Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
Global high-mix volume high-speed PCBA manufacturer
9:00 -18:00, Mon. - Fri. (GMT+8)
9:00 -12:00, Sat. (GMT+8)
(Except Chinese public holidays)
HomePage > Blog > Knowledge Base > Computer Board Explained: Definition, Types, and Manufacturing
The computer board is the core component of modern computing devices. It is commonly found in laptops, desktops, servers, embedded systems and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, serving as the foundation for the operation of each device. The computer board, also known as the computer circuit board, main circuit board or computer PCB board, is mainly responsible for connecting and controlling various key electronic components to make them work together.
This article will introduce what a computer board is, what common types of computer boards there are, how PC circuit boards are manufactured, and how to choose the appropriate computer circuit board.
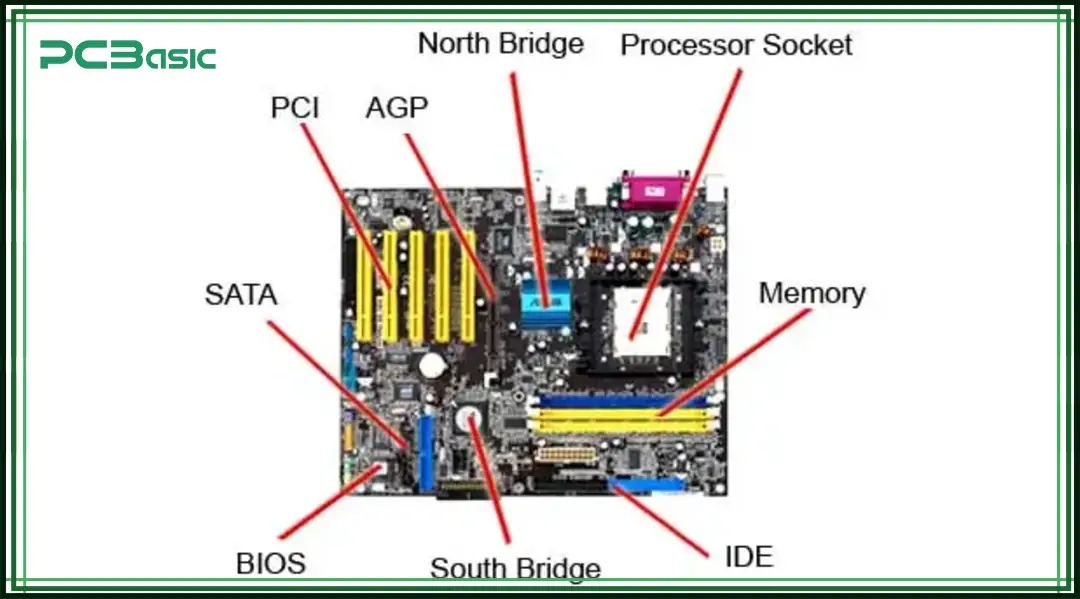
A computer board is a kind of printed circuit board (PCB) specially designed for computing devices. It is the core structure of the electronic system, responsible for mounting and connecting the CPU, memory, storage interfaces, and various input and output ports.
In common consumer electronics, the main circuit board is usually referred to as the motherboard. For smaller devices, such as embedded systems or single-board computers (SBCs), different forms of computer boards are used.
Simply speaking, the computer circuit board is like the communication center inside the computer. It enables the processor, memory and various peripherals to be interconnected and work properly. Without it, the various components of the equipment would not be able to operate in coordination and would not be able to receive power.
Structurally, a computer PCB board is composed of multiple layers of copper circuits and pads. These circuits are sandwiched in fiberglass or resin sheets to form a robust circuit platform on which electronic components can be firmly soldered.
Different types of computer boards are designed according to their functions and usage scenarios. Each type of board has a different structure and application. The following are several of the most common types of computer boards:
1. Motherboard (Main Circuit Board)
The motherboard is a core component in desktop computers, laptops and servers, and it is also the main circuit board of the entire device. It provides a main platform for connecting and coordinating all key hardware.
A typical motherboard includes the following interfaces and slots: CPU socket, RAM slots, GPU slot (PCIe), Storage interfaces (for SSDs or HDDs), Network and audio interfaces, Input/output ports (such as USB, HDMI, and audio).
