array) IC packages have balls instead of pins. The CPU installation is done by applying solder paste on each solder ball, and then heat is applied to make the solder paste melt and make firm connections. Sometimes, the solder balls under the CPU's integrated circuit can malfunction or fail due to overheating, mechanical stress, or thermal cycling. This compromises the CPU performance or causes failure. That’s where the CPU reballing comes into play. CPU reballing is a technique used to repair or address CPU solder ball connection errors.
If you are a gaming enthusiast, you must have heard about the Xbox series to experience an immense gaming experience. The CPU used in the Xbox sometimes encounters issues due to overheating. CPU reballing is used to address these issues.
Modern computing systems heavily rely on GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and CPUs (Central Processing Units). These CPUs mostly come in BGA (Ball Grid Array) packages that are mounted on the motherboard. BGA package ICs do not have pins; instead, they have solder balls. These solder balls can malfunction due to overheating or poor thermal cycling. To rectify such issues, the CPU reballing technique is applied, such that the old solder balls are replaced with new solder balls.
The need for CPU reballing is necessary in the following scenarios.
1. CPU reballing is a cost-effective solution that offers a reballing of the CPU without needing to replace the whole CPU.
2. In the course of operation, CPUs generate heat, which can lead to the solder balls collapsing or failing. This needs immediate repair that is done using CPU reballing by replacing the faulty solder balls of CPUs with new solder balls.
3. Sometimes, poor soldering processes are utilized in mass production, which can lead to cracks in solder balls over time. This needs immediate CPU reballing to address the cracks to prevent any failure.
4. If a device is not properly handled, it is possible that the solder balls get damaged and cause the device to malfunction. This needs attention and CPU reballing.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
There are several types of CPUs in the context of CPU reballing. CPU, in terms of reballing, refers to the styles of CPU packages where the reballing process is applicable.
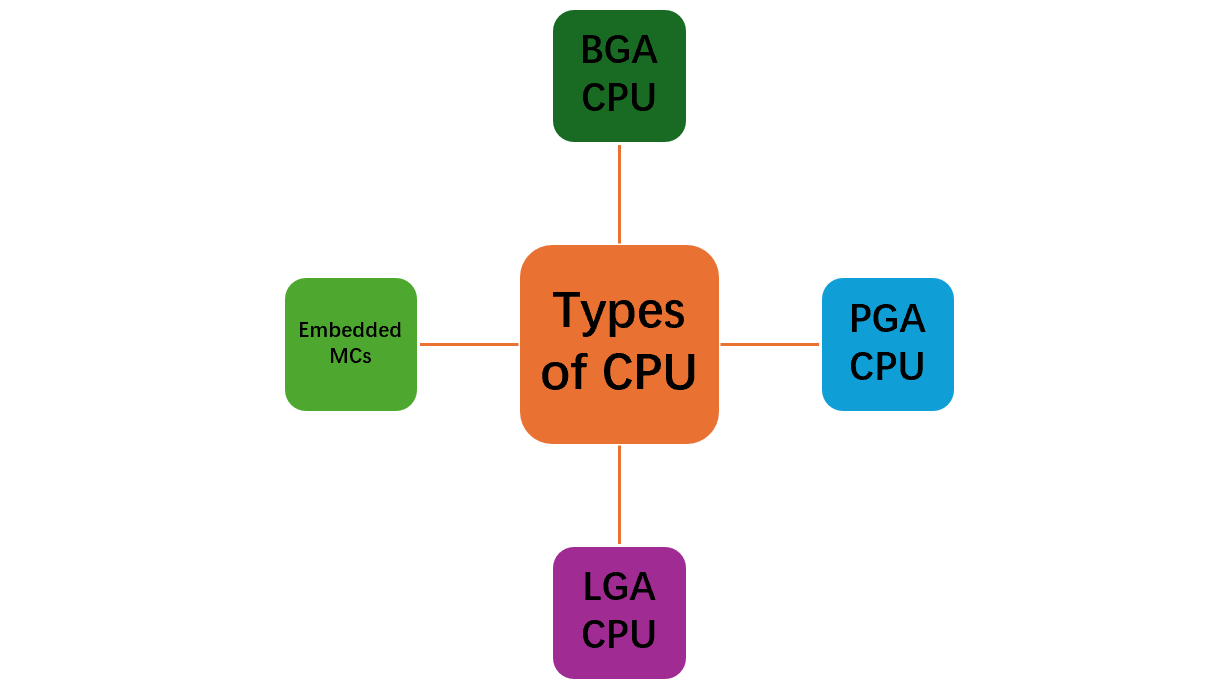
1. BGA CPU
These are Ball Grid Array (BGA) CPUs and are mostly common in smartphones, laptops, and other electronic gadgets. The small solder balls are found beneath the BGA chip. CPU reballing is required if one or more of these balls are found to be faulty.
