Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > PCB Hardware: Essential PCB Components for Reliable Mounting
In almost all modern electronic board systems, the printed circuit board (PCB) is a fundamental component. It is not only used for electrical connections but also serves as a structural platform to support components. Although circuits and components are often focused on in engineering design, PCB hardware is also very important in maintaining structural stability and facilitating maintenance.
Whether in industrial equipment, communication products, automotive electronics or consumer electronics, the correct PCB mounting is related to the reliability, heat dissipation effect and shock resistance of the products. This article will introduce the common types of PCB mounting hardware, the materials used, the selection methods, and how to correctly mount circuit boards to improve product quality and stability.

PCB hardware refers to a type of mechanical parts for mounting, which are used to support, secure, and, in some cases, provide electrical insulation. They are used to safely install PCB electronics into the enclosure, baseplate or other structures.
These hardware components do not participate in signal transmission, but they are very important in the structural design of circuit boards. They can help stabilize and support the electronic board to prevent shaking or loosening. In addition, PCB hardware can accurately maintain the spacing between PCBs to avoid contact or interference. Meanwhile, it can also prevent the circuit board from bending or deforming due to stress. Finally, PCB hardware improves assembly efficiency and facilitates maintenance and replacement in the future.
In other words, circuit board mounting hardware can turn a PCB board into a practical module with good structural strength and mounting reliability.
There are various types of PCB mounting hardware available on the market, which are suitable for different mounting methods, usage environments and design requirements. Below are the most common types: Below are the most common types:
1. Spacers and Standoffs
Spacers are usually hollow, unthreaded tubes and need to be used in conjunction with screws. Standoffs are equipped with internal or external threads and can be directly secured with screws. These types of hardware are used to maintain a certain spacing between the PCB electronics board and the mounting surface or between two PCBs. They can be used to prevent electrical short circuits and leave space for solder joints or airflow.
These components are made of both plastic and metal materials, with various sizes, and are suitable for most PCB electronics assembly requirements.
2. Screws, Nuts, and Washers
Screws and nuts can provide the basic fastening force. Washers can distribute the pressure and prevent the circuit board from loosening or getting damaged due to vibration. These are standard fasteners used to firmly secure the PCB hardware to the bracket or enclosure. Common materials include nylon (for insulation) and stainless steel (for high strength and corrosion resistance).
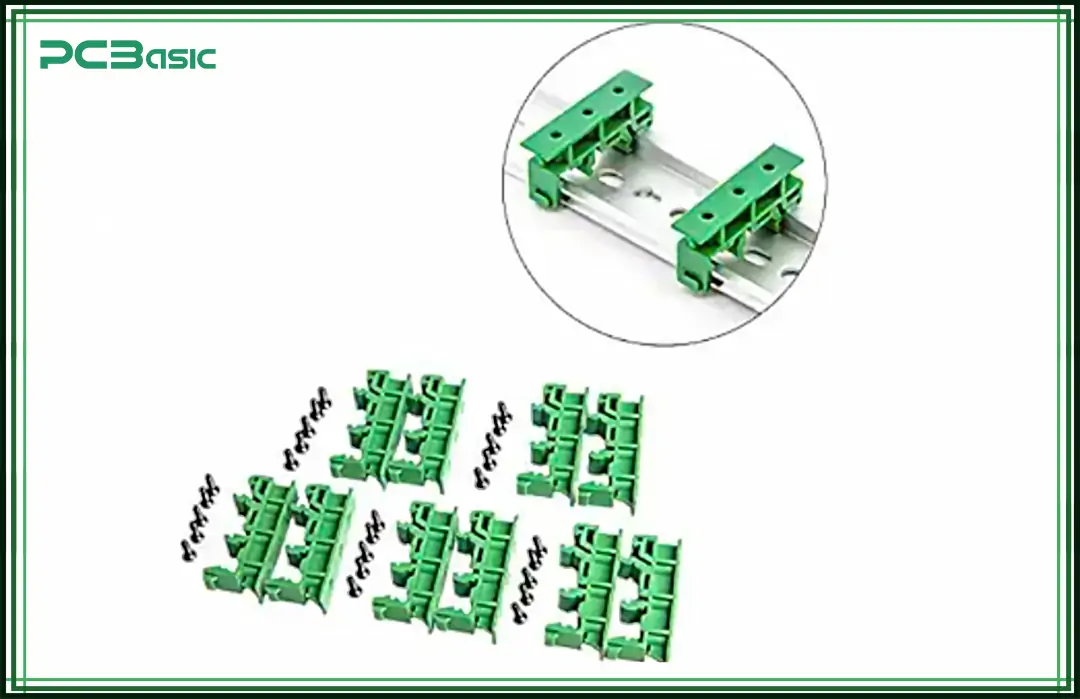
PCB mounting brackets are used to fix PCBs inside enclosures or mechanical systems. The common shapes are L-shaped and U-shaped. These brackets are often used in rack-mounted equipment, power modules and industrial control devices. They can firmly secure the electronic board to the housing or support structure and are especially suitable for vertical installation or application environments with vibrations.
4. Card Guides and Pullers
Card guides are used to slide PCB electronics boards into slots or enclosures, making installation and removal easier. They help prevent damage to the edges of the PCB and are ideal for modular or replaceable devices. Some card guides also feature heat dissipation functions to assist with thermal management. Pullers are typically used together with card guides to safely remove the board from the slot.
5. Ejectors and Extractors
Ejectors and extractors are commonly used in modular or plug-in systems, such as communication equipment and industrial control systems. These components are small levers or handles mounted on the edge of the PCB. They assist in removing plug-in PCBs from slots, especially in compact devices where manual extraction is difficult.
6. LED Mounting Hardware