This kind of computer circuit board is usually structurally complex, with many layers, multiple power, signal and ground layer channels, as well as a large number of connectors and expansion interfaces. It is the basis for building a complete computing system.
2. Single Board Computers (SBCs)
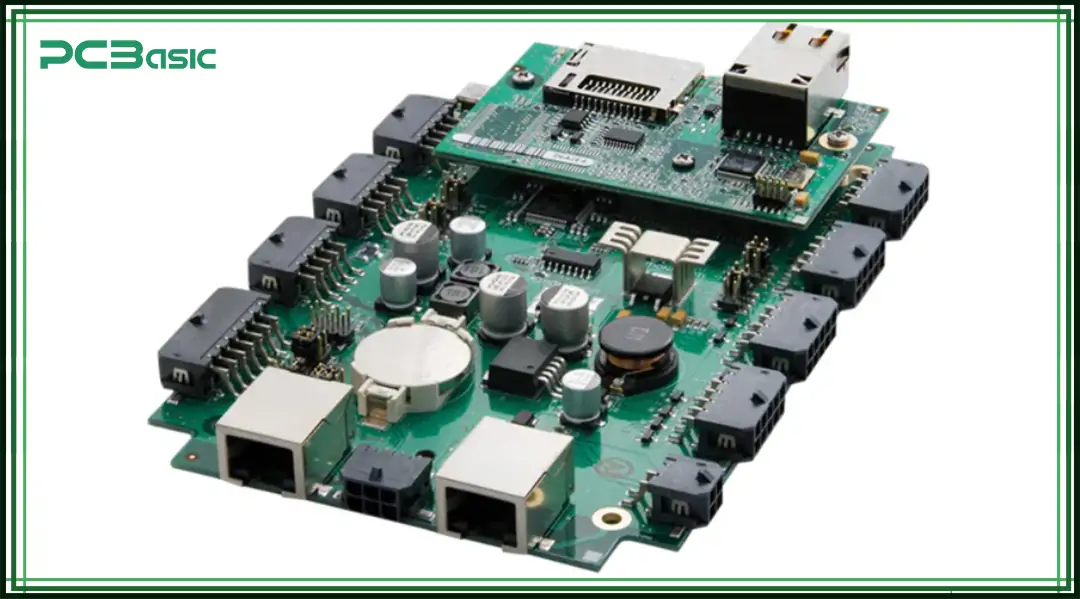

The single board computer integrates the processor, memory, storage and I/O interfaces all on a small PC circuit board. This design does not require additional expansion cards or slots. It is small in size and fully functional.
Common SBC products include Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone and NVIDIA Jetson Nano.
SBCs are widely used in embedded system development, programming education, IoT (Internet of Things) devices and prototyping projects.
Due to its high integration, low price and small size, the SBC is highly suitable for application scenarios with limited space or budget.
3. Graphics Card (GPU Board)
Although a graphics card is an expansion device, it is essentially a kind of computer PCB board with specific functions. It is used for image and video processing and has internal integration GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), VRAM (Video RAM) and Heatsinks and fans for cooling.
The graphics card is connected to the main circuit board via the PCIe interface, providing graphics processing capabilities for applications such as games, design, and artificial intelligence.
4. I/O and Peripheral Expansion Boards
This type of computer circuit board is used to increase the functional interfaces of computers. Common types include USB expansion board (Add additional USB ports), sound card (to enhance audio quality) and Network Interface Card (NIC) (for enhancing or upgrading network connection capabilities).
They are usually installed in the expansion slots on the main circuit board in the form of card inserts, and some may also be directly soldered onto the motherboard.
These boards enable users to flexibly expand functions as needed without having to replace the entire computer board.
5. Embedded Controller Boards
Embedded controller computer boards are often used in professional scenarios such as industrial control, medical equipment, and automation systems. This type of computer circuit board usually only performs specific tasks, such as sensor data acquisition, motor control and real-time monitoring and alarm.
They have high requirements for stability and response speed and must operate reliably in harsh environments such as high temperatures, high humidity, and electromagnetic interference. Therefore, they usually have a wide-temperature design, anti-interference ability and long-term supply guarantee.
These different types of computer boards together constitute the hardware basis of various computing devices. Selecting the appropriate type of board card based on the structure, application and performance requirements of the equipment is an important step in system design.