2. PGA CPU
These are Pin Grid Array (PGA) CPUs and are mostly found in desktop computers and servers. The array of pins is found beneath the chip instead of balls. If some of the pins of PGAs are damaged, the whole CPU must be replaced, and it is not possible to apply the CPU reballing process over it. However, if the pins are only bent, they can be repaired.
3. LGA CPU
LGA stands for Land Grid Array and is mostly used in desktops. Unlike the BGA or PGA, the balls or pins are not beneath the IC; instead, the socket is available directly on the motherboard. Therefore, if there is something wrong with the pins, it is the motherboard that needs repair, not the CPU. CPU reballing is hence not required in LGA.
4. Embedded Microcontrollers
Some embedded microcontrollers like STM32 also come in BGA style. These microcontrollers are extensively used in IoT boards. These boards required CPU reballing if some issues were found. These microcontrollers mostly come in different packages like BGA, QFN, and TQFP.
Solder plays a key role in the CPU reballing process. The correct type of solder used in the CPU reballing process ensures the reliability and longevity of the device.
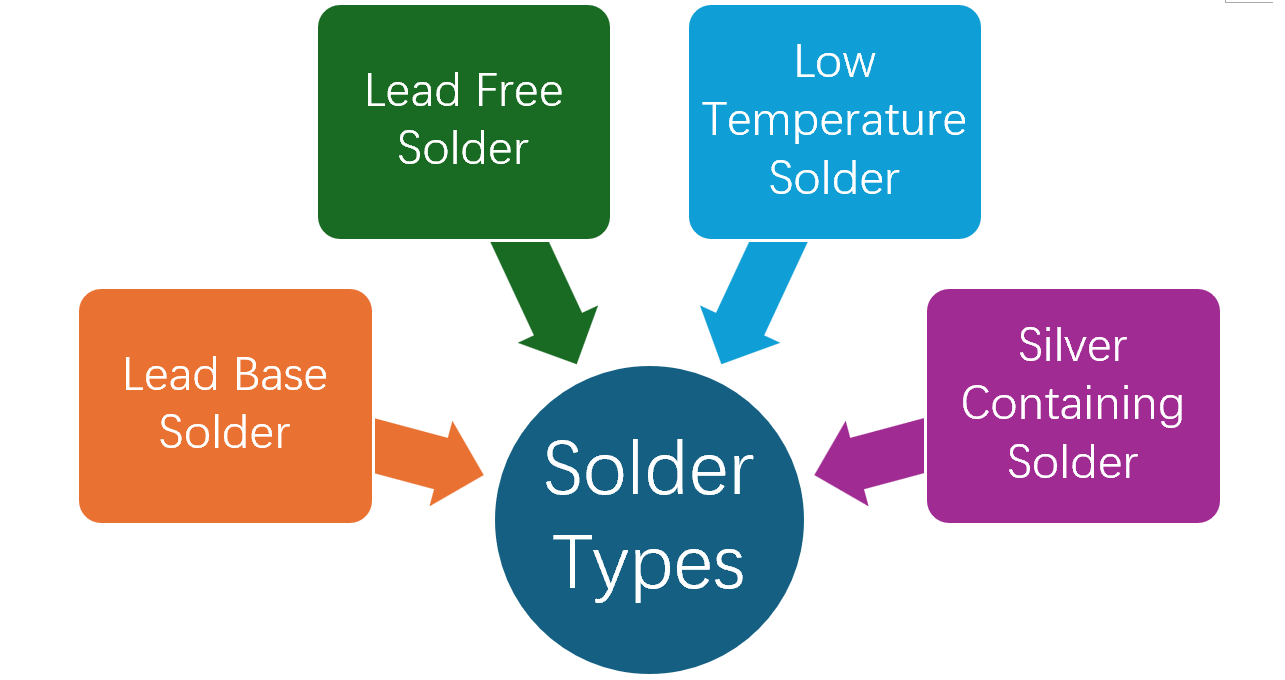
|
Solder Type |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Lead-Based Solder |
Easy rework and excellent wetting characteristics |
contains lead, which makes it toxic |
|
Lead Free Solder |
It is RoHS compliant and used in consumer electronics. |
High melting temperature
|
|
Low Temperature Solder |
It has low temperatures that make it less prone to heat damage. |
Poor thermal management |
|
Silver Containing Solder |
Greater mechanical stress and excellent thermal management. |
Costly |
CPU reballing is a process that is used to replace old or faulty solder balls with new ones. This CPU reballing process required careful attention and specialized tools such as an infrared preheater, reballing station, BGA reballing stencils, flux, soldering iron, and a microscope, etc.