LED light pipes and clips help securely mount LED indicators on the electronic board. They ensure the LED aligns correctly with the front panel, improving visibility and consistency of status indicators. This type of hardware is commonly used in routers, control panels, household appliances, and other devices that utilize LED indicators.
7. Fan Mounts and Fuse Holders
In high-power PCB electronics, additional cooling and circuit protection are often required. Small fans can be directly mounted on the PCB using dedicated circuit board hardware, improving heat dissipation. Fuse clips or holders are used to protect the circuit by breaking the connection in the event of an overload.
These hardware components improve product reliability and extend service life. They are essential for high-performance electronic devices.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Material selection has a direct impact on the strength, stability, and lifespan of PCB hardware. If the wrong material is used, it can lead to hardware failure, electrical short circuits, or structural issues with the circuit board. Therefore, when choosing circuit board mounting hardware, it is important to consider the application environment and functional requirements. Below are three common material types:
1. Plastic Materials (Nylon, Polycarbonate)
Plastic PCB mounting hardware is lightweight and non-conductive. It provides good insulation and does not rust, making it suitable for humid or corrosive environments. Components like spacers, standoffs, and screws made from nylon or polycarbonate are widely used in commercial electronics. Plastic also offers some flexibility, which helps absorb vibration.
2. Metal Materials (Brass, Stainless Steel, Aluminum)
Metal circuit board hardware has high strength and is ideal for supporting heavier boards. Stainless steel provides excellent mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. Brass and aluminum are lighter and offer better thermal conductivity. Most metal hardware is conductive, which makes it useful for grounding. These materials are commonly used in industrial systems or for high-load structures, such as PCB mounting brackets for power modules.
3. Composite and Coated Materials
Some PCB mounting brackets use a metal core covered with a plastic or insulated coating. This design combines the strength of metal with the insulation of plastic. It is a good choice when both structural support and electrical safety are needed. In environments with electromagnetic interference (EMI) or electrostatic discharge (ESD), this type of hardware is more reliable.
When selecting circuit board mounting hardware, consider several factors: the weight of the board, the need for heat dissipation, the presence of EMI, and available mounting space. Choosing the right material improves safety, stability, and overall reliability.

Choosing the right PCB mounting hardware is very important in circuit board design. Different applications require different hardware structures, materials, and functions. Below are some key factors to consider:
1. Board Size and Weight
If the board is large or heavy, you need stronger support. For example, using metal PCB mounting brackets can increase the overall strength. This helps prevent the board from sagging, bending, or falling off. It is especially useful in industrial equipment and large control systems.
2. Operating Environment
The environment has a big impact on the choice of circuit board hardware. In high-vibration settings like automotive electronics, it is best to use locking screws or vibration-resistant hardware to keep the board secure. In humid, salty, or corrosive environments, plastic or coated metal hardware is recommended to avoid rust or damage.
3. Electrical Requirements
For electrical safety, avoid placing metal standoffs near signal paths to prevent interference or short circuits. If grounding is not needed, use insulated PCB mounting hardware. This type of hardware can isolate circuits and reduce the risk of short circuits.
4. Maintainability
If the board needs to be removed or replaced often, choose a mounting circuit board solution that is easy to install and remove. Card guides, ejectors, or spring-loaded clips allow for tool-free handling. This improves maintenance efficiency and protects the board from damage during service.
5. Thermal Management
In high-power or high-temperature applications, thermal control is important. Metal spacers can transfer heat from electronic boards to the chassis or heat sink. Some PCB hardware can also be used with thermal pads or thermal paste to improve heat dissipation. This helps keep the system running reliably and extends its service life.

Effective PCB mounting improves the reliability, maintainability, and structural stability of a product throughout its entire lifecycle. The following are practical mounting tips for most electronic board designs:
1. Plan Mounting Holes During Layout
Mounting holes should be planned early during PCB layout. It’s best to place them symmetrically to reduce the risk of board warping. Also, leave enough clearance around each hole to prevent cracks during assembly or use.
2. Use Proper Torque and Thread Size
When tightening screws, apply the correct torque. Too much force can deform or break the electronic board. Thread size should match the material and type of the spacer or screw to ensure a secure fit without damaging the board.
3. Reduce Vibration and Stress
For applications with shock or vibration, use rubber washers or spring-loaded PCB mounting brackets to absorb impact. This helps extend the life of both the hardware and the board. If EMI is a concern, choose circuit board mounting hardware with grounding features to improve electromagnetic compatibility.
4. Ensure Access for Testing
If the board requires frequent maintenance, add pullers, card guides, or other support hardware to simplify installation and removal. Avoid using oversized PCB mounting brackets that may block access to debug or test ports.
5. Follow Industry Standards
When designing PCB electronics and selecting mounting hardware, follow IPC or other relevant standards to ensure consistency and reliability. For industrial use, it is also recommended to choose circuit board hardware that meets UL or other safety certifications.
Although often overlooked, PCB hardware is a core element of structural integrity in any electronic board system. Whether using basic standoffs or reinforced PCB mounting brackets, selecting the right PCB mounting hardware ensures safe, stable, and maintainable assembly.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