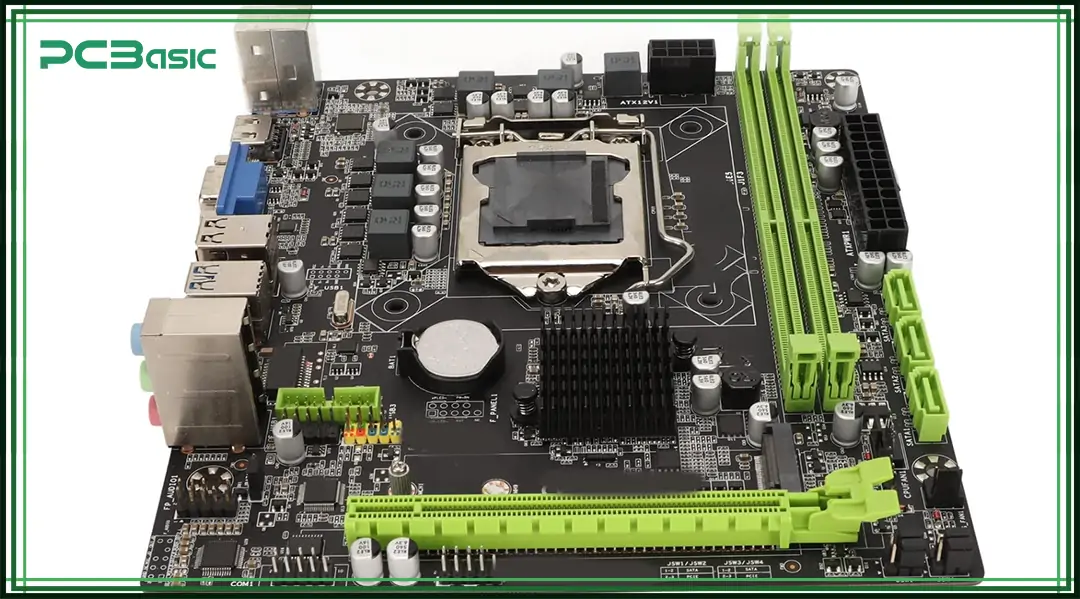
The motherboard is widely regarded as the main circuit board in traditional computers. It is responsible for connecting and controlling the CPU, memory, storage devices and various peripherals. At the same time, it also manages the power allocation of the entire device and the data communication within the system.
A typical motherboard includes a CPU slot for installing the processor, a chipset for controlling data flow, a memory slot for installing RAM modules, storage interfaces (such as SATA or M.2) for connecting hard drives and solid state drives, and a PCIe expansion slot for adding graphics cards, network cards and other devices. In addition, the motherboard also integrates BIOS or UEFI firmware for system startup, as well as a power interface to supply power to the entire board and connected components.
Modern PC circuit boards may have as many as 12 layers, including the signal layer, power layer and ground layer, to support high-speed data transmission and stable power distribution. The main circuit board of a computer largely determines the scalability, performance ceiling and compatible hardware types of the entire computer.
 About PCBasic
About PCBasic
Time is money in your projects – and PCBasic gets it. PCBasic is a PCB assembly company that delivers fast, flawless results every time. Our comprehensive PCB assembly services include expert engineering support at every step, ensuring top quality in every board. As a leading PCB assembly manufacturer, we provide a one-stop solution that streamlines your supply chain. Partner with our advanced PCB prototype factory for quick turnarounds and superior results you can trust.
Making a computer board is a highly precise process. Every step must ensure that the electrical signals are clear, the connections are reliable, and the structure is strong and durable. Problems like short circuits or open circuits must be avoided. Below are the basic steps to produce a computer PCB board, explained in a clear and straightforward way:
1. PCB Design and Layout
Engineers use professional CAD software to design the layout of the computer circuit board. This includes drawing the wiring paths, placing components, adding vias (holes), and planning the stack-up for multilayer boards. The design must be very accurate—any mistake can lead to a board that doesn’t work.
2. Substrate and Copper Lamination
The core of the board is an insulating material, usually FR4 fiberglass. A thin copper layer is pressed onto the surface. This copper will later become the board’s circuits. Lamination bonds the copper to the base, preparing it for the next step.
3. Image Transfer and Etching
A light-sensitive coating is applied to the copper. Then, a circuit pattern is exposed onto the surface using UV light. After that, the board goes through chemical etching. Unwanted copper is removed, and the needed copper traces and pads remain. This step forms the final circuit paths on the computer PCB board.