1. Hot Air Rework Station: This rework station is used to provide controlled hot air to the CPU and other components in the reballing process.
2. Infrared Preheater: The Infrared preheater is used along with the hot air station. It ensures the uniform heat distribution during the CPU reballing process.
3. BGA Reballing Stencils: The BGA reballing stencils are the metal sheets on which the solder ball patterns are present for a specific CPU.
4. Solder Balls or Solder Paste: In the CPU reballing process, solder balls or solder paste are required to replace the faulty solder balls or joints.
5. Flux: In the process of CPU reballing, flux is used to remove or attach the chip from the board.
6. Soldering Iron: A soldering iron is a helpful tool for cleaning the pads.
7. Cleaning Tools: Isopropyl alcohol is commonly used to clean flux residues from the CPU after the CPU reballing process.
8. Microscope: CPU reballing involves working with extremely small components that require a microscope to inspect the solder joints before and after reballing.
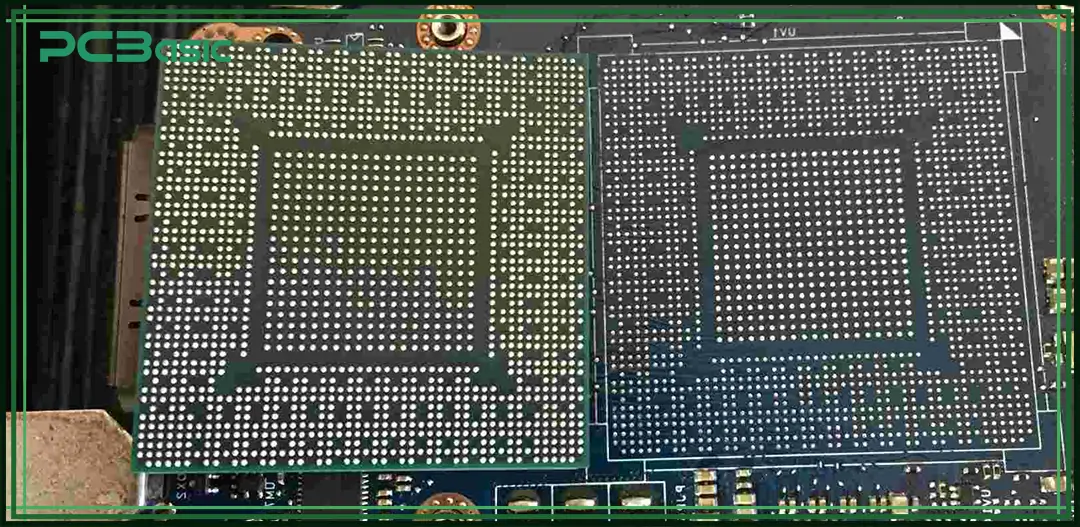
The CPU reballing process is a complex procedure that involves removing the chip from the board, cleaning it, and then reattaching it to the board after replacing the faulty solder balls with new solder balls. This is usually done when the CPU is malfunctioning or not working as required, e.g., unnecessary reboots, etc. The solder balls, over time, may be damaged due to overheating or mechanical stress.
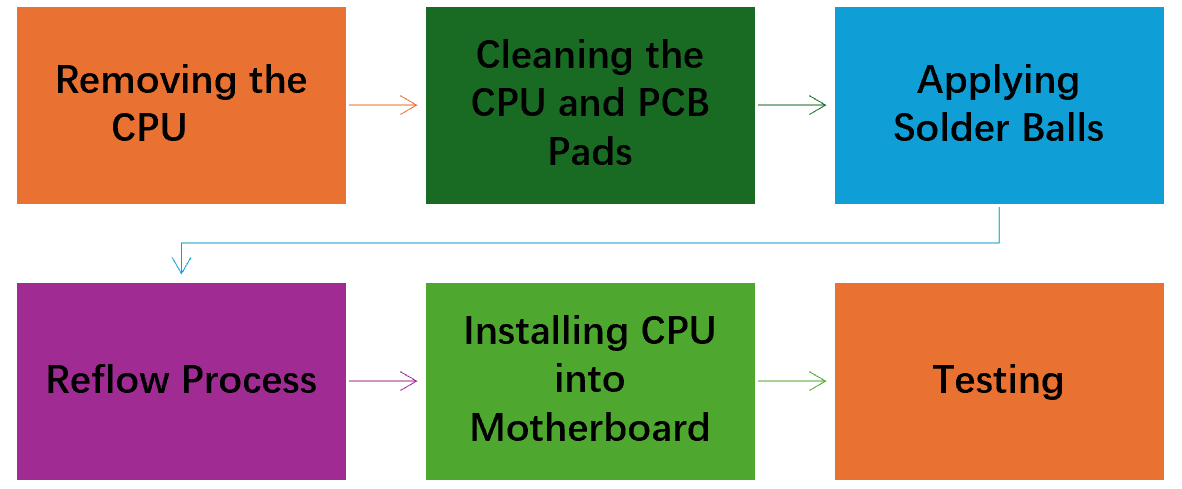
1. Removing the CPU: In the first step, using the hot air station, the CPU is removed from the motherboard. Using an infrared preheater, the CPU underneath is warmed to reduce the thermal stress. Once the solder melts, the CPU is easily removed from the motherboard.
2. Cleaning the CPU and PCB Pads: Now, the removed CPU and pads on the motherboard are cleaned to remove any residue, if any. The wick and isopropyl alcohol are mostly used for cleaning purposes.
3. Applying Solder Balls and Reflow Process: Now, the BGA stencil is placed on the chip, and solder balls are carefully placed on the surface so that the balls sit correctly each hole. Now, flux is applied, and the chip is passed through the reflow process. The solder paste melts and makes the firmly connections of balls with the pads of the chip.
4. Installing the CPU into the Motherboard: The final step in the CPU reballing process is the installation of the reballing CPU into the motherboard. The CPU is placed accurately on the motherboard, exactly where the CPU footprint is available. Once the CPU is accurately placed, the chip is passed through the reflow process. The solder paste will melt, and the CPU will be firmly attached to the motherboard.
5. Testing: Final testing is done to ensure that the CPU reballing process was successful. Basic level testing is performed once the board is reassembled, such as Power tests and BIOS etc.
The CPU reballing process is a high-demand technique used to address the faulty ball connections between the chip and the motherboard. The original balls of BGA may crack or fail due to overheating or other reasons. The reballing of the CPU process involves removing balls, cleaning the CPU and board pads, and reinstalling the pads on the CPU. The CPU reballing gives the motherboard another life without being replaced with a new one, but it is often an expensive service. It is therefore dependent on the need, types of CPU, the extent of errors in CPU chips, the equipment used, and whether the process is done for an individual or in a high-volume professional setting.
|
Criteria |
CPU Reballing |
CPU Replacement |
|
Cost |
CPU Reballing is cheaper as it does not require replacing the whole CPU |
It is relatively expensive. |
|
Turnaround Time |
Generally, takes hours or up to 1 day, depending on the skill set of the technician. |
Faster compared to the reballing process |
|
Risk Level |
High risk of CPU damage if not handled properly |
Lower risk |
|
Longevity |
If properly done, it can last longer |
A new CPU generally has a longer life compared to a repaired CPU |
|
Ideal For |
CPUs that are hard to replace |
When the CPU is obsolete or damaged |
|
Parts Availability |
No parts are needed; the existing CPU is repaired. |
A new CPU is required to replace the existing one |
In conclusion, CPU reballing is an important skill for engineers to repair the CPU's solder ball connection faults. Solder balls present on the integrated circuit of the CPU can malfunction or fail due to overheating, mechanical stress, or thermal cycling. This compromises the CPU performance or causes failure. Therefore, understanding the CPU reballing process, types, and tools required for CPU reballing is important for engineers to make informed decisions.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