4. Drilling and Plating
Next, precision machines drill small holes through the board. These holes connect the different layers of the board. After drilling, the hole walls are plated with copper so that electrical signals can travel between layers.
5. Solder Mask and Silkscreen
A green solder mask is added to protect the board and prevent short circuits during soldering. Then, silkscreen printing is used to add labels, such as part numbers and port names, on the computer circuit board. This helps during assembly and later maintenance.
6. SMT Assembly
Electronic parts like resistors, capacitors, and chips are placed on the computer board using automated machines. Then, the board goes through a reflow oven, where heat melts the solder and firmly connects each part to the board.
7. Inspection and Testing
Finally, every PC circuit board goes through strict testing. This includes AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) to find solder issues, X-ray inspection to check hidden connections, and full functional testing to ensure the board works correctly and reliably.
Each of these steps is critical for building a high-quality computer board. The manufacturing process directly affects the performance, stability, and lifespan of the board in its final device.
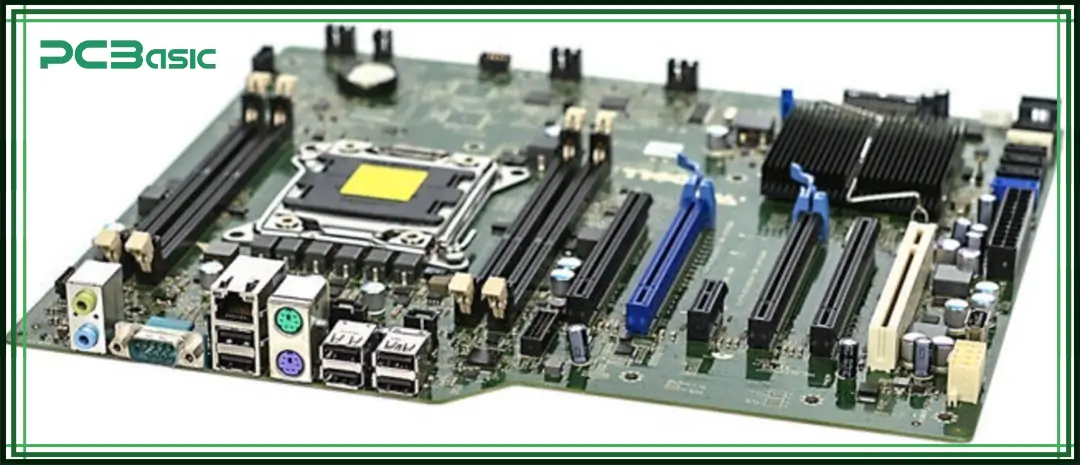
Choosing the right computer board depends on your use case, performance needs, and working environment. Here are some common factors to consider:
Form Factor
Make sure the size of the main circuit board fits your case or device space. Common board sizes include ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX.
CPU Compatibility
Choose a computer board that supports the CPU socket and chipset you plan to use. This ensures proper performance and compatibility.
Memory and Storage Interfaces
Check if the computer circuit board has enough memory slots and supports the storage interfaces you need, such as SATA or NVMe.
Expansion and Connectivity
Pick a computer board with the right PCIe slots and USB ports based on your device needs. This allows easy connection to graphics cards, network cards, or other peripherals.
Industrial or Consumer Use
For industrial environments, choose computer circuit boards that are resistant to heat, moisture, and corrosion. This improves reliability and lifespan.
Power Efficiency
For portable or embedded systems, select a low-power computer PCB board. This helps reduce heat and extend battery life.
These points can help you choose the best computer board for your project or device, ensuring long-term and stable performance.
The computer board is the core foundation of every computing system. Whether it is the traditional main circuit board, the compact single board computer, or the functionally customized PC circuit board, they are all indispensable components of modern electronic devices.
Understanding the structure, types and manufacturing processes of computer circuit boards will help engineers, developers and consumers make wiser hardware choices. From high-performance desktop computers to energy-efficient Internet of Things terminals, the computer PCB board remains an irreplaceable core in the digital world.

Assembly Enquiry
Instant Quote
Phone contact

+86-755-27218592
In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
Wechat Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
WhatsApp Support

In addition, we've prepared a Help Center. We recommend checking it before reaching out, as your question and its answer may already be clearly explained there.
